Abstract
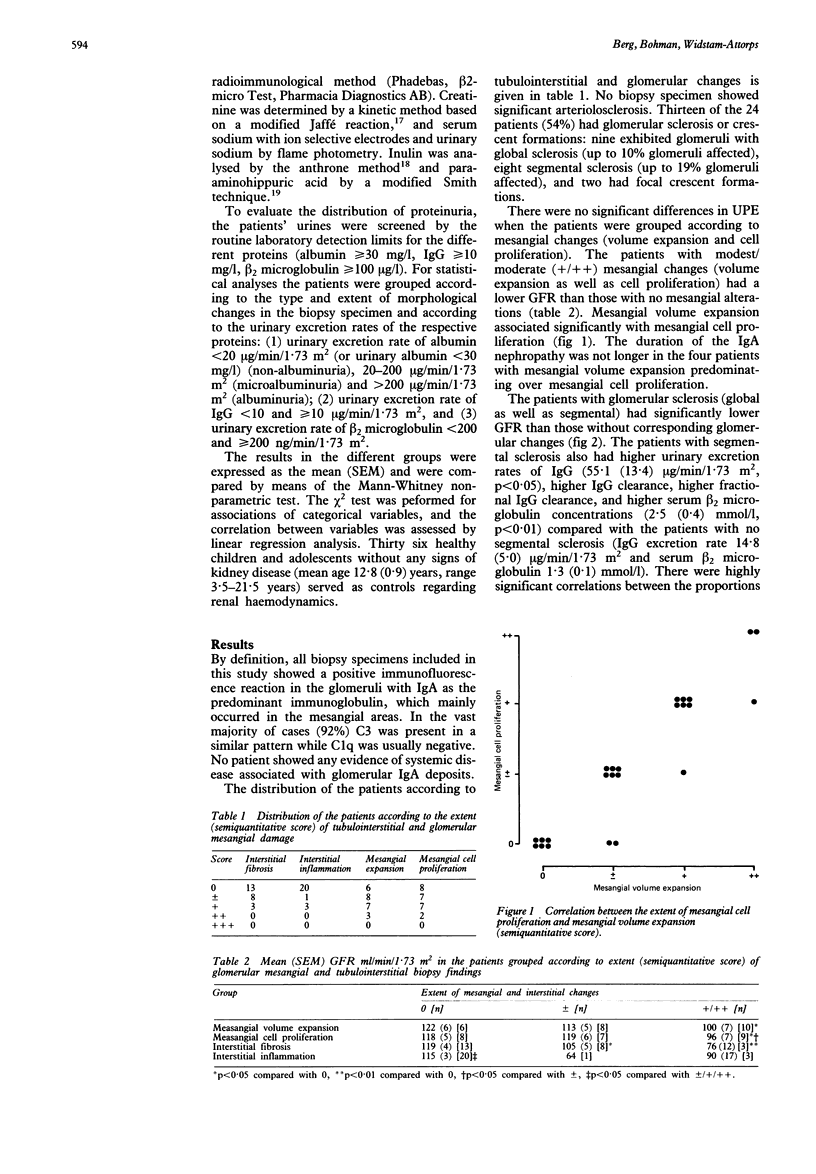
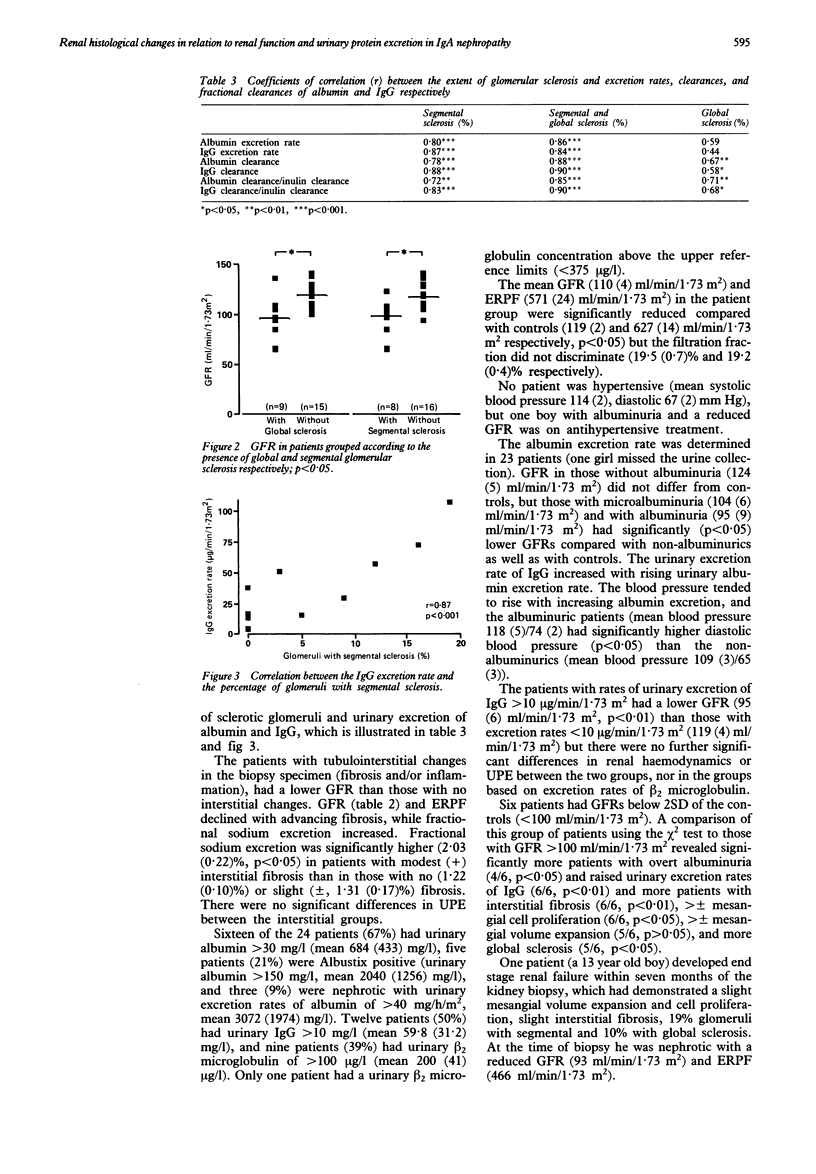
Renal function and urinary protein excretion (UPE) were investigated at the time of kidney biopsy in 24 children with IgA nephropathy. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) were measured by clearances of inulin and para-aminohippuric acid. For UPE albumin, IgG, beta 2 microglobulin, and creatinine were analysed. Glomerular global/segmental sclerosis and crescents in the biopsy specimens were assessed, and glomerular and tubulointerstitial changes classified on a five degree scale. The patients with tubulointerstitial or mesangial biopsy changes or glomerular sclerosis had significantly lower GFR than those without corresponding lesions. Patients with segmental sclerosis also had higher excretion rates of IgG, which increased with increasing segmental sclerosis. Six patients had GFRs below 2SD of the controls. Within the group of patients with reduced GFR overt albuminuria, a raised excretion rate of IgG, interstitial fibrosis, and advanced mesangial lesions were more frequent. A rising excretion rate of IgG seems to indicate both reduced GFR and increasing segmental glomerulosclerosis and may be a marker of progressive disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A multicenter study of IgA nephropathy in children. A report of the Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group. Kidney Int. 1982 Dec;22(6):643–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg U., Bohlin A. B. Renal hemodynamics in minimal change nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Int J Pediatr Nephrol. 1982 Sep;3(3):187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chida Y., Tomura S., Takeuchi J. Renal survival rate of IgA nephropathy. Nephron. 1985;40(2):189–194. doi: 10.1159/000183477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson A. R., Seymour A. E., Thompson A. J., Haynes W. D., Chan Y. L., Jackson B. IgA nephropathy: a syndrome of uniform morphology, diverse clinical features and uncertain prognosis. Clin Nephrol. 1977 Nov;8(5):459–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croker B. P., Dawson D. V., Sanfilippo F. IgA nephropathy. Correlation of clinical and histologic features. Lab Invest. 1983 Jan;48(1):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico G., Minetti L., Ponticelli C., Fellin G., Ferrario F., Barbiano di Belgioioso G., Imbasciati E., Ragni A., Bertoli S., Fogazzi G. Prognostic indicators in idiopathic IgA mesangial nephropathy. Q J Med. 1986 Apr;59(228):363–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987 Sep;64(245):709–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiner H. D., Cabili S., Baldwin D. S., Schacht R. G., Gallo G. R. Intrarenal vascular sclerosis in IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol. 1982 Oct;18(4):183–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILGER H. H., KLUMPER J. D., ULLRICH K. J. Wasserrückresorption und Ionentransport durch die Sammelrohrzellen der Säugetierniere; mikroanalytische Untersuchungen. Pflugers Arch. 1958;267(3):218–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00362426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood S. A., Velosa J. A., Holley K. E., Donadio J. V., Jr IgA-IgG nephropathy: predictive indices of progressive disease. Clin Nephrol. 1981 Aug;16(2):55–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Tateno S., Hiki Y., Shigematsu H. IgA nephropathy: prognostic significance of proteinuria and histological alterations. Nephron. 1983;34(3):146–153. doi: 10.1159/000183000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusumoto Y., Takebayashi S., Taguchi T., Harada T., Naito S. Long-term prognosis and prognostic indices of IgA nephropathy in juvenile and in adult Japanese. Clin Nephrol. 1987 Sep;28(3):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy M., Gonzalez-Burchard G., Broyer M., Dommergues J. P., Foulard M., Sorez J. P., Habib R. Berger's disease in children. Natural history and outcome. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985 May;64(3):157–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P., Ohlsson P., Björkhem I. Combined enzymic-Jaffé method for determination of creatinine in serum. Clin Chem. 1981 Jan;27(1):18–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mina S. N., Murphy W. M. IgA nephropathy. A comparative study of the clinicopathologic features in children and adults. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jun;83(6):669–675. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls K. M., Fairley K. F., Dowling J. P., Kincaid-Smith P. The clinical course of mesangial IgA associated nephropathy in adults. Q J Med. 1984 Spring;53(210):227–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell A. E., Northam B. E. New automated dye-binding method for serum albumin determination with bromcresol purple. Clin Chem. 1978 Jan;24(1):80–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambausek M., Seelig H. P., Andrassy K., Waldherr R., Kehry I., Lenhard V., Ritz E. Mesangiale IgA-Glomerulonephritis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1983 Jan 28;108(4):125–130. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1069513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Finkelstein N., Aliminosa L., Crawford B., Graber M. THE RENAL CLEARANCES OF SUBSTITUTED HIPPURIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND OTHER AROMATIC ACIDS IN DOG AND MAN. J Clin Invest. 1945 May;24(3):388–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI101618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa N., Iijima K., Maehara K., Yoshiara S., Yoshiya K., Matsuo T., Okada S. Mesangial changes in IgA nephropathy in children. Kidney Int. 1987 Oct;32(4):585–589. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa N., Iijima K., Matsuyama S., Suzuki J., Kameda A., Okada S., Nakamura H. Repeat renal biopsy in children with IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol. 1990 Apr;33(4):160–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


