Abstract
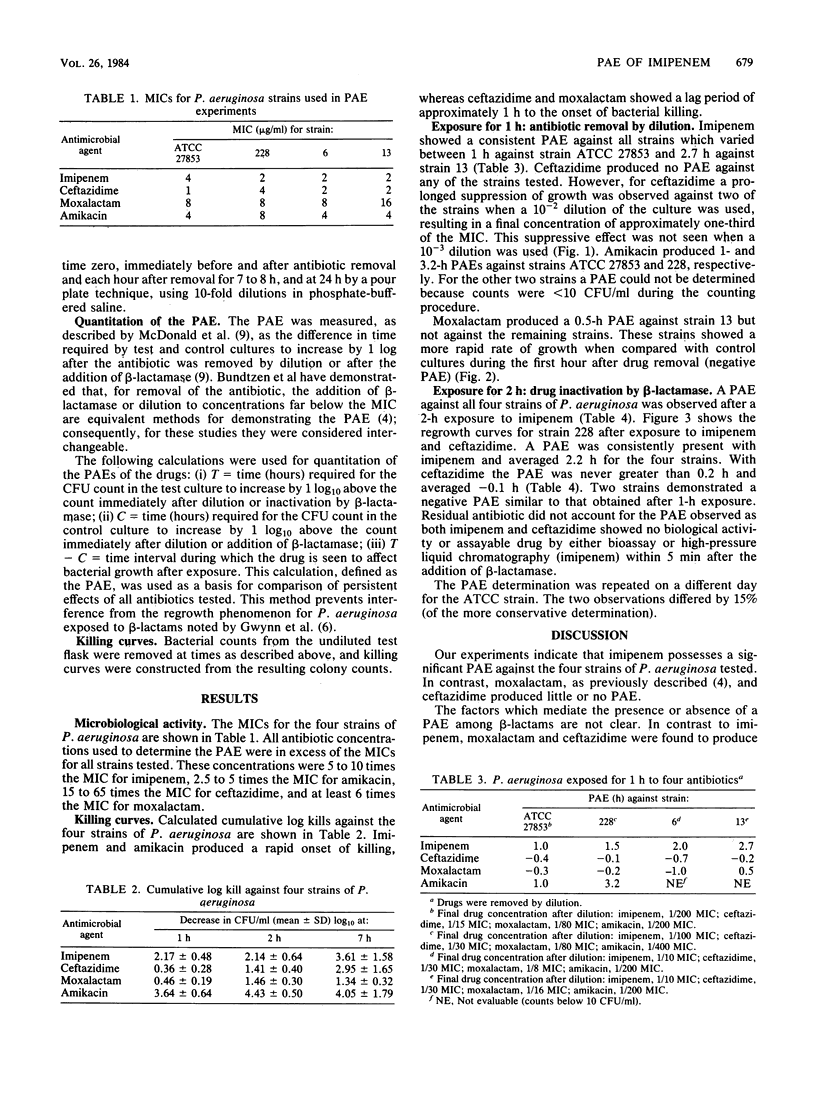
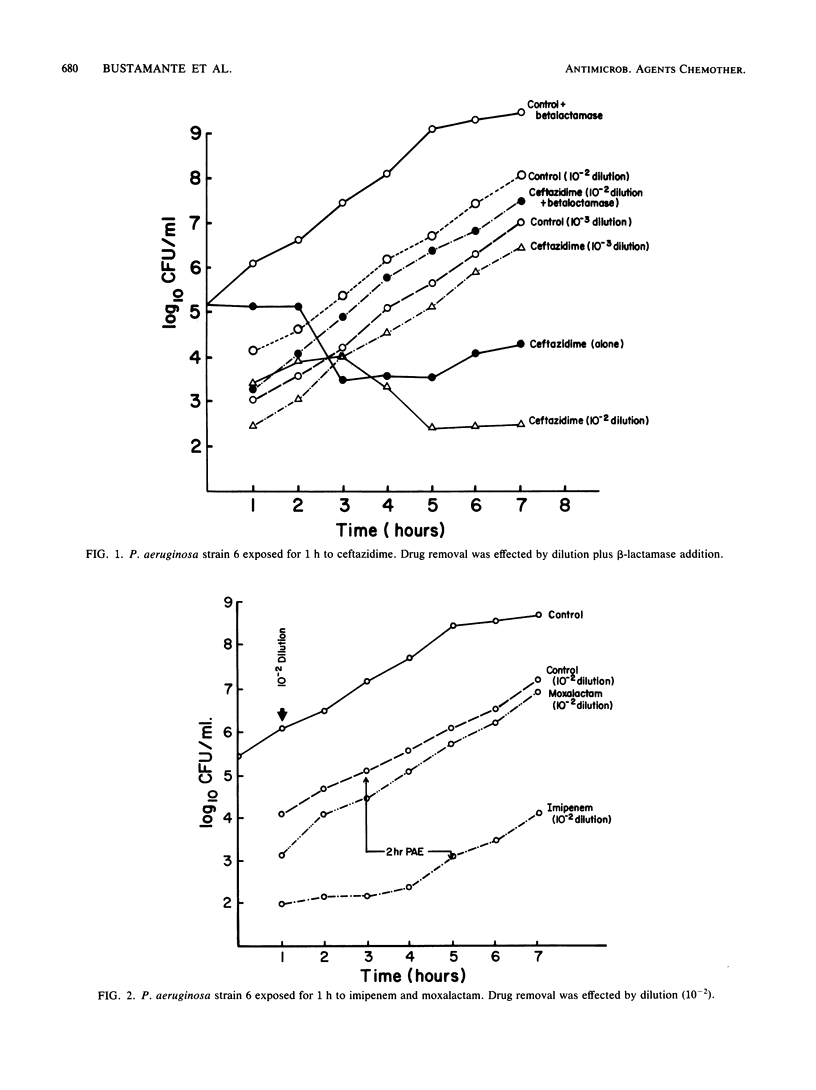
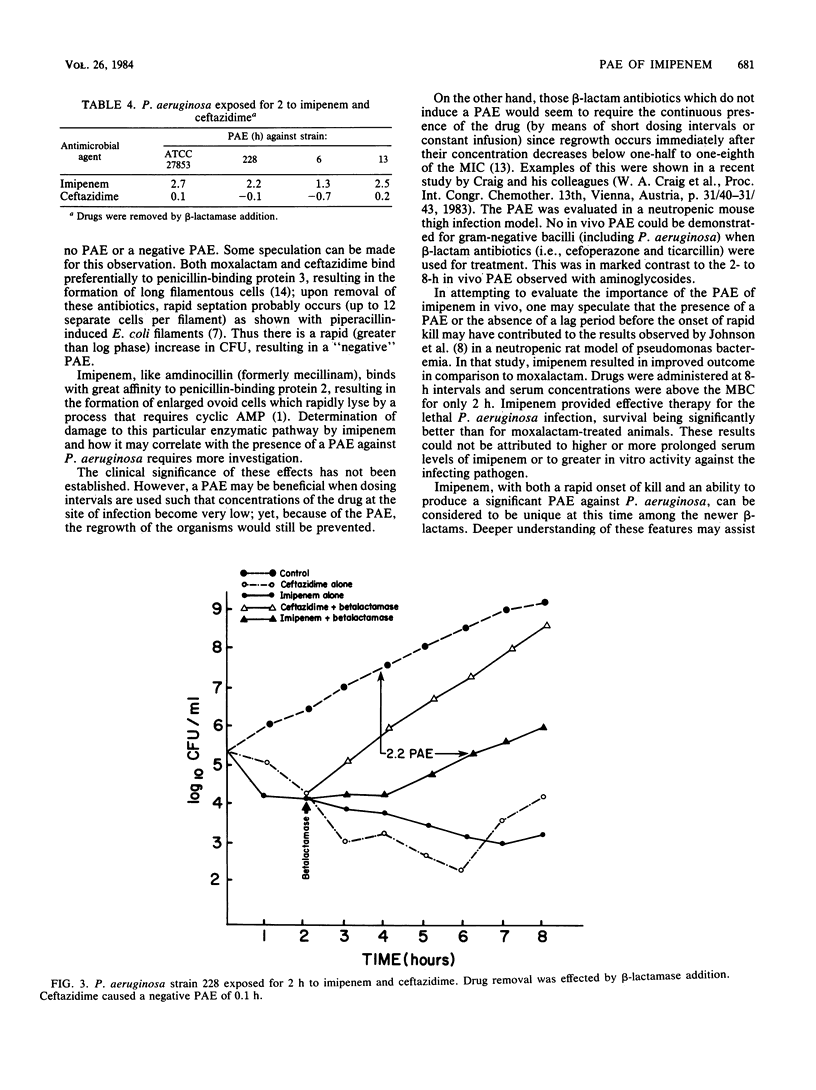
Imipenem (formerly N-formimidoyl thienamycin) and ceftazidime were investigated for their postantibiotic effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Four strains of P. aeruginosa in the logarithmic phase of growth were exposed for 1 and 2 h to concentrations of antibiotics achievable in human serum. Recovery periods of test cultures were evaluated after dilution or addition of beta-lactamase. A consistent postantibiotic effect against all strains was obtained with imipenem but not with ceftazidime. Although ceftazidime did not have a postantibiotic effect, it did suppress the growth of the organisms at concentrations equivalent to one-third of the MIC. The clinical implications of these effects need further evaluation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aono R., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. High and selective resistance to mecillinam in adenylate cyclase-deficient or cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor protein-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):839–845. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.839-845.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Pan T. Effect of cephalothin on growth patterns of micro-organisms. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Oct;29(10):1092–1095. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundtzen R. W., Gerber A. U., Cohn D. L., Craig W. A. Postantibiotic suppression of bacterial growth. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):28–37. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H., Musselman A. D. THE SLOW RECOVERY OF BACTERIA FROM THE TOXIC EFFECTS OF PENICILLIN. J Bacteriol. 1949 Oct;58(4):475–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.4.475-490.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynn M. N., Webb T. L., Rolinson G. N. Regrowth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria after the bactericidal action of carbenicillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):263–269. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Nakamuta S., Hirata S., Koike M. Resumption of cell division in piperacillin-induced filaments of Escherichia coli B/r. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jun;9(6):451–459. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.6.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Calia F. M., Snyder M. J., Warren J. W., Schimpff S. C. Imipenem therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteraemia in neutropenic rats. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Dec;12 (Suppl 500):89–96. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_d.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. J., Craig W. A., Kunin C. M. Persistent effect of antibiotics on Staphylococcus aureus after exposure for limited periods of time. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):217–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. F., Luse S. The Action of Penicillin on Staphylococcus: Further Observations on the Effect of a Short Exposure. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jul;56(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.1.75-81.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. F., Marsh H. C. Action of Penicillin on Staphylococcus. J Bacteriol. 1946 Feb;51(2):181–186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. From penicillin-binding proteins to the lysis and death of bacteria: a 1979 view. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):434–467. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. A., Rolinson G. N. The recovery period following exposure of bacteria to penicillins. Chemotherapy. 1979;25(1):14–22. doi: 10.1159/000237817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


