Abstract
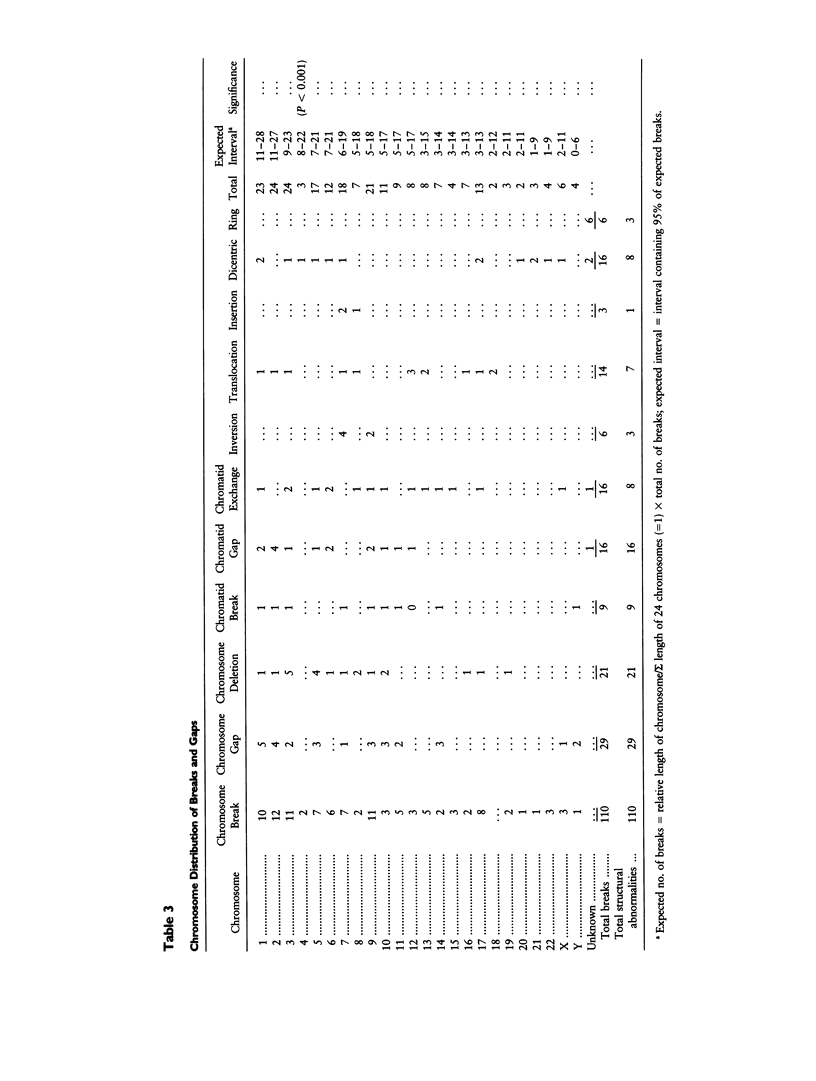
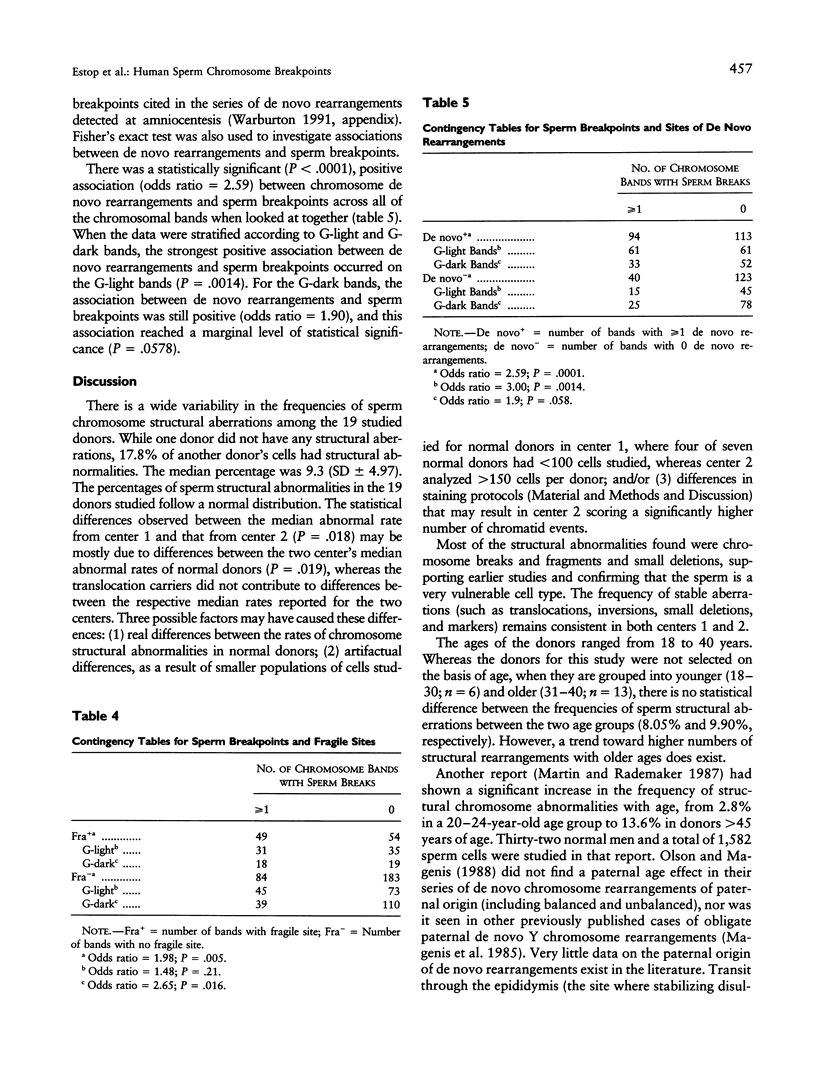
Sperm chromosome analysis of 19 sperm donors with either normal or balanced karyotypes was carried out in order to explore the nature of sperm chromosome structural aberrations. A total of 2,389 cells (range 36-298/donor) were karyotyped after in vitro penetration of hamster eggs. The median percentage of sperm structural aberrations was 9.3% (SD +/- 4.7; range 0%-17.8%), with a total of 247 breakpoints, of which 220 could be characterized fully. Two sets of donors were studied in two different centers: center 1 (United States) and center 2 (Spain). The frequencies of nonrejoined and rejoined chromosome-type aberrations were very similar between center 1 and center 2: 83.6% and 10.0%, and 75.0% and 10.3%, respectively. Chromatid-type aberrations were more frequent in center 2 (14.7%) than in center 1 (6.4%) (P = .037). Chromosome 4 had less than the expected number of breakpoints (P < .001). A positive significant correlation was found between sperm breakpoints reported in this study and sites of balanced chromosome de novo rearrangements detected at prenatal diagnosis and reported in the literature (P = .0001).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aula P., von Koskull H. Distribution of spontaneous chromosome breaks in human chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1976 May 19;32(2):143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00291497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benet J., Fuster C., Genescà A., Navarro J., Miró R., Egozcue J., Templado C. Expression of fragile sites in human sperm and lymphocyte chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1989 Feb;81(3):239–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00278996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benet J., Genescà A., Navarro J., Egozcue J., Templado C. Cytogenetic studies in motile sperm from normal men. Hum Genet. 1992 May;89(2):176–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00217119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benet J., Navarro J., Genescà A., Egozcue J., Templado C. Chromosome abnormalities in human spermatozoa after albumin or TEST-Yolk capacitation. Hum Reprod. 1991 Mar;6(3):369–375. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a137342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriff B. F., Gordon L. A., Moore D., 2nd, Carrano A. V. An analysis of structural aberrations in human sperm chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;47(1-2):29–36. doi: 10.1159/000132500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehling U. H., Neuhäuser-Klaus A. Induction of specific-locus and dominant-lethal mutations by cyclophosphamide and combined cyclophosphamide-radiation treatment in male mice. Mutat Res. 1988 May;199(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estop A. M., Cieply K., Vankirk V., Munne S., Garver K. Cytogenetic studies in human sperm. Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;87(4):447–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00197166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estop A. M., Levinson F., Cieply K., Vankirk V. The segregation of a translocation t(1;4) in two male carriers heterozygous for the translocation. Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;89(4):425–429. doi: 10.1007/BF00194315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genescà A., Caballín M. R., Miró R., Benet J., Germà J. R., Egozcue J. Repair of human sperm chromosome aberrations in the hamster egg. Hum Genet. 1992 May;89(2):181–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00217120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. H. A detailed method for obtaining preparations of human sperm chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1983;35(4):252–256. doi: 10.1159/000131876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. H., Rademaker A. W., Ko E., Barclay L., Hildebrand K. A comparison of the frequency and type of chromosomal abnormalities in human sperm after different sperm capacitation conditions. Biol Reprod. 1992 Aug;47(2):268–270. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod47.2.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. H., Rademaker A. W. The effect of age on the frequency of sperm chromosomal abnormalities in normal men. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;41(3):484–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Tobari I. Chromosomal analysis in mouse eggs fertilized in vitro with sperm exposed to ultraviolet light (UV) and methyl and ethyl methanesulfonate (MMS and EMS). Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;198(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Ayme S., Mattei J. F., Aurran Y., Giraud F. Distribution of spontaneous chromosome breaks in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;23(1-2):95–102. doi: 10.1159/000131309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munne S., Estop A. The effect of in-vitro ageing on mouse sperm chromosomes. Hum Reprod. 1991 May;6(5):703–708. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a137412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro J., Benet J., Martorell M. R., Templado C., Egozcue J. Segregation analysis in a man heterozygous for a pericentric inversion of chromosome 7 (p13;q36) by sperm chromosome studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):214–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudak E., Jacobs P. A., Yanagimachi R. Direct analysis of the chromosome constitution of human spermatozoa. Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):911–913. doi: 10.1038/274911a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santaló J., Estop A. M., Egozcue J. The chromosome complement of first-cleavage mouse embryos after in vitro fertilization. J In Vitro Fert Embryo Transf. 1986 Apr;3(2):99–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01139354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templado C., Navarro J., Benet J., Genescà A., Pérez M. M., Egozcue J. Human sperm chromosome studies in a reciprocal translocation t(2;5). Hum Genet. 1988 May;79(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00291704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templado C., Navarro J., Requena R., Benet J., Ballesta F., Egozcue J. Meiotic and sperm chromosome studies in a reciprocal translocation t(1;2)(q32;q36). Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;84(2):159–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00208932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton D. De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements and extra marker chromosomes identified at prenatal diagnosis: clinical significance and distribution of breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):995–1013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Working P. K., Butterworth B. E. An assay to detect chemically induced DNA repair in rat spermatocytes. Environ Mutagen. 1984;6(3):273–286. doi: 10.1002/em.2860060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]