Abstract
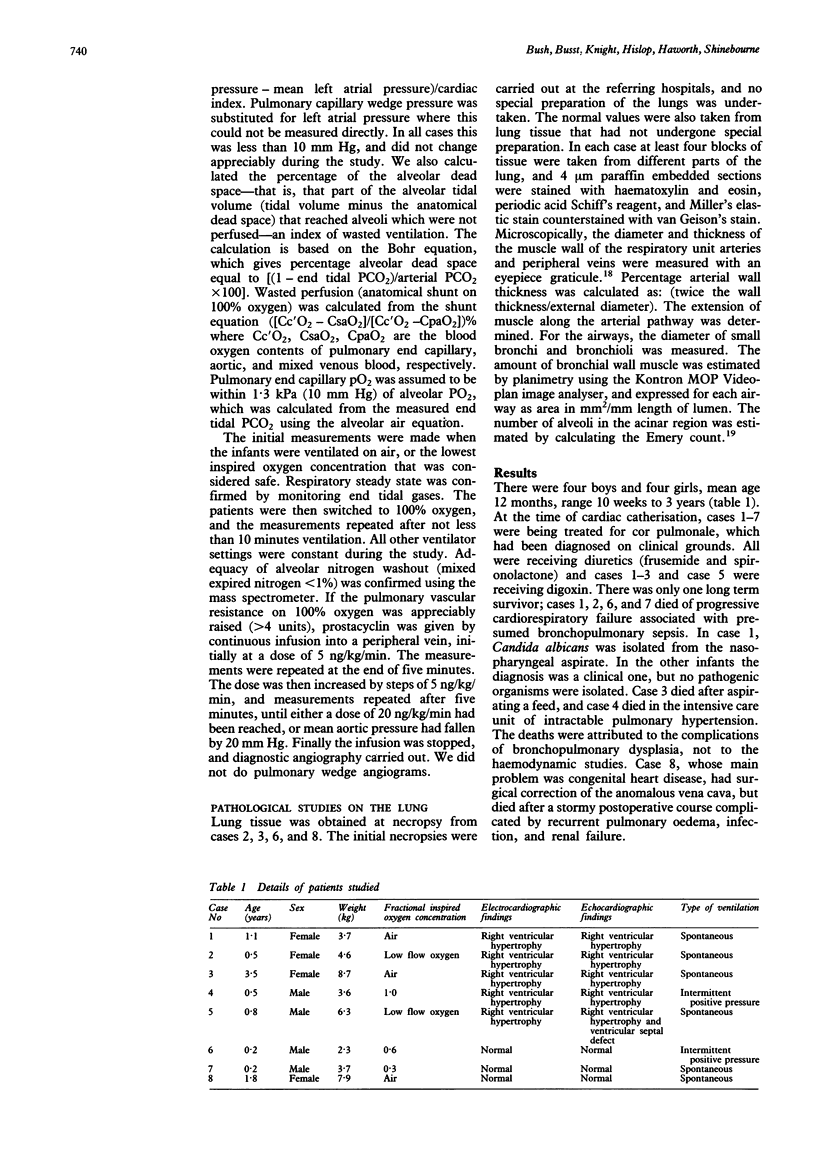
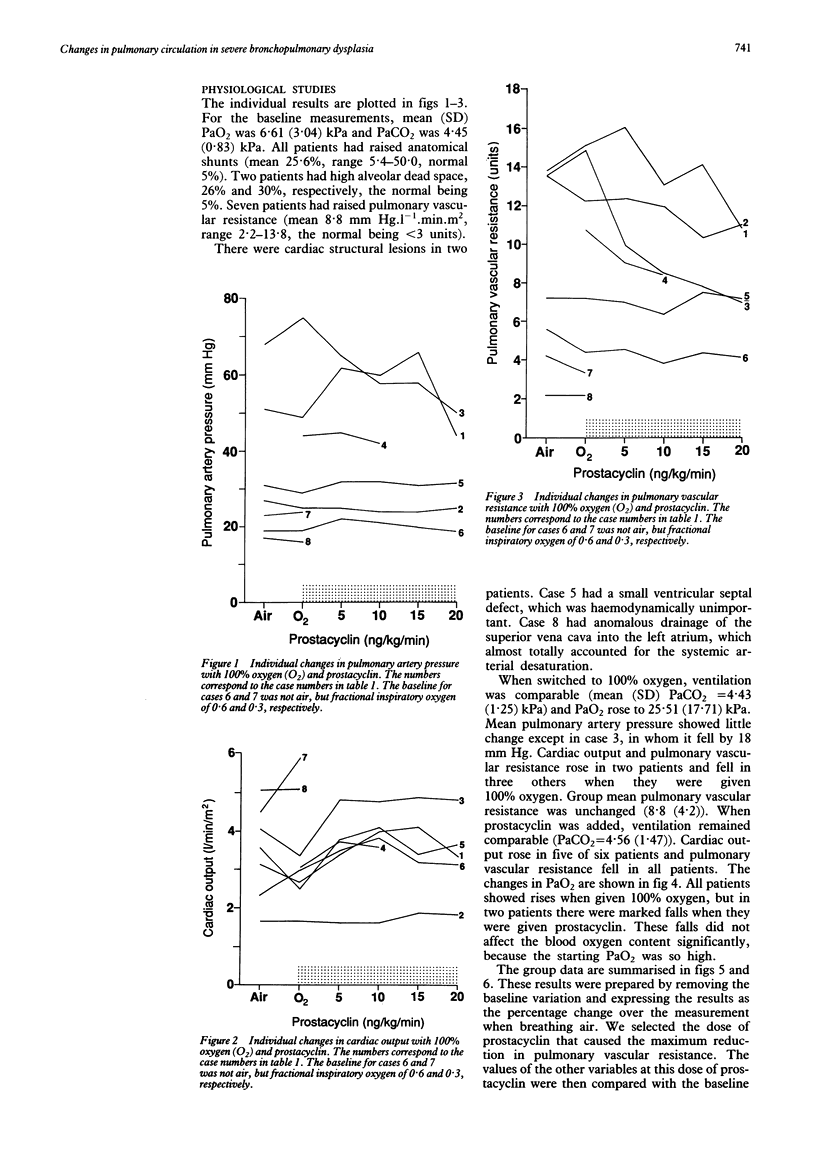
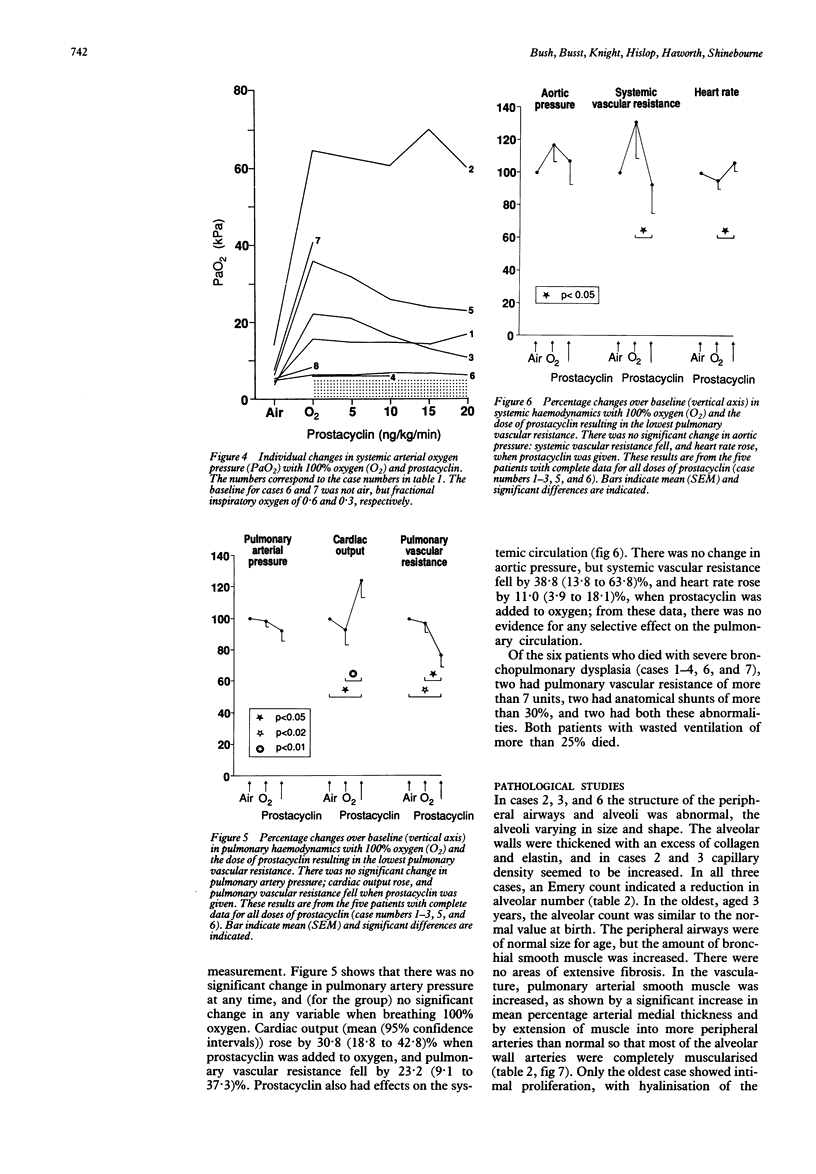
Eight patients with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia underwent cardiac catheterisation. Seven had a pulmonary vascular resistance greater than 3 mm Hg.l-1 min.m2 (mean 8.9, range 2.2-13.8). All had raised intrapulmonary shunts (mean 25.6%, range 5.4-50%, normal less than 5%). Two had a high alveolar dead space, and two had unsuspected congenital heart disease. Epoprostenol (prostacyclin), but not 100% oxygen, caused a significant fall in pulmonary vascular resistance. Death was associated with a high pulmonary vascular resistance and a high shunt. Morphometric studies in three cases showed normal numbers of airways, but increased thickness of bronchial muscle. The numbers of alveoli were reduced and the walls thickened. There was increased medial thickness in small pulmonary arteries with distal extension of muscle. In the oldest child some vessels were obliterated by fibrosis. We speculate that measurements of pulmonary vascular resistance and shunt may have prognostic value; that a trial of pulmonary vasodilators other than oxygen might be worthwhile in patients with poor prognosis; and that abnormalities of the pulmonary circulation contribute to the difficulties of managing patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Full text
PDF
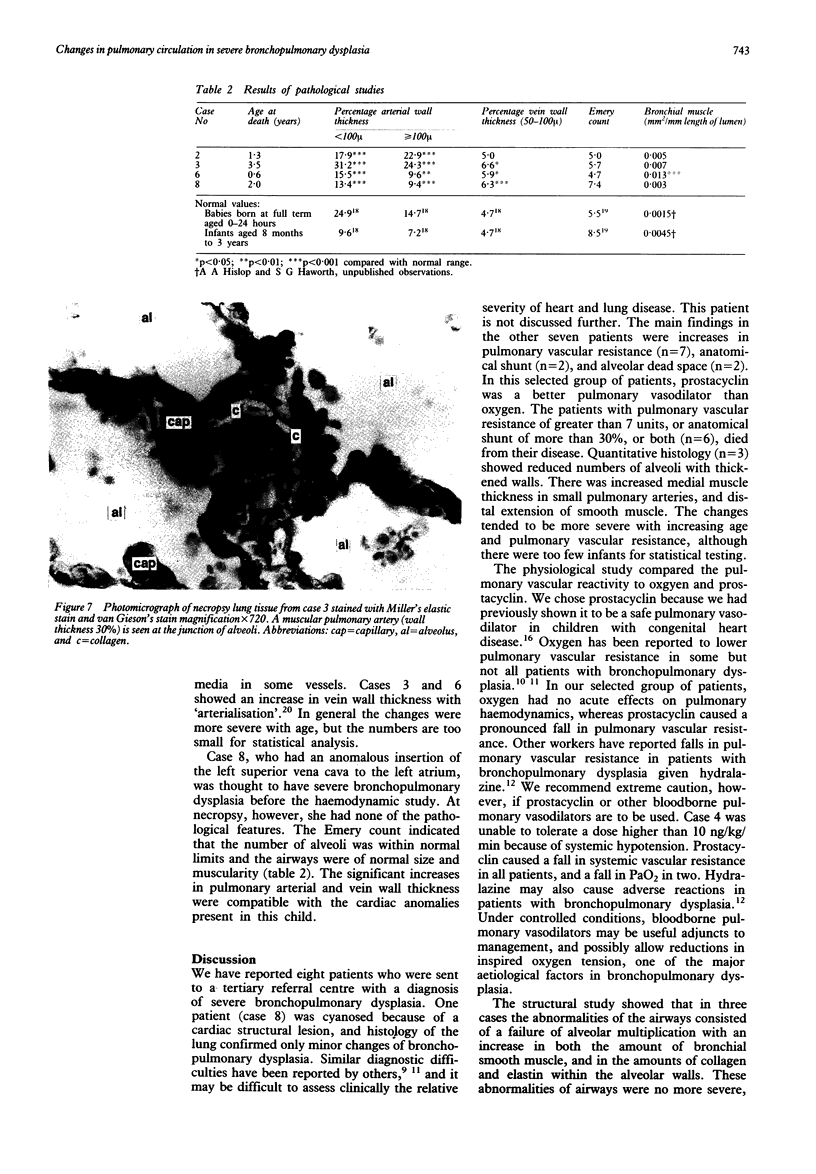


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abman S. H., Accurso F. J., Bowman C. M. Unsuspected cardiopulmonary abnormalities complicating bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Oct;59(10):966–970. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.10.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancalari E., Gerhardt T. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986 Feb;33(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34967-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman W., Jr, Katz R., Yabek S. M., Dillon T., Fripp R. R., Papile L. A. Long-term follow-up of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1986 Jul;109(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80570-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman W., Jr, Yabek S. M., Dillon T., Burstein R., Corlew S. Evaluation of infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia using cardiac catheterization. Pediatrics. 1982 Nov;70(5):708–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boat T. F., Kleinerman J. I., Fanaroff A. A., Matthews L. W. Toxic effects of oxygen on cultured human neonatal respiratory epithelium. Pediatr Res. 1973 Jul;7(7):607–615. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197307000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan M. H., Hardie M. J., Reilly B. J., Swyer P. R. Pulmonary function studies during the first year of life in infants recovering from the respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1973 Aug;52(2):169–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush A., Busst C., Booth K., Knight W. B., Shinebourne E. A. Does prostacyclin enhance the selective pulmonary vasodilator effect of oxygen in children with congenital heart disease? Circulation. 1986 Jul;74(1):135–144. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. N., Zarfin Y., Groenveld M., Bryan M. H. Low flow oxygen therapy in infants. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Oct;58(10):795–798. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.10.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. J., Denison D. M. The measurement of metabolic gas exchange and minute volume by mass spectrometry alone. Respir Physiol. 1979 Feb;36(2):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(79)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMERY J. L., MITHAL A. The number of alveoli in the terminal respiratory unit of man during late intrauterine life and childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1960 Dec;35:544–547. doi: 10.1136/adc.35.184.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman G., Perkin R. M., Anas N. G., Sperling D. R., Hicks D. A., Rowen M. Pulmonary hypertension in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1988 Jan;112(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenough A., Roberton N. R. Morbidity and survival in neonates ventilated for the respiratory distress syndrome. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Feb 23;290(6468):597–600. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6468.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrod J. R., L'Heureux P., Wangensteen O. D., Hunt C. E. Long-term follow-up of severe respiratory distress syndrome treated with IPPB. J Pediatr. 1974 Feb;84(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80623-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth S. G., Hall S. M., Panja M., Patel M. Peripheral pulmonary vascular and airway abnormalities in adolescents with rheumatic mitral stenosis. Int J Cardiol. 1988 Mar;18(3):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(88)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth S. G., Hislop A. A. Pulmonary vascular development: normal values of peripheral vascular structure. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Sep 1;52(5):578–583. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A. A., Wigglesworth J. S., Desai R., Aber V. The effects of preterm delivery and mechanical ventilation on human lung growth. Early Hum Dev. 1987 May;15(3):147–164. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(87)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hislop A., Reid L. Pulmonary arterial development during childhood: branching pattern and structure. Thorax. 1973 Mar;28(2):129–135. doi: 10.1136/thx.28.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman G. R. Digital computer subroutine for the conversion of oxygen tension into saturation. J Appl Physiol. 1966 Jul;21(4):1375–1376. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.4.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northway W. H., Jr, Rosan R. C., Porter D. Y. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 16;276(7):357–368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702162760701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn J. F. Oxygen--friend and foe. J R Soc Med. 1985 Aug;78(8):618–622. doi: 10.1177/014107688507800803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H. M., Mellins R. B. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Unresolved neonatal acute lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):694–709. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney M. A., Cotton E. K. Home management of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 1976 Dec;58(6):856–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendas A., Brown E. R., Avery M. E., Reid L. M. Prematurity, hypoplasia of the pulmonary vascular bed, and hypertension: fatal outcome in a ten-month-old infant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 May;121(5):873–880. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.5.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth J. A., Tabachnik E., Duncan W. J., Reilly B. J., Levison H. Pulmonary function and bronchial hyperreactivity in long-term survivors of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 1981 Sep;68(3):336–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobonya R. E., Logvinoff M. M., Taussig L. M., Theriault A. Morphometric analysis of the lung in prolonged bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res. 1982 Nov;16(11):969–972. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198211000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker J. T. Pathologic features of long-standing "healed" bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a study of 28 3- to 40-month-old infants. Hum Pathol. 1986 Sep;17(9):943–961. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80646-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taghizadeh A., Reynolds E. O. Pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia following hyaline membrane disease. Am J Pathol. 1976 Feb;82(2):241–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepper R. S., Pagtakhan R. D., Taussig L. M. Noninvasive determination of total respiratory system compliance in infants by the weighted-spirometer method. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Sep;130(3):461–466. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.3.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Oppermann H. C., Vawter G. F., Reid L. M. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a morphometric study with emphasis on the pulmonary vasculature. Pediatr Pathol. 1984;2(4):469–487. doi: 10.3109/15513818409025895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenvoort C. A. Morphologic changes in intrapulmonary veins. Hum Pathol. 1970 Jun;1(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]