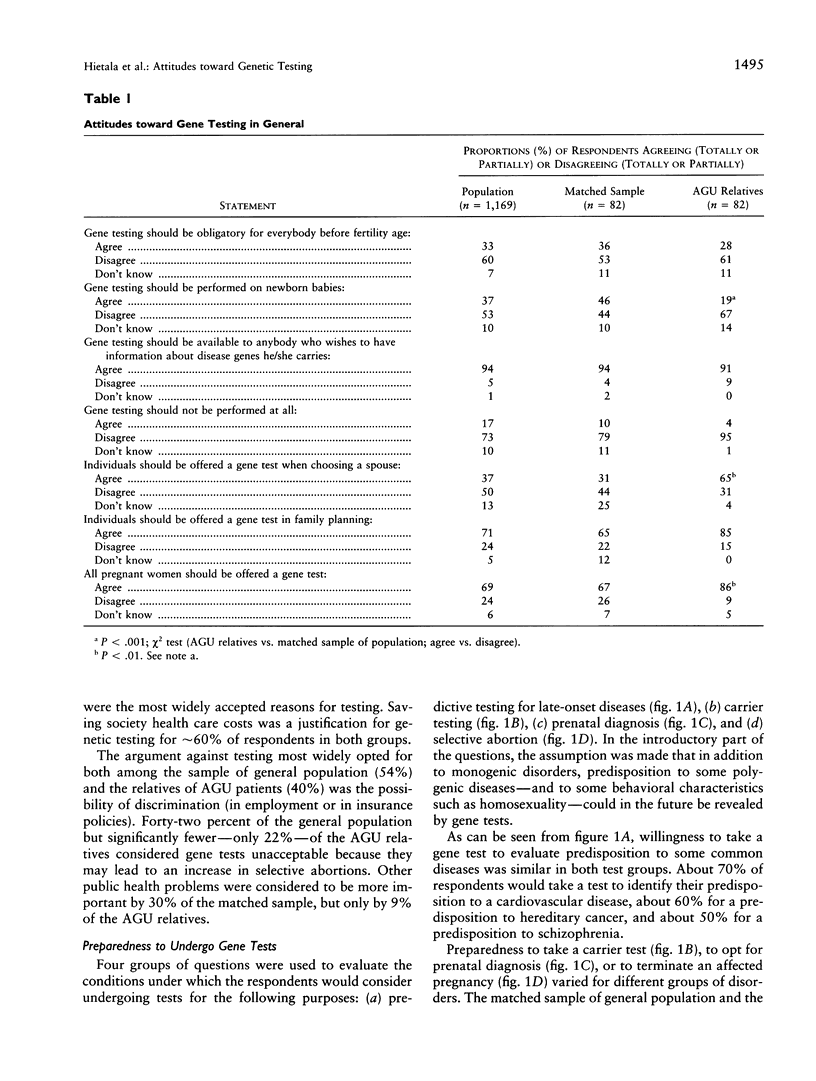
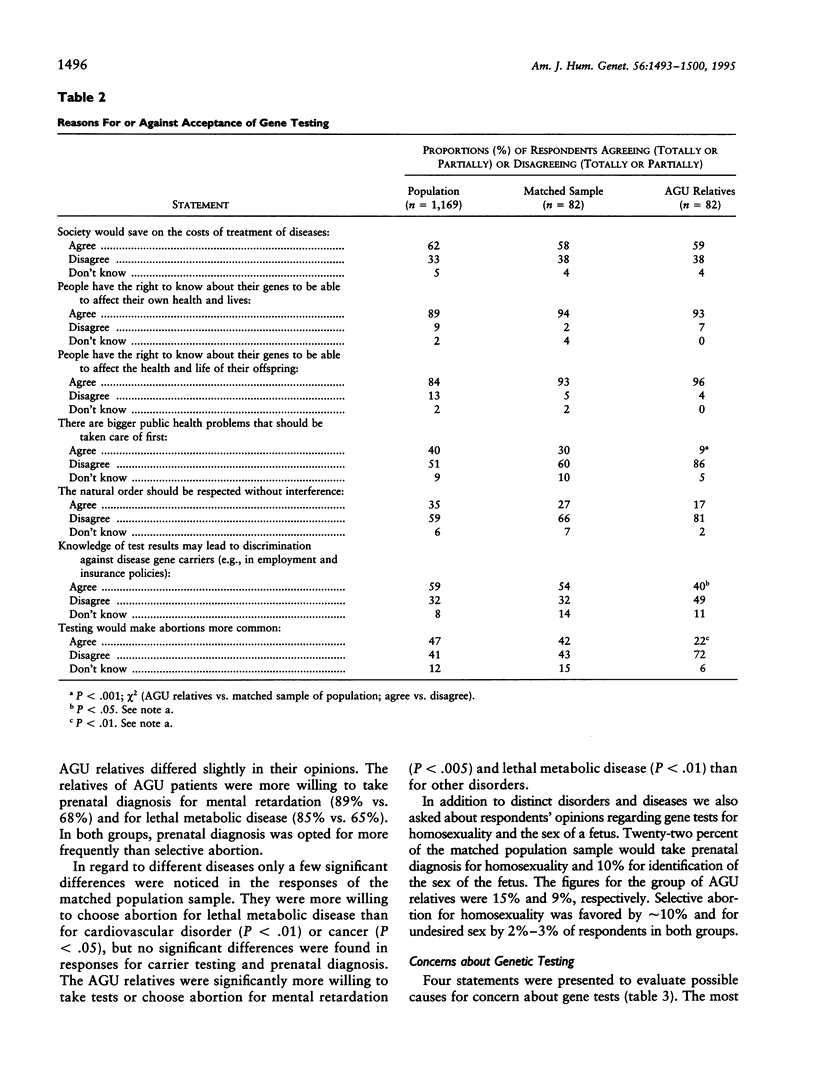
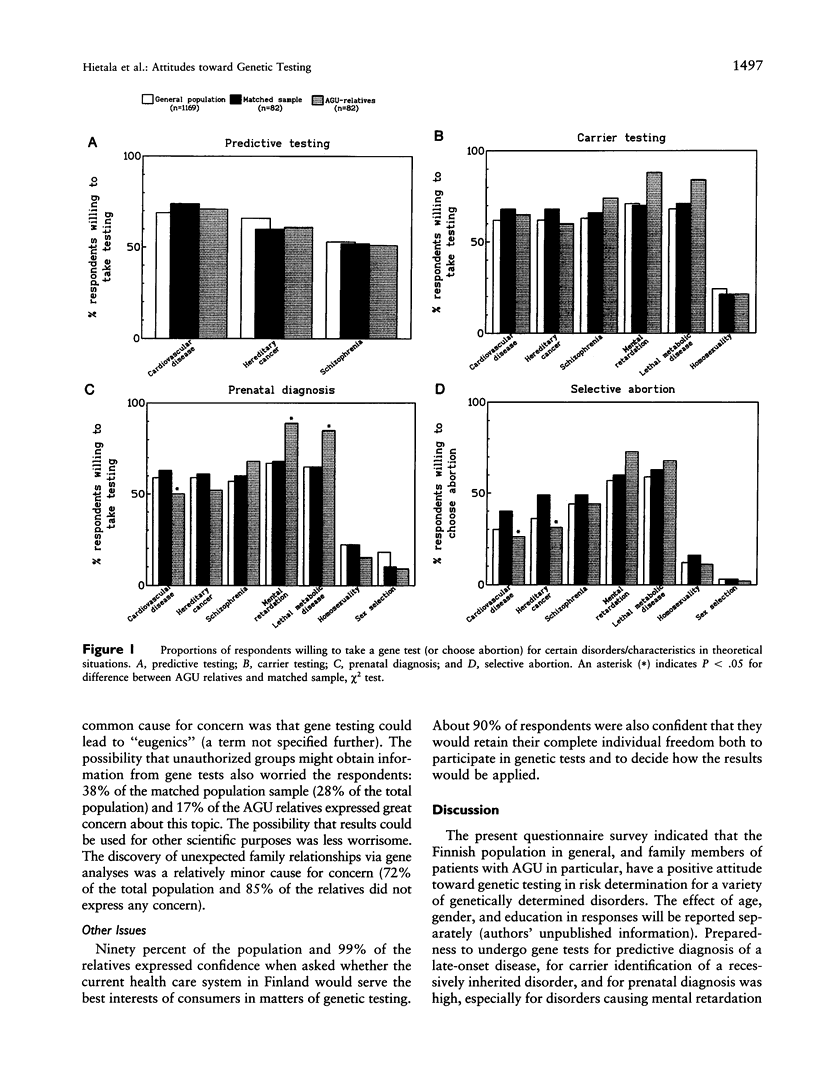
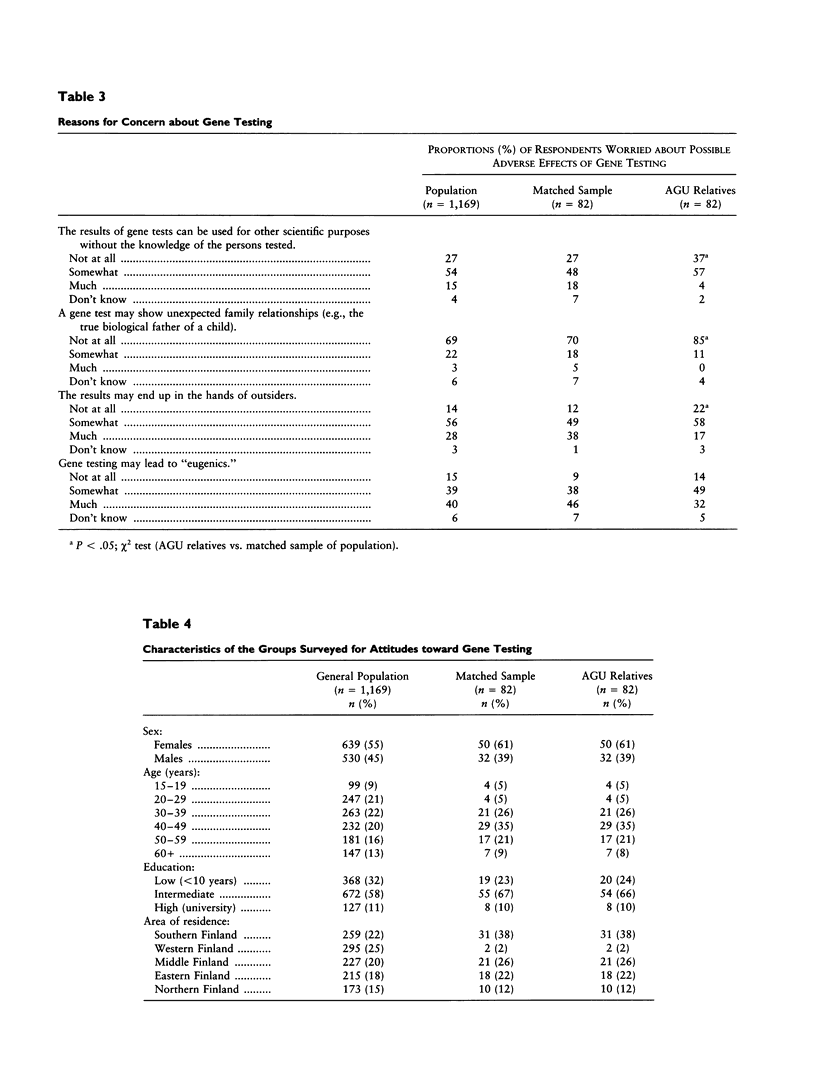
Abstract
In the present study we explore the attitudes of the Finnish population toward genetic testing by conducting a questionnaire study of a stratified sample of the population as well as of family members of patients with a severe hereditary disease, aspartylglucosaminuria (AGU). The questionnaire evaluated attitudes toward gene tests in general and also respondents' preparedness to undergo gene tests for predictive testing, carrier detection, prenatal diagnosis, and selective abortion, in theoretical situations. The results of the study indicate that both the Finnish population in general and family members of AGU patients have a favorable attitude toward genetic testing. However, a commonly expressed reason against testing was that test results might lead to discrimination in employment or insurance policies. Based on the responses, we predict that future genetic testing programs will most probably be met with a high acceptance rate by the Finnish population.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekker H., Denniss G., Modell M., Bobrow M., Marteau T. The impact of population based screening for carriers of cystic fibrosis. J Med Genet. 1994 May;31(5):364–368. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.5.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clow C. L., Scriver C. R. Knowledge about and attitudes toward genetic screening among high-school students: the Tay-Sachs experience. Pediatrics. 1977 Jan;59(1):86–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway S. P., Allenby K., Pond M. N. Patient and parental attitudes toward genetic screening and its implications at an adult cystic fibrosis centre. Clin Genet. 1994 Jun;45(6):308–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1994.tb04037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decruyenaere M., Evers-Kiebooms G., Denayer L., Van den Berghe H. Cystic fibrosis: community knowledge and attitudes towards carrier screening and prenatal diagnosis. Clin Genet. 1992 Apr;41(4):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. M. Principles and practicalities of carrier screening: attitudes of recent parents. J Med Genet. 1992 May;29(5):313–319. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.5.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hietala M., Grön K., Syvänen A. C., Peltonen L., Aula P. Prospects of carrier screening of aspartylglucosaminuria in Finland. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(4):296–300. doi: 10.1159/000472427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan F., Clow C., Scriver C. R. Cystic fibrosis carrier screening by DNA analysis: a pilot study of attitudes among participants. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):240–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennie M., Compton M., Gilfillan A., Axton R. A., Liston W. A., Pullen I., Whyte D., Brock D. J. Prenatal screening for cystic fibrosis: attitudes and responses of participants. Clin Genet. 1993 Aug;44(2):102–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1993.tb03856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J., Scriver C. R., Clow C. L., Kaplan F. What young people think and do when the option for cystic fibrosis carrier testing is available. J Med Genet. 1993 Jul;30(7):538–542. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.7.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley P. T., Lipkin M., Jr, Fisher L. Screening and genetic counseling for beta-thalassemia trait in a population unselected for interest: comparison of three counseling methods. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):677–689. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvänen A. C., Ikonen E., Manninen T., Bengtström M., Söderlund H., Aula P., Peltonen L. Convenient and quantitative determination of the frequency of a mutant allele using solid-phase minisequencing: application to aspartylglucosaminuria in Finland. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):590–595. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90452-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tambor E. S., Bernhardt B. A., Chase G. A., Faden R. R., Geller G., Hofman K. J., Holtzman N. A. Offering cystic fibrosis carrier screening to an HMO population: factors associated with utilization. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;55(4):626–637. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. K., Mayall E. S., Lamb J., Chapple J., Williamson R. Psychological and social consequences of community carrier screening programme for cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1992 Jul 25;340(8813):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90477-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. K., Williamson R., Chapple J. Attitudes to carrier screening for cystic fibrosis: a survey of health care professionals, relatives of sufferers and other members of the public. Br J Gen Pract. 1991 Jun;41(347):237–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Allison M. E., Bentley T. J., Lim S. M., Watson E., Chapple J., Adam S., Boulton M. Community attitudes to cystic fibrosis carrier testing in England: a pilot study. Prenat Diagn. 1989 Oct;9(10):727–734. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970091008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeesman S., Clow C. L., Cartier L., Scriver C. R. A private view of heterozygosity: eight-year follow-up study on carriers of the Tay-Sachs gene detected by high school screening in Montreal. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Aug;18(4):769–778. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A. Disease gene mapping in isolated human populations: the example of Finland. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):857–865. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


