Abstract
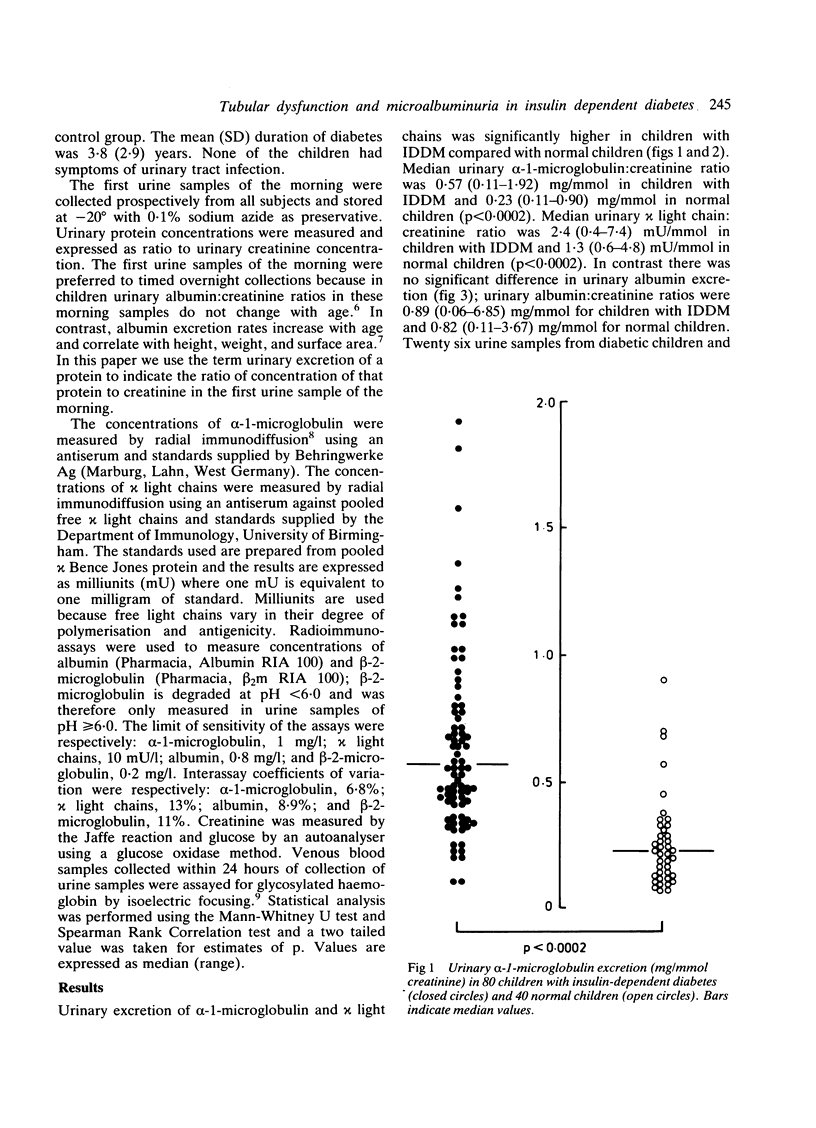
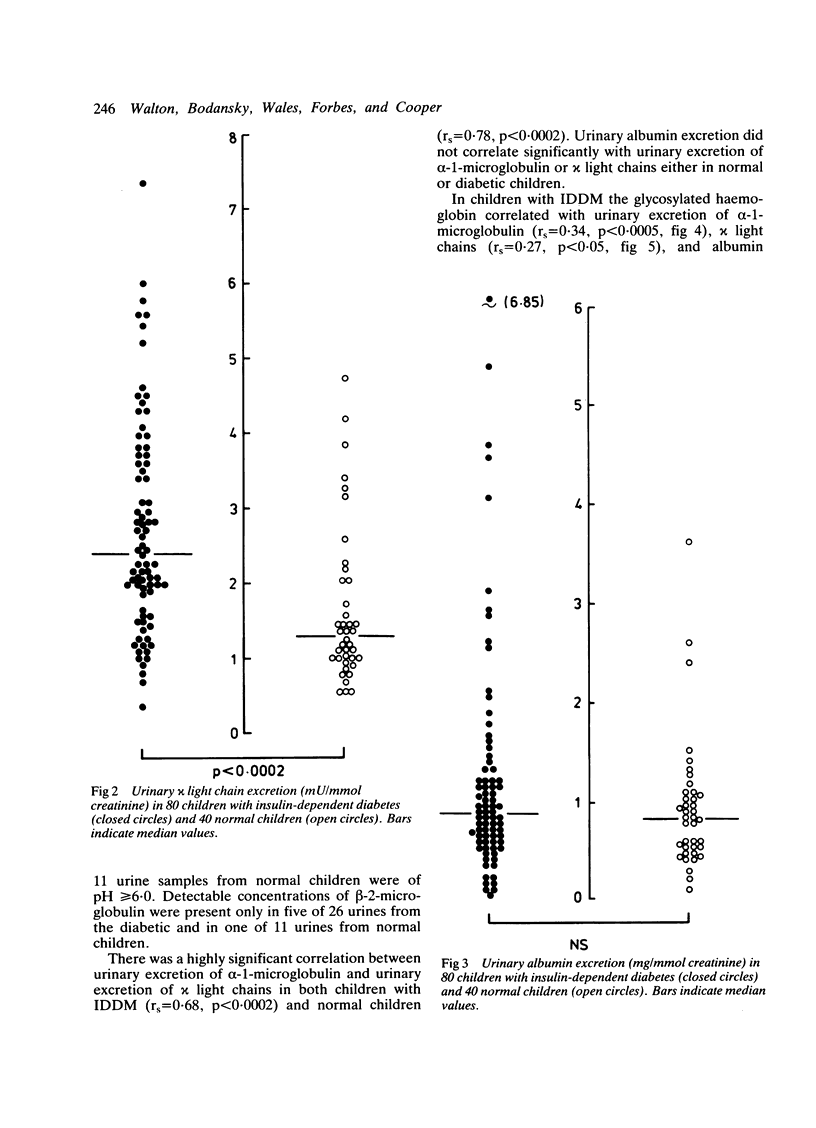
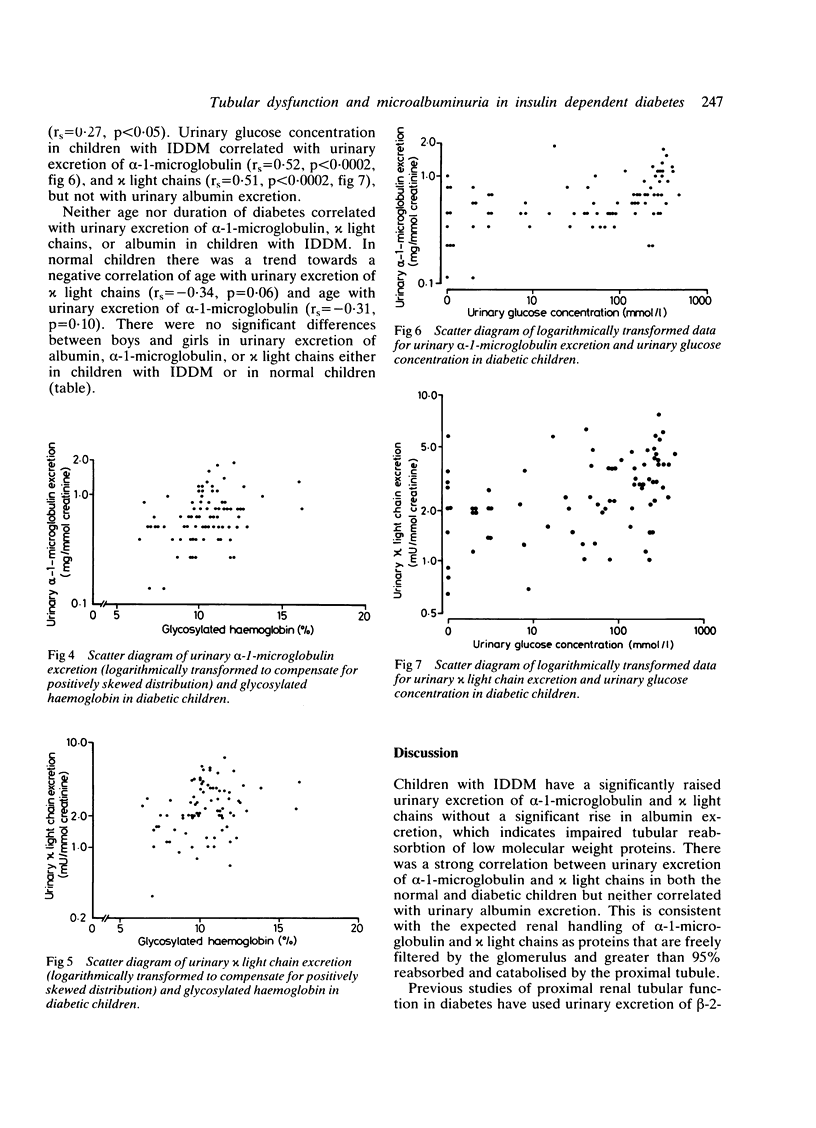
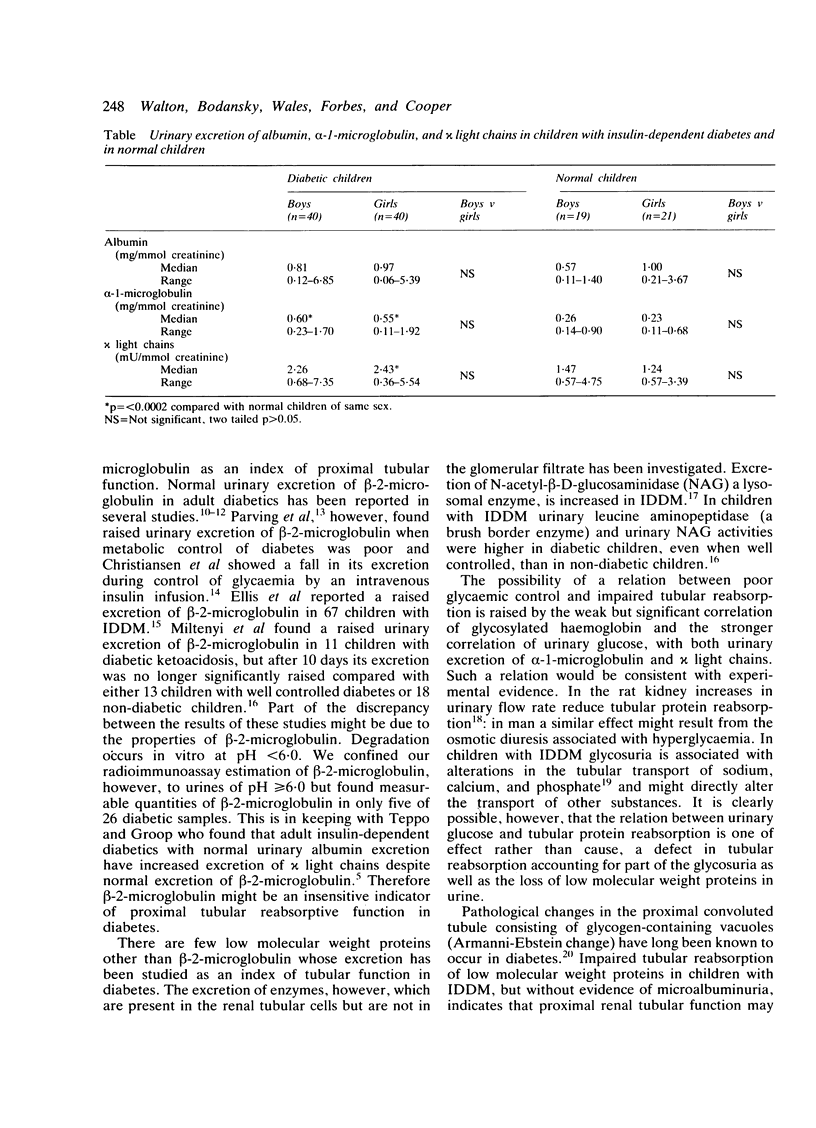
The nature of microproteinuria in the early years of insulin-dependent diabetes was investigated in a cross sectional study of 80 children with insulin-dependent diabetes and 40 normal children. Urinary excretion of three low molecular weight proteins: alpha-1-microglobulin, beta-2-microglobulin and kappa light chains was used as an index of proximal renal tubular function. The first urine samples of the morning were collected and excretion of proteins measured was expressed as ratio of protein to creatinine. There was a strong correlation between excretion of alpha-1-microglobulin and chi light chains and their excretion was significantly higher in diabetic children indicating decreased proximal tubular reabsorbtion. The excretion of beta-2-microglobulin was found to be an unsatisfactory index of proximal tubular function. Urinary albumin excretion was not significantly raised in diabetic children and did not correlate with urinary alpha-1-microglobulin or chi light chain excretion. Glycaemic control might influence proximal tubular function as both urinary glucose concentration and glycosylated haemoglobin showed correlations with urinary alpha-1-microglobulin excretion and with urinary chi light chain excretion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan Y. L., Straus W. Influence of the tubular flow rates on the endocytic uptake and the excretion of horseradish peroxidase by rat kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):271–277. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J. S., Frandsen M., Parving H. H. The effect of intravenous insulin infusion on kidney function in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1981 Mar;20(3):199–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00252628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. G., Postlethwaite R. J., Price D. A., Burn J. L., Houlton C. A., Fielding B. A. Urinary albumin excretion in school children. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jul;59(7):625–630. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.7.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditzel J., Brøchner-Mortensen J. Tubular reabsorption rates as related to elevated glomerular filtration in diabetic children. Diabetes. 1983 May;32 (Suppl 2):28–33. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.s28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D., Becker D. J., Daneman D., Lobes L., Jr, Drash A. L. Proteinuria in children with insulin-dependent diabetes: relationship to duration of disease, metabolic control, and retinal changes. J Pediatr. 1983 May;102(5):673–680. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80232-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J. A., Crockson R. A., Mijovic C., Cooper E. H., Bradwell A. R., Barnett A. H. Low molecular weight proteinuria in insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes Res. 1986 May;3(4):203–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Virella M. F., Virella G., Rosebrock G., Sagel J., Gonzalez J., Colwell J. Early diagnosis of renal malfunction in diabetics. Abnormal proteinuria revealed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Diabetologia. 1979 Mar;16(3):165–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01219793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltényi M., Körner A., Tulassay T., Szabó A. Tubular dysfunction in type I diabetes mellitus. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Oct;60(10):929–931. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.10.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Noer I., Deckert T., Evrin P. E., Nielsen S. L., Lyngsoe J., Mogensen C. E., Rorth M., Svendsen P. A., Trap-Jensen J. The effect of metabolic regulation on microvascular permeability to small and large molecules in short-term juvenile diabetics. Diabetologia. 1976 May;12(2):161–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00428983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE S., WAUGH D. The pathology of Armanni-Ebstein diabetic nephropathy. Am J Pathol. 1957 Nov-Dec;33(6):1035–1057. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stickland M. H., Perkins C. M., Wales J. K. The Measurement of Haemoglobin A1c by isoelectric focussing in diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1982 May;22(5):315–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00253573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teppo A. M., Groop L. Urinary excretion of plasma proteins in diabetic subjects. Increased excretion of kappa light chains in diabetic patients with and without proliferative retinopathy. Diabetes. 1985 Jun;34(6):589–594. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.6.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Hill R. D., Jarrett R. J., Argyropoulos A., Mahmud U., Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1982 Jun 26;1(8287):1430–1432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Jarrett R. J., McCartney M., Keen H. Increased glomerular permeability to albumin induced by exercise in diabetic subjects. Diabetologia. 1978 May;14(5):293–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01223019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Mackintosh D., Bilous R. W., Pickup J. C., Keen H. Proteinuria in diabetes mellitus: role of spontaneous and experimental variation of glycemia. Kidney Int. 1982 May;21(5):714–720. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G., Keen H. The patterns of proteinuria in diabetes mellitus. Relevance to pathogenesis and prevention of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 1984 Jul;33(7):686–692. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.7.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vittinghus E., Mogensen C. E. Graded exercise and protein excretion in diabetic man and the effect of insulin treatment. Kidney Int. 1982 May;21(5):725–729. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting P. H., Ross I. S., Borthwick L. Serum and urine N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase in diabetics on diagnosis and subsequent treatment, and stable insulin dependent diabetics. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Mar 15;92(3):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


