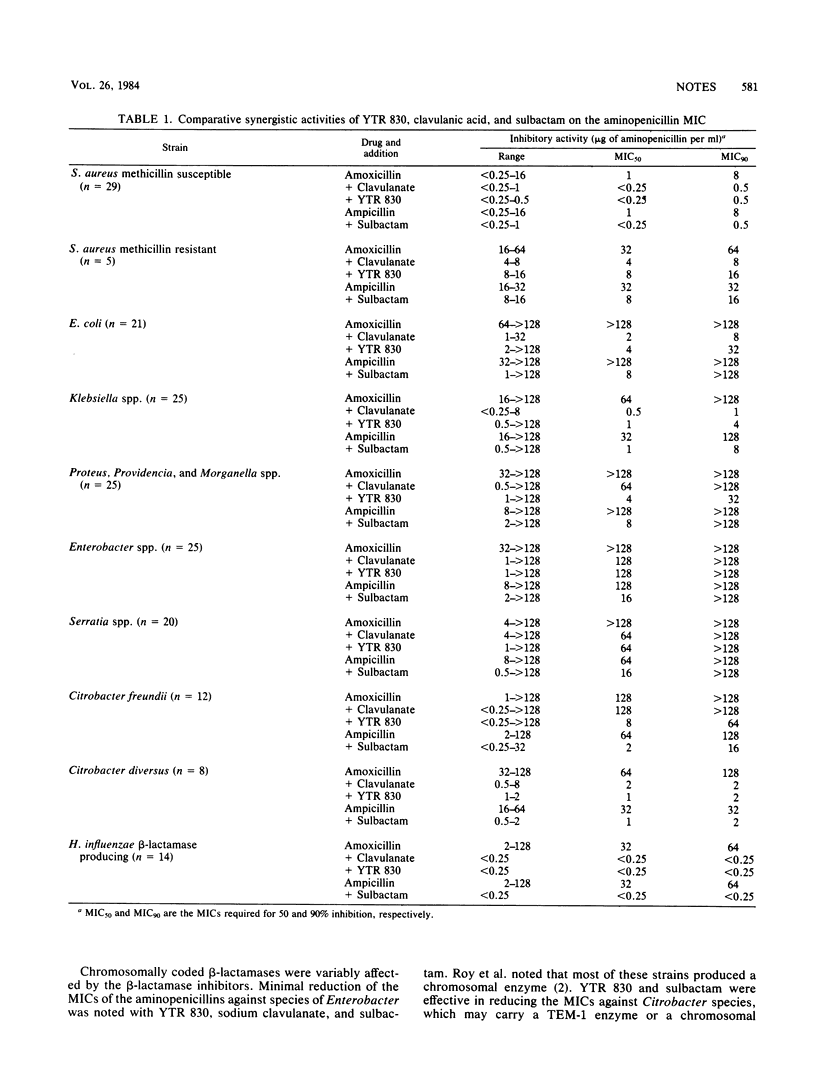
Abstract
YTR 830, a new beta-lactamase inhibitor, was compared with clavulanic acid and sulbactam against aminopenicillin-resistant clinical isolates. At a concentration of 8 micrograms/ml, YTR 830 was as effective as clavulanate or sulbactam in reducing the aminopenicillin MICs. Combined with amoxicillin, YTR 830 is a potentially useful agent for therapy of many bacterial infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Roy C., Foz A., Segura C., Tirado M., Fuster C., Reig R. Plasmid-determined beta-lactamases identified in a group of 204 ampicillin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Nov;12(5):507–510. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.5.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


