Abstract
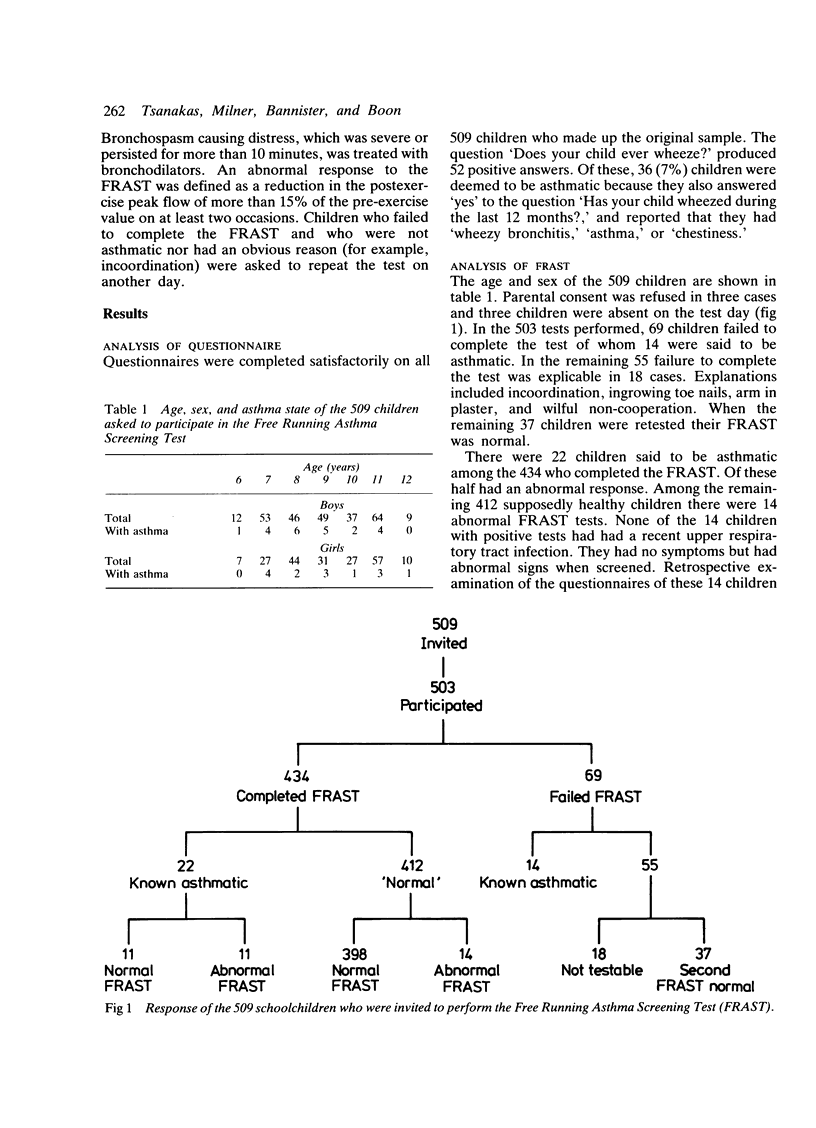
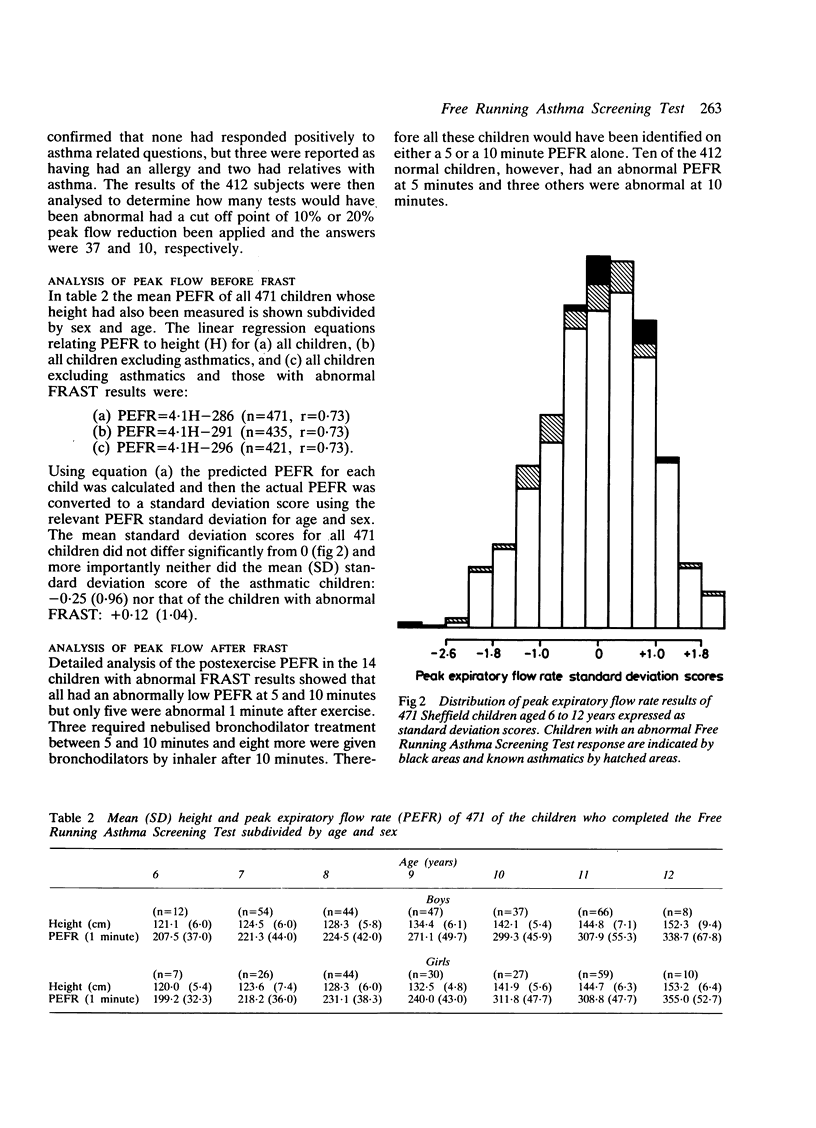
The free running asthma screening test (FRAST) was evaluated in 503 Sheffield schoolchildren aged 6 to 12 years and compared with responses to an asthma questionnaire. The FRAST measured peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) before and at 1, 5, and 10 minutes after maximum voluntary running for at least 5 minutes in a standardised environment. A fall in PEFR of greater than 15% in at least two postexercise readings was defined as abnormal. Six (1%) children did not do the test and 69 (14%) failed to complete it. Of these, 14 were known asthmatics, 18 were not testable, and 37 were normal when retested. There were 14 abnormal FRAST results among 412 'normal' children who completed the test and 10 of these were subsequently diagnosed asthmatic. None of 14 children with an abnormal FRAST result had been identified as wheezy, chesty, or asthmatic in the questionnaire. In this sample there was, on average, one child in every school class with unrecognised exercise induced bronchospasm. The FRAST is an acceptable, feasible, and cost effective way of identifying such potential asthmatics at school.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. R., Bailey P. A., Cooper J. S., Palmer J. C. Influence of morbidity, illness label, and social, family, and health service factors on drug treatment of childhood asthma. Lancet. 1981 Nov 7;2(8254):1030–1032. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H. R., Bailey P. A., Cooper J. S., Palmer J. C., West S. Medical care of asthma and wheezing illness in children: a community survey. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1983 Sep;37(3):180–186. doi: 10.1136/jech.37.3.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. D., Connolly N. M., Godfrey S. Comparison of bronchoconstriction induced by cycling and running. Thorax. 1971 Jul;26(4):396–401. doi: 10.1136/thx.26.4.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierman E. W., Kawabori I., Pierson W. E. Incidence of exercise-induced asthma in children. Pediatrics. 1975 Nov;56(5 PT-2):847–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard A., Ingemann-Hansen T., Schmidt A., Halkjaer-Kristensen J. Influence of temperature and relative humidity of inhaled gas on exercise-induced asthma. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 May;63(3):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colver A. F. Community campaign against asthma. Arch Dis Child. 1984 May;59(5):449–452. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.5.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey S., Silverman M., Anderson S. D. Problems of interpreting exercise-induced asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973 Oct;52(4):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(73)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. A., Winslow N. R., Speight A. N., Hey E. N. Prevalence and spectrum of asthma in childhood. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Apr 16;286(6373):1256–1258. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6373.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro G. G., Pierson W. E., Furukawa C. T., Bierman C. W. A comparison of the effectiveness of free-running and treadmill exercise for assessing exercise-induced bronchospasm in clinical practice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Dec;64(6 Pt 2):609–611. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Anderson S. D. Standardization of exercise tests in asthmatic children. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Dec;47(256):882–889. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.256.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speight A. N., Lee D. A., Hey E. N. Underdiagnosis and undertreatment of asthma in childhood. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Apr 16;286(6373):1253–1256. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6373.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsanakas J. N., Bannister O. M., Boon A. W., Milner R. D. The 'Sport-tester': a device for monitoring the free running test. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Sep;61(9):912–914. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.9.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsanakas J. N., Primhak R. A., Milner R. D., Hatzimichael A., Karpouzas J. G. Unexpectedly high peak expiratory flow rates in normal Greek children. Eur J Pediatr. 1983 Oct;141(1):46–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00445668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


