Abstract
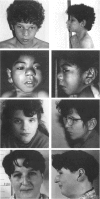
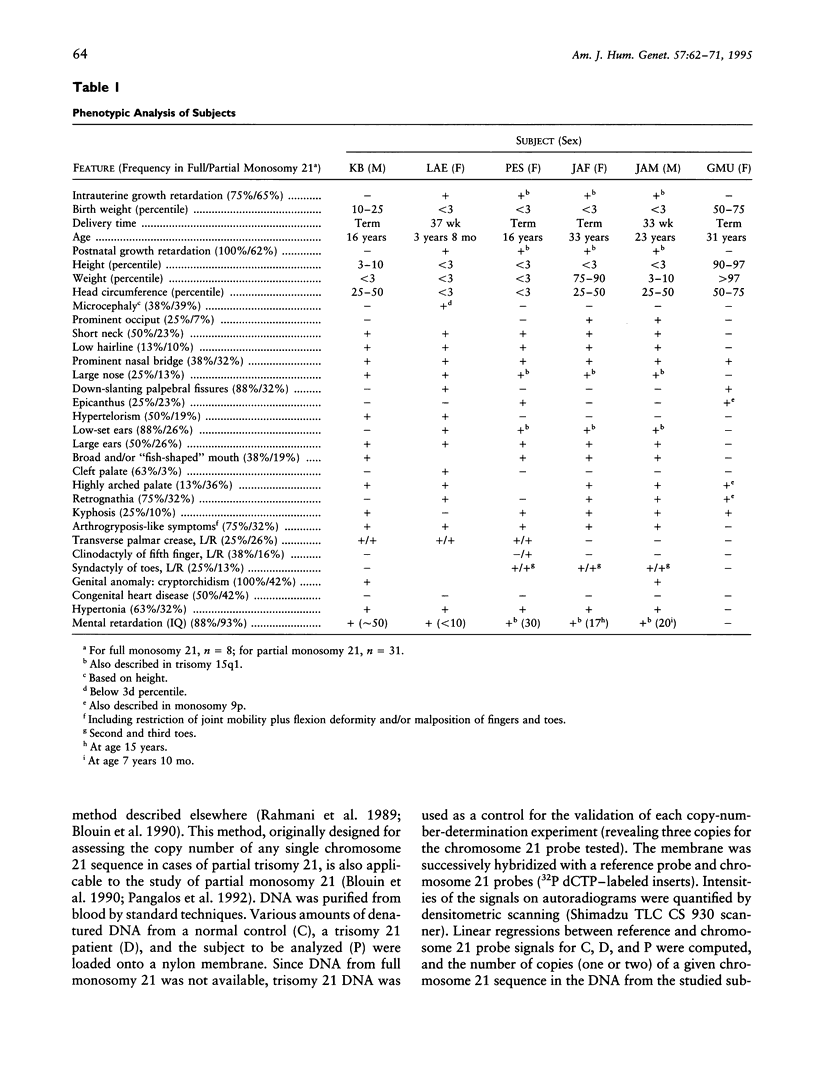
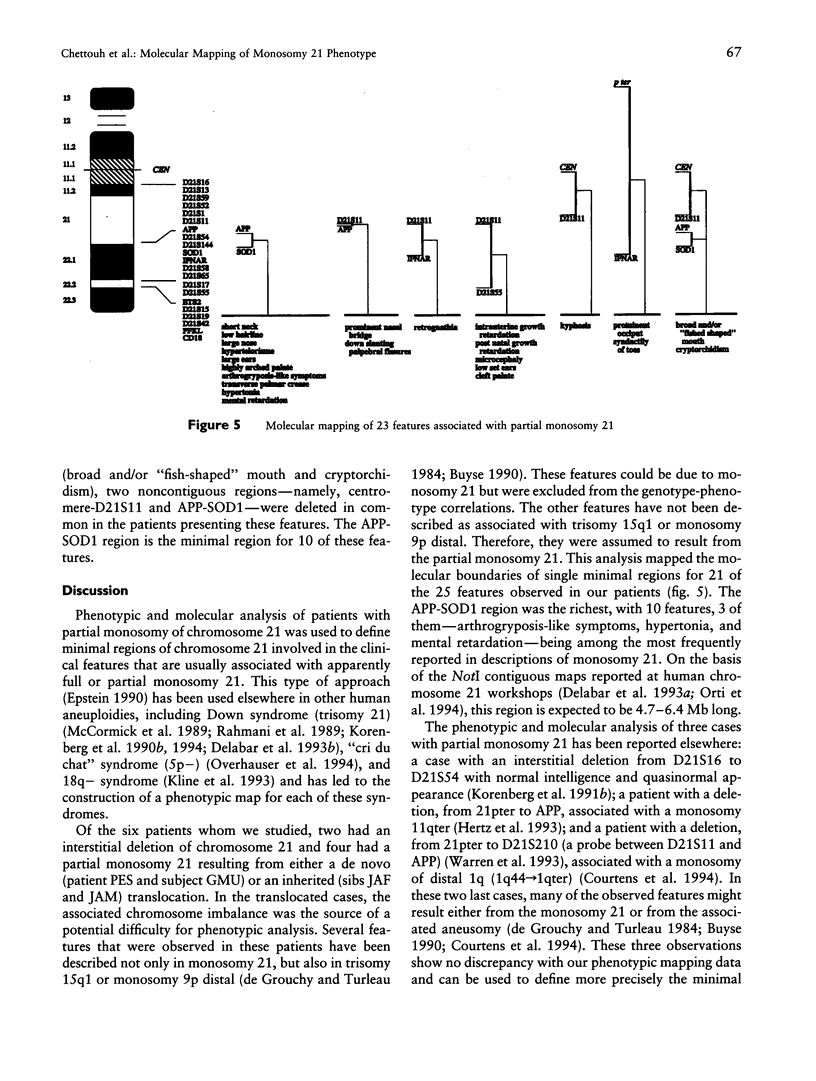
We compared the phenotypes, karyotypes, and molecular data for six cases of partial monosomy 21. Regions of chromosome 21, the deletion of which corresponds to particular features of monosomy 21, were thereby defined. Five such regions were identified for 21 features. Ten of the features could be assigned to the region flanked by genes APP and SOD1: six facial features, transverse palmar crease, arthrogryposis-like symptoms, hypertonia, and contribution to mental retardation. This region, covering the interface of bands 21q21-21q22.1, is 4.7–6.4 Mb long and contains the gene encoding the glutamate receptor subunit GluR5 (GRIK1).
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman A. D., Fackler J. C., Tuck-Muller C. M., Tarpey M. M., Freeman B. A., Rogers M. C. Partial monosomy 21, diminished activity of superoxide dismutase, and pulmonary oxygen toxicity. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 23;318(25):1666–1669. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806233182506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Boulter J., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Deneris E. S., Moll C., Borgmeyer U., Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloning of a novel glutamate receptor subunit, GluR5: expression in the nervous system during development. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90213-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin J. L., Rahmani Z., Chettouh Z., Prieur M., Fermanian J., Poissonnier M., Leonard C., Nicole A., Mattei J. F., Sinet P. M. Slot blot method for the quantification of DNA sequences and mapping of chromosome rearrangements: application to chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):518–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulukos K. E., Pognonec P., Begue A., Galibert F., Gesquière J. C., Stéhelin D., Ghysdael J. Identification in chickens of an evolutionarily conserved cellular ets-2 gene (c-ets-2) encoding nuclear proteins related to the products of the c-ets proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):697–705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Kim S., Price E. R., de Lange T., Tantravahi U., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. A map of the distal region of the long arm of human chromosome 21 constructed by radiation hybrid mapping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter N. J., Mayes J. S., Say B., Wilson D. P. Partial deletion 21: case report with biochemical studies and review. J Med Genet. 1987 Nov;24(11):706–709. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.11.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Bernard M. P., Ding J. F., Ramirez F. Cloning and characterization of five overlapping cDNAs specific for the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5925–5934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov I., Rigault P., Guillou S., Ougen P., Billaut A., Guasconi G., Gervy P., LeGall I., Soularue P., Grinas L. Continuum of overlapping clones spanning the entire human chromosome 21q. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):380–387. doi: 10.1038/359380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. M., Putnam T. I. An 18p21q translocation in a patient with presumptive "monosomy G". Am J Dis Child. 1972 Dec;124(6):908–910. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110180110016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtens W., Petersen M. B., Noël J. C., Flament-Durand J., Van Regemorter N., Delneste D., Cochaux P., Verschraegen-Spae M. R., Van Roy N., Speleman F. Proximal deletion of chromosome 21 confirmed by in situ hybridization and molecular studies. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jul 1;51(3):260–265. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320510318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Burmeister M., Price E. R., Kim S., Myers R. M. Radiation hybrid mapping: a somatic cell genetic method for constructing high-resolution maps of mammalian chromosomes. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):245–250. doi: 10.1126/science.2218528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. G., Jenkins E. C., Klinger H. P., Weed R. G. A child with presumptive monosomy 21 (45,XY,-21) in a family in which some members are Gq-. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;17(2):65–77. doi: 10.1159/000130691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Chettouh Z., Rahmani Z., Theophile D., Blouin J. L., Bono R., Kraus J., Barton J., Patterson D., Sinet P. M. Gene-dosage mapping of 30 DNA markers on chromosome 21. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):887–889. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90177-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Créau N., Sinet P. M., Ritter O., Antonarakis S. E., Burmeister M., Chakravarti A., Nizetic D., Ohki M., Patterson D. Report of the Fourth International Workshop on Human Chromosome 21. Genomics. 1993 Dec;18(3):735–745. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Theophile D., Rahmani Z., Chettouh Z., Blouin J. L., Prieur M., Noel B., Sinet P. M. Molecular mapping of twenty-four features of Down syndrome on chromosome 21. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(2):114–124. doi: 10.1159/000472398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Jonasson J., Laurèn K., Lejeune J., Lindsten J., Petersen G. B., Saldaña-Garcia P. An unbalanced 4q-21q translocation identified by the R but not by the G and Q chromosome banding techniques. Ann Genet. 1973 Mar;16(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziuba P., Dziekanowska D., Hübner H. A female infant with monosomy 21. Hum Genet. 1976 Mar 12;31(3):351–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00270866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J. The consequences of chromosome imbalance. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;7:31–37. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estabrooks L. L., Rao K. W., Donahue R. P., Aylsworth A. S. Holoprosencephaly in an infant with a minute deletion of chromosome 21(q22.3). Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jul;36(3):306–309. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320360312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries K., Mundel G., Rosenblatt M. De novo simultaneous reciprocal translocation and deletion. J Med Genet. 1978 Apr;15(2):152–154. doi: 10.1136/jmg.15.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., D'Hondt F., Goddeeris P., van den Berghe H. Full monosomy 21: a clinically recognizable syndrome? Hum Genet. 1977 Jun 30;37(2):155–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00393578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Horisberger M., Kraus J., Tantravahi U., Korenberg J., Rao V., Reddy S., Patterson D. Analysis of human chromosome 21: correlation of physical and cytogenetic maps; gene and CpG island distributions. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P., Uhrich S., Disteche C., Cheng E. Fetal t(5p;21q) misdiagnosed as monosomy 21: a plea for in situ hybridization studies. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Oct 1;52(4):416–418. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320520405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P., Reeves R. H., Jabs E. W., Yang X., Dackowski W., Rochelle J. M., Brown R. H., Jr, Haines J. L., O'Hara B. F., Uhl G. R. Chromosomal localization of glutamate receptor genes: relationship to familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurological disorders of mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3053–3057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripenberg U., Elfving J., Gripenberg L. A 45,XX,21--child: attempt at a cytological and clinical interpretation of the karyotype. J Med Genet. 1972 Mar;9(1):110–115. doi: 10.1136/jmg.9.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran K. H., Breg W. R., Mahoney M. J. 21 monosomy in a retarded female infant. J Med Genet. 1974 Dec;11(4):386–389. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.4.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz B., Brandt C. A., Petersen M. B., Pedersen S., König U., Strømkjaer H., Jensen P. K. Application of molecular and cytogenetic techniques to the detection of a de novo unbalanced t(11q;21q) in a patient previously diagnosed as having monosomy 21. Clin Genet. 1993 Aug;44(2):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1993.tb03853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herva R., Koivisto M., Seppänen U. 21-Monosomy in a liveborn male infant. Eur J Pediatr. 1983 Mar;140(1):57–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00661907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbek S., Friedrich U., Brostrom K., Petersen G. B. Monosomy for the centromeric and juxtacentromeric region of chromosome 21. Humangenetik. 1974;24(3):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00283583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston C. S., Chudley A. E. Separating monosomy-21 from the "arthrogryposis basket". J Can Assoc Radiol. 1981 Dec;32(4):220–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeuchi T., Kondo I., Sasaki M., Kaneko Y., Kodama S. Unbalanced 13q/21q translocation: a revised study of the case previously reported as 21-monosomy. Hum Genet. 1976 Aug 30;33(3):327–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00286861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., O'Connor K., Lee A., Roberts T. M., Springer T. A. Cloning of the beta subunit of the leukocyte adhesion proteins: homology to an extracellular matrix receptor defines a novel supergene family. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline A. D., White M. E., Wapner R., Rojas K., Biesecker L. G., Kamholz J., Zackai E. H., Muenke M., Scott C. I., Jr, Overhauser J. Molecular analysis of the 18q- syndrome--and correlation with phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 May;52(5):895–906. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Chen X. N., Schipper R., Sun Z., Gonsky R., Gerwehr S., Carpenter N., Daumer C., Dignan P., Disteche C. Down syndrome phenotypes: the consequences of chromosomal imbalance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4997–5001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Croyle M. L., Cox D. R. Isolation and regional mapping of DNA sequences unique to human chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;41(6):963–978. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Kalousek D. K., Anneren G., Pulst S. M., Hall J. G., Epstein C. J., Cox D. R. Deletion of chromosome 21 and normal intelligence: molecular definition of the lesion. Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;87(2):112–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00204163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Kawashima H., Pulst S. M., Ikeuchi T., Ogasawara N., Yamamoto K., Schonberg S. A., West R., Allen L., Magenis E. Molecular definition of a region of chromosome 21 that causes features of the Down syndrome phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Aug;47(2):236–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent C., Dutrillaux B., Biemont M. C., Genoud J., Bethenod M. Translocation t(14q-; 21q + ) chez le père. Trisomie 14 et monosomie 21 partielles chez la fille. Ann Genet. 1973 Dec;16(4):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levanon D., Danciger E., Dafni N., Groner Y. Construction of a cDNA clone containing the entire coding region of the human liver-type phosphofructokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1182–1187. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieman-Hurwitz J., Dafni N., Lavie V., Groner Y. Human cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase cDNA clone: a probe for studying the molecular biology of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2808–2811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Pajares I., Martin-Ancel A., Cabello P., Delicado A., Garcia-Alix A., San Roman C. De novo t(5p;21q) in a patient previously diagnosed as monosomy 21. Clin Genet. 1993 Feb;43(2):94–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1993.tb04457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick M. K., Schinzel A., Petersen M. B., Stetten G., Driscoll D. J., Cantu E. S., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Watkins P. C., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular genetic approach to the characterization of the "Down syndrome region" of chromosome 21. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinniss M. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Stetten G., Petersen M. B., Boman H., Engel E., Greenberg F., Hertz J. M., Johnson A., Laca Z. Mechanisms of ring chromosome formation in 11 cases of human ring chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;50(1):15–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnis M. G., Chakravarti A., Blaschak J., Petersen M. B., Sharma V., Avramopoulos D., Blouin J. L., König U., Brahe C., Matise T. C. A linkage map of human chromosome 21:43 PCR markers at average intervals of 2.5 cM. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):562–571. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi N., Buckton K. E. Interstitial deletion of chromosome 21. Clin Genet. 1982 Oct;22(4):215–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb01436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Chu M. L., Faro S. H., Clark W. J., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Cloning a cDNA for the pro-alpha 2 chain of human type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen F., Trånebjaerg L. A case of partial monosomy 21q22.2 associated with Rieger's syndrome. J Med Genet. 1984 Jun;21(3):218–221. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.3.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto P. G., Toledo S., Richieri-Costa A., Otto P. A., Vianna-Morgante A. M., Kasahara S. Partial monosomy 13 and 21 due to a familial 13/21 translocation. Hum Genet. 1978 Apr 24;41(3):243–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00284757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overhauser J., Huang X., Gersh M., Wilson W., McMahon J., Bengtsson U., Rojas K., Meyer M., Wasmuth J. J. Molecular and phenotypic mapping of the short arm of chromosome 5: sublocalization of the critical region for the cri-du-chat syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):247–252. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangalos C., Théophile D., Sinet P. M., Marks A., Stamboulieh-Abazis D., Chettouh Z., Prieur M., Verellen C., Rethoré M. O., Lejeune J. No significant effect of monosomy for distal 21q22.3 on the Down syndrome phenotype in "mirror" duplications of chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;51(6):1240–1250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellissier M. C., Philip N., Voelckel-Baeteman M. A., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F. Monosomy 21: a new case confirmed by in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1987 Jan;75(1):95–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00273852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Warren A. C., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 27 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan M. C., Morton C. C., Stevenson R. E., Tanzi R. E., Stewart G. D., Watkins P. C., Gusella J. F., Amos J. A. Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a de novo t(5p;21q) in a patient previously diagnosed as monosomy 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):511–519. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip N., Baeteman M. A., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F. Three new cases of partial monosomy 21 resulting from one ring 21 chromosome and two unbalanced reciprocal translocations. Eur J Pediatr. 1984 Apr;142(1):61–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00442594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani Z., Blouin J. L., Creau-Goldberg N., Watkins P. C., Mattei J. F., Poissonnier M., Prieur M., Chettouh Z., Nicole A., Aurias A. Critical role of the D21S55 region on chromosome 21 in the pathogenesis of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5958–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethoré M. O., Dutrillaux B. Translocation 46,XX, t(15; 21) (q13; q22,1) chez la mère de deux enfants atteints de trisomie 15 et de monosomie 21 partielles. Ann Genet. 1973 Dec;16(4):271–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethoré M. O., Lafourcade J., Couturier J., Harpey J. P., Hamet M., Engler R., Alcindor L. G., Lejeune J. Augmentation d'activité de l'adénine phosphoribosyl transférase chez un enfant trisomique 16q22.2 to 16 qter par translocation t(16;21)(q22.2;q22.2)pat. Ann Genet. 1982;25(1):36–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. F., Wyandt H. E., Kelly T. E. De novo 21q interstitial deletion in a retarded boy with ulno-fibular dysostosis. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jan;20(1):173–180. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera H., Rivas F., Plascencia L., Cantú J. M. "Pure" monosomy 21 pter leads to q21 in a girl born to a couple 46,XX,t(14;21)(p12;q22) and 46,XY,t(5;18)(q32;q22). Ann Genet. 1983;26(4):234–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland B., Cox D. M., Hoar D. I., Fowlow S. B., Robertson A. S. A familial interstitial deletion of the long arm of chromosome 21. Clin Genet. 1990 Jun;37(6):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinzel A. Letter: Does full monosomy 21 exist? A comment to the paper: A male infant with monosomy 21 by Y. Kaneko, T. Ikeuchi, M. Sasaki, Y. Satake and S. Kuwajima Humangenetik 29, 1-7 (1975). Hum Genet. 1976 Apr 15;32(1):105–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00569984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H. The TINS/TiPS Lecture. The molecular biology of mammalian glutamate receptor channels. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Sep;16(9):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Harris P., Galt J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Cloned DNA probes regionally mapped to human chromosome 21 and their use in determining the origin of nondisjunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4125–4132. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wexler N. S., Gusella J. F., Haines J. L. A genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21: analysis of recombination as a function of sex and age. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):551–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzé G., Lutfalla G., Gresser I. Genetic transfer of a functional human interferon alpha receptor into mouse cells: cloning and expression of its cDNA. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90738-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Camp G., Stinissen P., Vandenberghe A., Van Broeckhoven C. A polymorphic locus [D21S144] is detected by probe pVC12 on chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4420–4420. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljoen D. L., Speleman F., Smart R., Van Roy N., du Toit J., Leroy J. Putative monosomy 21 in two patients: clinical findings and investigation using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Clin Genet. 1992 Sep;42(3):105–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. C., McInnis M. G., Kalaitsidaki M., Cox T. K., Blaschak J., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. D21S210: a highly polymorphic (GT)n marker closely linked to the beta-amyloid protein precursor (APP) gene. Hum Genet. 1993 Mar;91(1):87–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00230232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. C., Tanzi R. E., Gibbons K. T., Tricoli J. V., Landes G., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Gusella J. F. Isolation of polymorphic DNA segments from human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6075–6088. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski K., Dambska M., Jenkins E. C., Sklower S., Brown W. T. Monosomy 21 syndrome: further delineation including clinical, neuropathological, cytogenetic and biochemical studies. Clin Genet. 1983 Feb;23(2):102–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb01856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulfsberg E. A., Carrel R. E., Klisak I. J., O'Brien T. J., Sykes J. A., Sparkes R. S. Normal superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD-1) activity with deletion of chromosome band 21q21 supports localization of SOD-1 locus to 21q22. Hum Genet. 1983;64(3):271–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00279408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Ogasawara N., Gotoh A., Komiya H., Nakai H., Kuroki Y. A case of 21q--syndrome with normal SOD-1 activity. Hum Genet. 1979 May 10;48(3):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00272832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao X. L., Jenkins E. C. Translocation 4p;21q identified by FISH in a case previously described as "presumptive monosomy 21". Am J Med Genet. 1994 Oct 1;52(4):491–492. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320520418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimitsu K., Hatano S., Kobayashi Y., Takeoka Y., Hayashidani M., Ueda K., Nomura K., Ohama K., Usui T. A case of 21q-syndrome with half normal SOD-1 activity. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):200–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00327128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]