Abstract
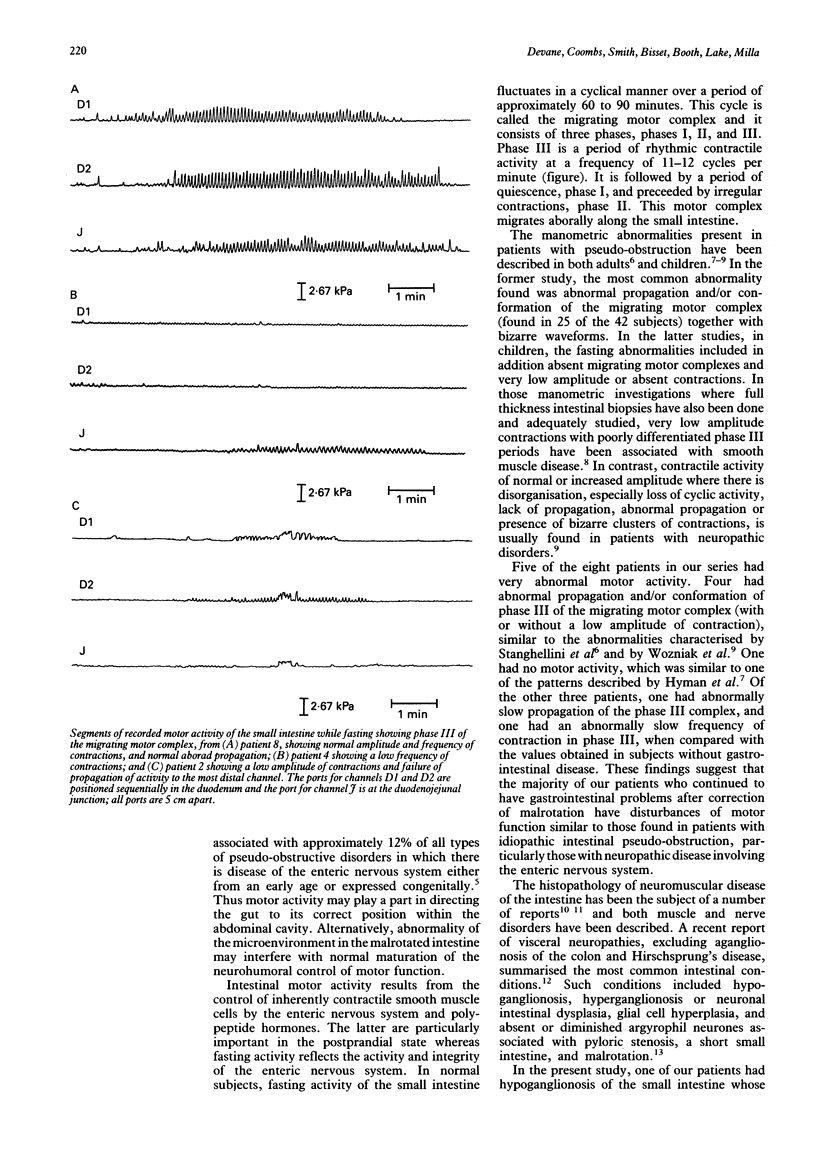
Persistent vomiting, diarrhoea, or intolerance of feeding, are well recognised problems in children after surgical correction of intestinal malrotation. Conversely, intestinal malrotation is a common accompaniment of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. We investigated motor activity of the small intestine during fasting in eight children who had persistent vomiting, intolerance of full enteral feeding, or severe diarrhoea after surgical correction of intestinal malrotation. Abnormality of motor function similar to that found in neuropathic pseudo-obstruction was found in seven of the eight patients. Persistence of symptoms after surgical correction of a malrotation is associated with a motility disturbance which seems to be due to a defect of intrinsic enteric innervation. Such a defect may be important in the aetiology of the malrotation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chayvialle J. A., Paulin C., Descos F., Dubois P. M. Ontogeny of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the human fetal digestive tract. Regul Pept. 1983 Feb;5(3):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton T. R., Harries J. T., Milla P. J. Disordered small intestinal motility: a rational basis for toddlers' diarrhoea. Gut. 1983 Oct;24(10):897–903. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.10.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman P. E., McDiarmid S. V., Napolitano J., Abrams C. E., Tomomasa T. Antroduodenal motility in children with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. J Pediatr. 1988 Jun;112(6):899–905. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M. The ontogeny of the neural crest in avian embryo chimaeras. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):663–669. doi: 10.1038/286663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro J., Sonsino E., Boige N., Nabarra B., Ferkadji L., Mashako L. M., Cezard J. P. Visceral neuropathies responsible for chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome in pediatric practice: analysis of 26 cases. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1990 Aug;11(2):179–195. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199008000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri P., Lake B. D., Nixon H. H., Mishalany H., Claireaux A. E. Neuronal colonic dysplasia: an unusual association of Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediatr Surg. 1977 Oct;12(5):681–685. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(77)90393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Res J. R., Redo S. F. Anomalies of intestinal rotation and fixation. Am J Surg. 1968 Dec;116(6):834–841. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(68)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann C. A., Jr, Ricci M. T., Krishnamurthy S., Schuffler M. D. Radiologic and histologic differentiation of neuromuscular disorders of the gastrointestinal tract: visceral myopathies, visceral neuropathies, and progressive systemic sclerosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Nov;143(5):933–941. doi: 10.2214/ajr.143.5.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini V., Camilleri M., Malagelada J. R. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: clinical and intestinal manometric findings. Gut. 1987 Jan;28(1):5–12. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryker S. J., Borody T. J., Phillips S. F., Kelly K. A., Dozois R. R., Beart R. W., Jr Motility of the small intestine after proctocolectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. Ann Surg. 1985 Mar;201(3):351–356. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198503000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. S., Smith B., Lloyd J. K. Functional intestinal obstruction due to deficiency of argyrophil neurones in the myenteric plexus. Familial syndrome presenting with short small bowel, malrotation, and pyloric hypertrophy. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Nov;51(11):837–841. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.11.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas J. H., Sachs P., Ament M. E. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome in pediatrics. Results of a national survey by members of the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988 May-Jun;7(3):323–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


