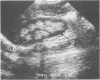
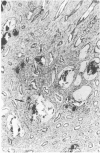
Abstract
The incidence of nephrocalcinosis in very low birthweight (less than 1500 g) premature infants was assessed by ultrasound scan and analysis of urine. Three of 36 infants had nephrocalcinosis. All had been receiving long term frusemide for bronchopulmonary dysplasia with simultaneous fluid restriction. Urinary investigations showed no consistent findings in babies with nephrocalcinosis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hufnagle K. G., Khan S. N., Penn D., Cacciarelli A., Williams P. Renal calcifications: a complication of long-term furosemide therapy in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 1982 Sep;70(3):360–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriquin H., Robitaille P. Renal calcium deposition in children: sonographic demonstration of the Anderson-Carr progression. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986 Jun;146(6):1253–1256. doi: 10.2214/ajr.146.6.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse D. M., Kaude J. V., Williams J. L., Bush D., Wright P. G. Sonographic diagnosis of furosemide-induced nephrocalcinosis in newborn infants. J Ultrasound Med. 1984 Dec;3(12):553–556. doi: 10.7863/jum.1984.3.12.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. S., Pollak A., Oh W. The pharmacologic effects of furosemide therapy in the low-birth-weight infant. J Pediatr. 1978 Jan;92(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyberth H. W., Rascher W., Schweer H., Kühl P. G., Mehls O., Schärer K. Congenital hypokalemia with hypercalciuria in preterm infants: a hyperprostaglandinuric tubular syndrome different from Bartter syndrome. J Pediatr. 1985 Nov;107(5):694–701. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80395-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]