Abstract
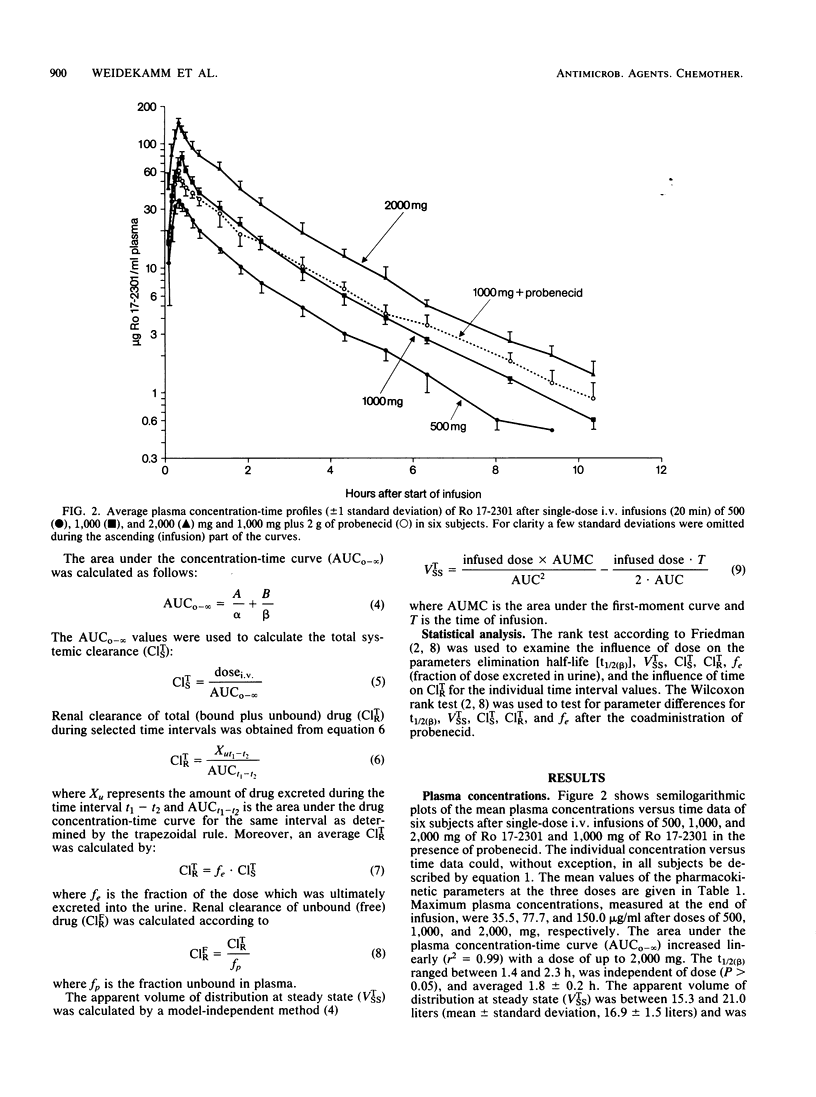
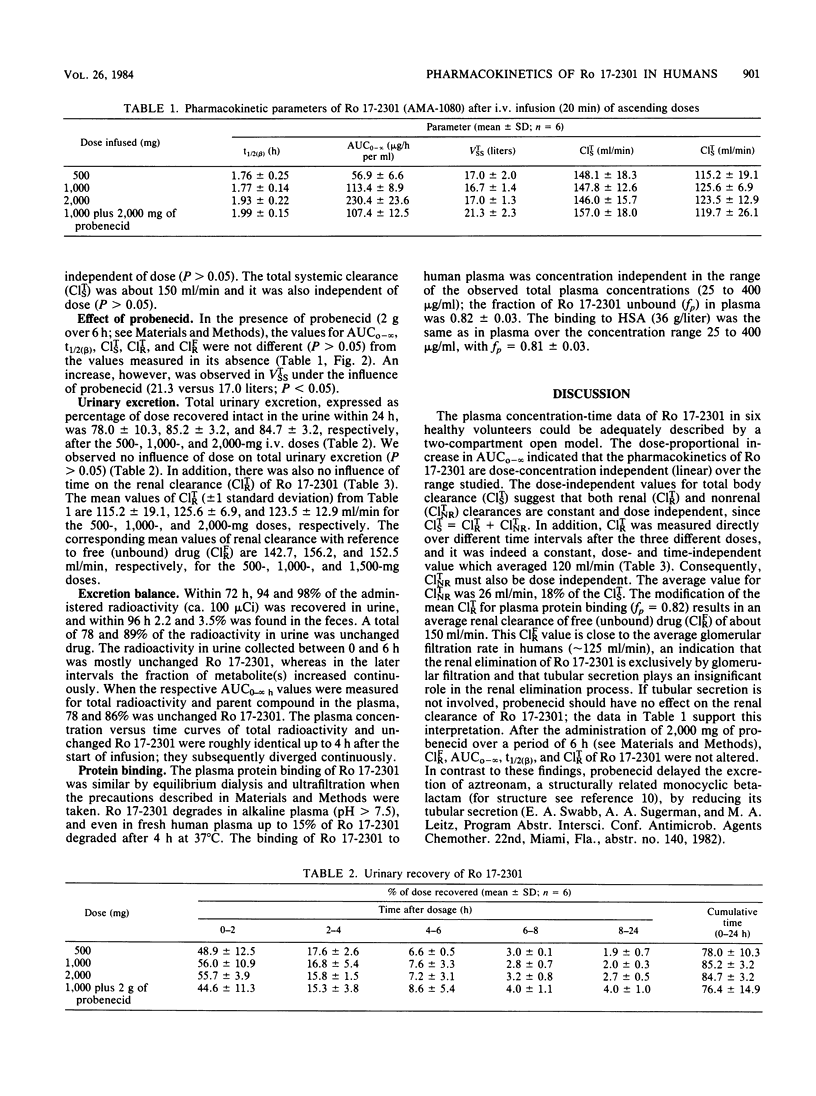
Ro 17-2301 (AMA-1080) is a new N-sulfonated monocyclic beta-lactam that is highly active against gram-negative bacteria, especially against Enterobacteriaceae and Haemophilus, Neisseria, and Pseudomonas spp. (Kondo et al., Proc. Int. Congr. Chemother. 13th, Vienna, Austria, p. 56/1-56/5, 1983). The single-dose pharmacokinetics of this compound were studied in six healthy male volunteers who received intravenous infusions of 500, 1,000, and 2,000 mg. A good linear correlation (r2 = 0.99) was found between the dose infused and the resulting area under the plasma concentration-time curve. Maximal plasma concentrations of 36, 78, and 150 micrograms/ml appeared after doses of 500, 1,000, and 2,000 mg, respectively. The mean terminal elimination half-life was 1.8 h (range, 1.4 to 2.3 h), the apparent volume of distribution at steady state was 17 liters, and the total systemic clearance was 150 ml/min. Within 72 h 78 to 89% of the dose was recovered intact from urine. After administration of 14C-labeled Ro 17-2301, 96% of the radioactivity was found in the urine and 3% was found in the feces. The concomitant administration of probenecid did not affect the renal clearance or urinary excretion of this beta-lactam, an indication that the renal elimination of this substance is only by glomerular filtration. Ro 17-2301 was 18% bound to human plasma protein, and this binding was independent of concentration between 25 and 400 micrograms/ml. Based on these data, the pharmacokinetics of this monocyclic beta-lactam should be predictable in the foreseen dose ranges.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Imada A., Kitano K., Kintaka K., Muroi M., Asai M. Sulfazecin and isosulfazecin, novel beta-lactam antibiotics of bacterial origin. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):590–591. doi: 10.1038/289590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. S., Brater D. C., Gambertoglio J. G., Benet L. Z. Disposition kinetics of ethambutol in man. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1980 Aug;8(4):335–346. doi: 10.1007/BF01059382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie S., Tozer T. N. Effect of altered plasma protein binding on apparent volume of distribution. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Sep;68(9):1203–1205. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Georgopapadakou N. H., Wells J. S. Monobactams--monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotics produced by bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):1–16. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


