Abstract
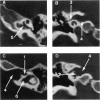
We report a large two-generation pedigree with seven affected males segregating for an X-linked mixed conductive sensorineural deafness. The patients present with atypical Mondini-like dysplasia, dilated petrous facial canal, dilatation of the internal auditory meatus fully connected with enlarged cochlear canals, and, in one patient, a wide bulbous posterior labyrinth. Obligatory carrier females are mildly affected. Molecular characterization of this family revealed a deletion of locus DXS169, in Xq21.1. Loci DXS72 and DXS26, which, respectively, flank DXS169 proximally and distally, were intact. Since a gene responsible for X-linked progressive mixed deafness with perilymphatic gusher (DFN3) has previously been assigned by deletion mapping to a slightly more distal interval between DXS26 and DXS121, this study indicates either two different deafness genes or the involvement of a very large region in Xq21.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayazi S. Choroideremia, obesity, and congenital deafness. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981 Jul;92(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75909-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach I., Brunner H. G., Beighton P., Ruvalcaba R. H., Reardon W., Pembrey M. E., van der Velde-Visser S. D., Bruns G. A., Cremers C. W., Cremers F. P. Microdeletions in patients with gusher-associated, X-linked mixed deafness (DFN3). Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):38–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach I., Robinson D., Thomas N., Ropers H. H., Cremers F. P. Physical fine mapping of genes underlying X-linked deafness and non fra (X)-X-linked mental retardation at Xq21. Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;89(6):620–624. doi: 10.1007/BF00221950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. F., Fain P. R. Definition and mapping of STSs at STR and RFLP loci in Xp11-Xq22. Genomics. 1993 Dec;18(3):712–716. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. G., van Bennekom A., Lambermon E. M., Oei T. L., Cremers W. R., Wieringa B., Ropers H. H. The gene for X-linked progressive mixed deafness with perilymphatic gusher during stapes surgery (DFN3) is linked to PGK. Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;80(4):337–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00273647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. H., Eelkema E. A., Furman J. M., Kamerer D. B. Familial sensorineural hearing loss: a correlative study of audiologic, radiographic, and vestibular findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1991 Aug;100(8):620–625. doi: 10.1177/000348949110000804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremers F. P., van de Pol D. J., Diergaarde P. J., Wieringa B., Nussbaum R. L., Schwartz M., Ropers H. H. Physical fine mapping of the choroideremia locus using Xq21 deletions associated with complex syndromes. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas G., Charachon R., Vasdev A., Mouret P., Richard J. Malformations du labyrinthe osseux et surdités. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 1991;108(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser G. R. Sex-linked recessive congenital deafness and the excess of males in profound childhood deafness. Ann Hum Genet. 1965 Nov;29(2):171–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1965.tb00512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber I., Bitner-Glindzicz M., de Kok Y. J., van der Maarel S. M., Ishikawa-Brush Y., Monaco A. P., Robinson D., Malcolm S., Pembrey M. E., Brunner H. G. X-linked mixed deafness (DFN3): cloning and characterization of the critical region allows the identification of novel microdeletions. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jul;3(7):1151–1154. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.7.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen T., Videbaek H., Olesen K. P. CT-scanning of the cochlea in Pendred's syndrome. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1989 Oct;14(5):389–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1989.tb00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson M. J., Parisier S. C., Jacobs M., Edelstein D. R. The large vestibular aqueduct syndrome in children. A review of 12 cases and the description of a new clinical entity. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1989 Jan;115(1):54–58. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1989.01860250056026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance W. E., Setleff R., McLeod A., Sweeney A., Cooper C., McConnell F. X-linked mixed deafness with congenital fixation of the stapedial footplate and perilymphatic gusher. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Mar;07(4):64–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Lesko J. G., Lewis R. A., Ledbetter S. A., Ledbetter D. H. Isolation of anonymous DNA sequences from within a submicroscopic X chromosomal deletion in a patient with choroideremia, deafness, and mental retardation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6521–6525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Moisan J. P., Grzeschik K. H., Hellkuhl B., Hors-Cayla M. C., Van Cong N., Weil D., Mandel J. L. Characterization of a set of X-linked sequences and of a panel of somatic cell hybrids useful for the regional mapping of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00278816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno H., Sando I. Anomaly of the round window a histopathological study using a graphic reconstruction method. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1988;15(3):147–154. doi: 10.1016/s0385-8146(88)80021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P. D., Reardon W., Pembrey M., Bellman S., Luxom L. X-linked deafness, stapes gushers and a distinctive defect of the inner ear. Neuroradiology. 1991;33(4):326–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00587816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P. D. The basal turn of the cochlea. Br J Radiol. 1992 May;65(773):370–374. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-65-773-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., Middleton-Price H. R., Malcolm S., Phelps P., Bellman S., Luxon L., Martin J. A., Bumby A., Pembrey M. E. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in X-linked deafness. Br J Audiol. 1992 Apr;26(2):109–114. doi: 10.3109/03005369209077878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., Middleton-Price H. R., Sandkuijl L., Phelps P., Bellman S., Luxon L., Pembrey M. E., Malcolm S. A multipedigree linkage study of X-linked deafness: linkage to Xq13-q21 and evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg T., Niebuhr E., Yang H. M., Parving A., Schwartz M. Choroideremia, congenital deafness and mental retardation in a family with an X chromosomal deletion. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet. 1987 Nov;8(3):139–143. doi: 10.3109/13816818709031459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Ballo R., Wallis G., Beighton P., Goldblatt J. X-linked mixed deafness with stapes fixation in a Mauritian kindred: linkage to Xq probe pDP34. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):299–301. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Kwitek A. E., May P. E., Polymeropoulos M. H., Ledbetter S. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the DXS453, DXS454 and DXS458 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4037–4037. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells S., Mould S., Robins D., Robinson D., Jacobs P. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of a familial microdeletion of Xq. J Med Genet. 1991 Mar;28(3):163–166. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.3.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West P. D., Gholkar A., Ramsden R. T. Wildervanck's syndrome--unilateral Mondini dysplasia identified by computed tomography. J Laryngol Otol. 1989 Apr;103(4):408–411. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100109077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Leivy S. W., Sofferman R. A., Wald S. L. Mondini dysplasia: spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid otorrhea. New perspectives in management. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1990;16(4-5):260–264. doi: 10.1159/000120538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachmann M., Fuchs E., Prader A. Progressive high frequency hearing loss: an additional feature in the syndrome of congenital adrenal hypoplasia and gonadotrophin deficiency. Eur J Pediatr. 1992 Mar;151(3):167–169. doi: 10.1007/BF01954375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]