Abstract
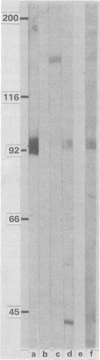
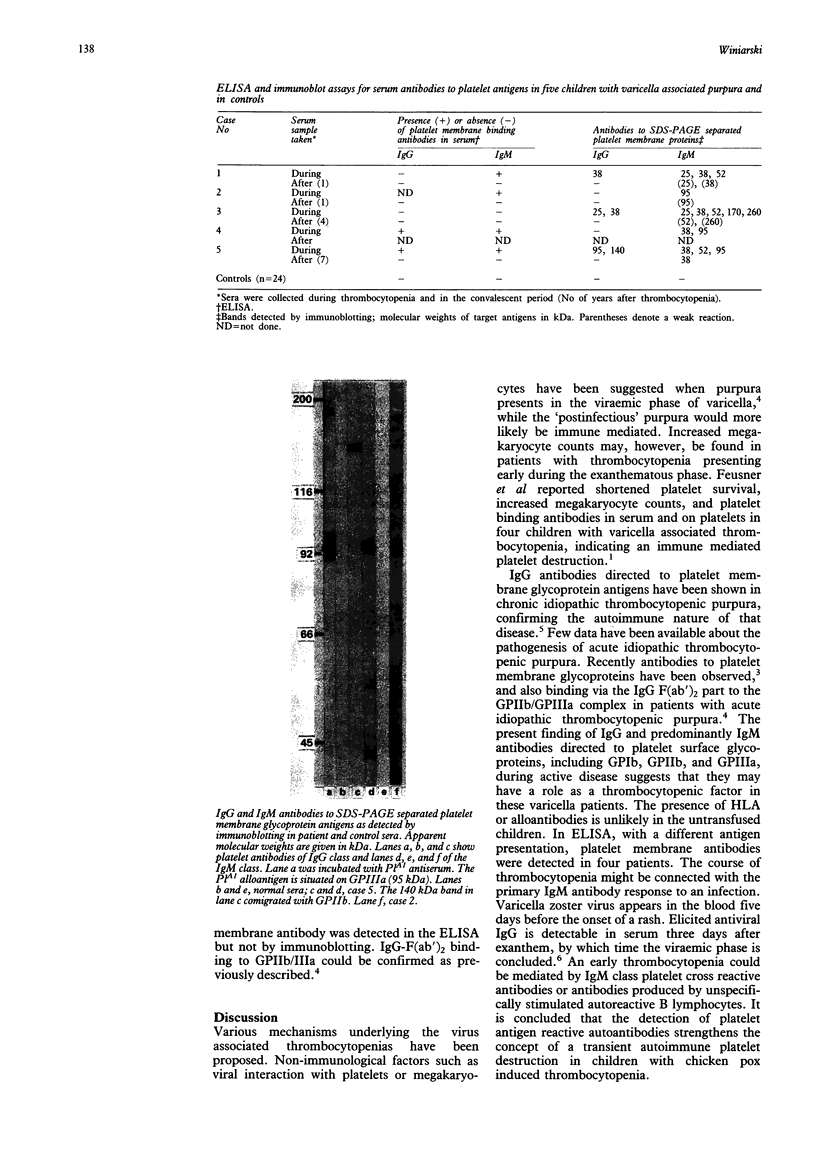
Serum IgG or, predominantly, IgM antibody binding to electrophoretically separated normal platelet membrane protein antigens were detected by immunoblotting in five children with thrombocytopenia associated with varicella. Glycoproteins GPIb, GPIIb, GPIIIa, and other 25-260 kilodalton (kDa) proteins were identified as target antigens, suggesting a transient autoimmune mechanism causing the thrombocytopenia.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano Y., Itakura N., Hiroishi Y., Hirose S., Ozaki T., Kuno K., Nagai T., Yazaki T., Yamanishi K., Takahashi M. Viral replication and immunologic responses in children naturally infected with varicella-zoster virus and in varicella vaccine recipients. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):863–868. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza C., Kuhn C. Viral infection of megakaryocytes in varicella with purpura. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Feb;61(2):203–208. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feusner J. H., Slichter S. J., Harker L. A. Mechanisms of thrombocytopenia in varicella. Am J Hematol. 1979;7(3):255–264. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830070308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiarski J., Ekelund E. Antibody binding to platelet antigens in acute and chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a platelet membrane ELISA for the detection of antiplatelet antibodies in serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Feb;63(2):459–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiarski J. IgG and IgM antibodies to platelet membrane glycoprotein antigens in acute childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1989 Sep;73(1):88–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]