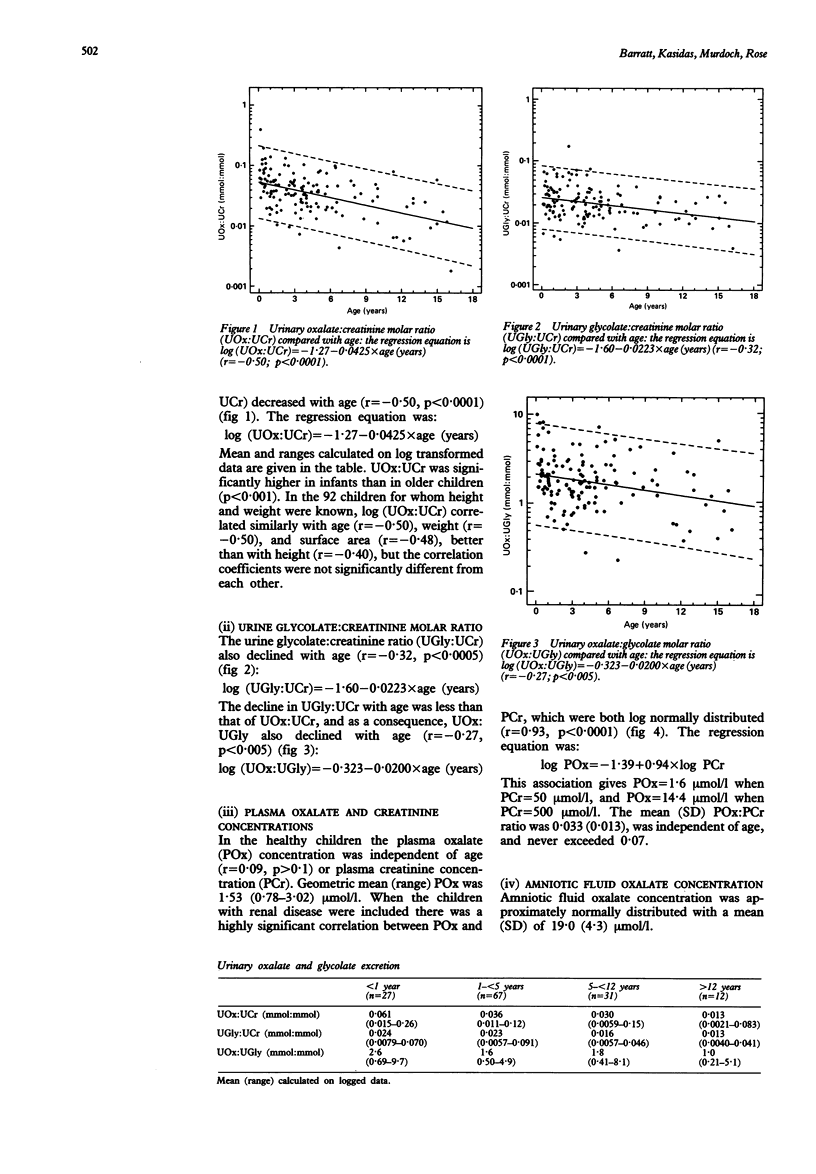
Abstract
The diagnosis of primary hyperoxaluria in young children is hampered by the lack of a reliable reference range for urinary oxalate excretion, especially in infants. We present data on urinary oxalate and glycolate excretion in 137 normal children, on the plasma oxalate concentration in 33 normal children and 53 with chronic renal failure, and on amniotic fluid oxalate concentration in 63 uncomplicated pregnancies. The urinary oxalate:creatinine molar ratios were log normally distributed: mean (range) values were less than 1 year 0.061 (0.015-0.26), 1-5 years 0.036 (0.011-0.12), 5-12 years 0.030 (0.0059-0.15), and greater than 12 years 0.013 (0.0021-0.083). Geometric mean (range) plasma oxalate concentration in the normal children was 1.53 (0.78-3.02) mumols/l and was independent of age. The mean (SD) plasma oxalate: creatinine molar ratio in these normal children and 50 with chronic renal failure was 0.033 (0.013), and was independent of age and renal function. Mean (SD) amniotic fluid oxalate concentration was 19.0 (4.3) mumols/l.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Constable A. R., Joekes A. M., Kasidas G. P., O'Regan P., Rose G. A. Plasma level and renal clearance of oxalate in normal subjects and in patients with primary hyperoxaluria or chronic renal failure or both. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Apr;56(4):299–304. doi: 10.1042/cs0560299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danpure C. J., Jennings P. R. Peroxisomal alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase deficiency in primary hyperoxaluria type I. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 26;201(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80563-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danpure C. J. Peroxisomal alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase and prenatal diagnosis of primary hyperoxaluria type 1. Lancet. 1986 Nov 15;2(8516):1168–1168. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90584-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs D. A., Watts R. W. The variation of urinary oxalate excretion with age. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jun;73(6):901–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasidas G. P., Rose G. A. A new enzymatic method for the determination of glycollate in urine and plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Aug 15;96(1-2):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasidas G. P., Rose G. A. Continuous-flow assay for urinary oxalate using immobilised oxalate oxidase. Ann Clin Biochem. 1985 Jul;22(Pt 4):412–419. doi: 10.1177/000456328502200415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasidas G. P., Rose G. A. Measurement of plasma oxalate in healthy subjects and in patients with chronic renal failure using immobilised oxalate oxidase. Clin Chim Acta. 1986 Jan 15;154(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(86)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leumann E., Matasović A., Niederwieser A. Primary hyperoxaluria type I: oxalate and glycolate unsuitable for prenatal diagnosis. Lancet. 1986 Aug 9;2(8502):340–340. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G. A., Arthur L. J., Chambers T. L., Kasidas G. P., Scott I. V. Successful treatment of primary hyperoxaluria in neonate. Lancet. 1982 Jun 5;1(8284):1298–1299. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92855-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


