Abstract
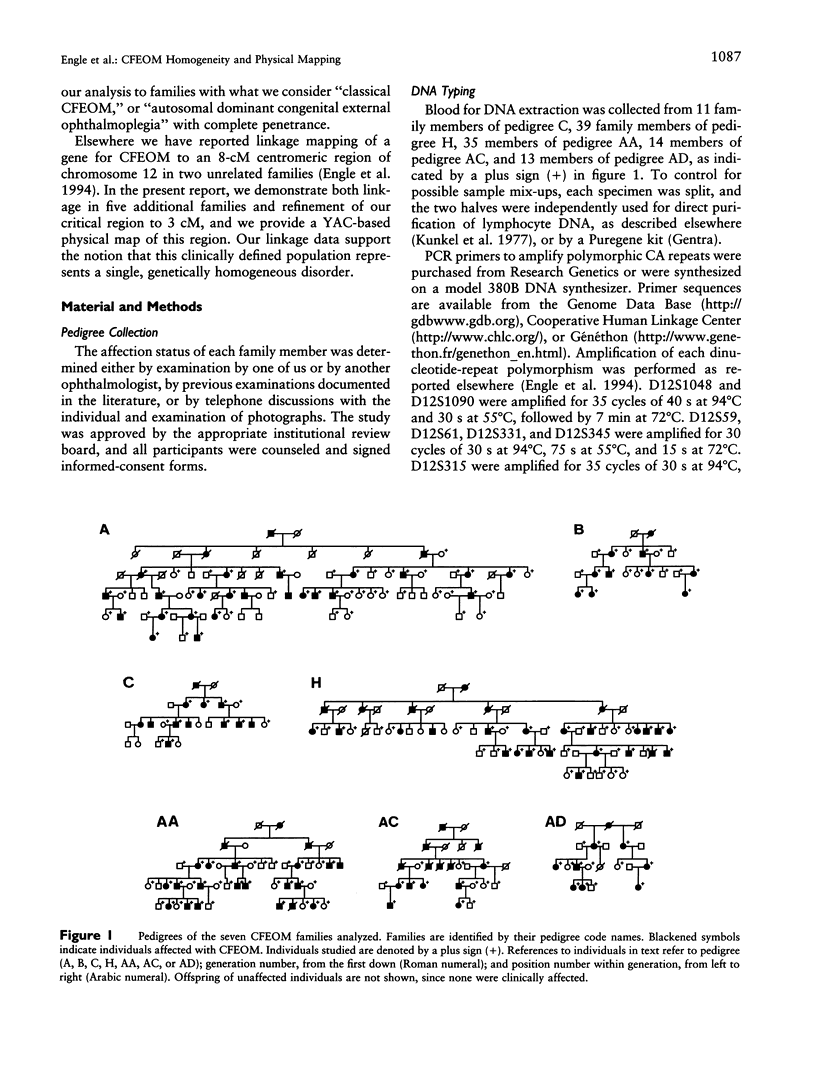
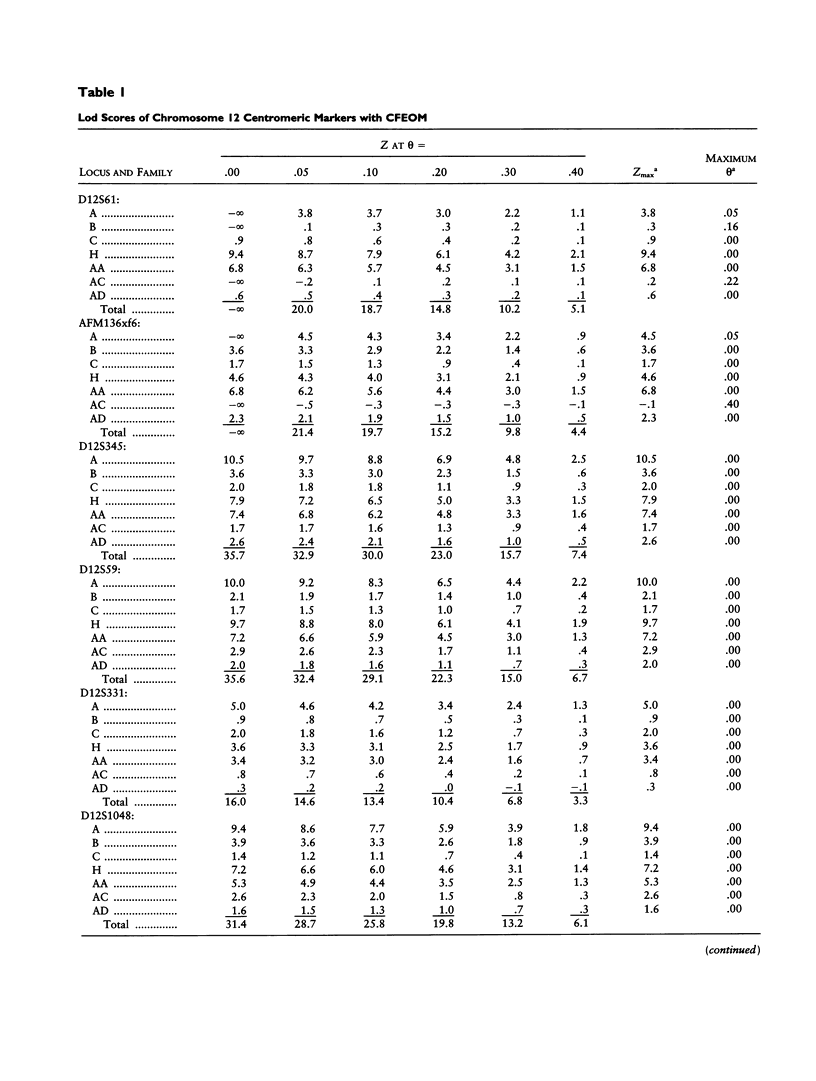
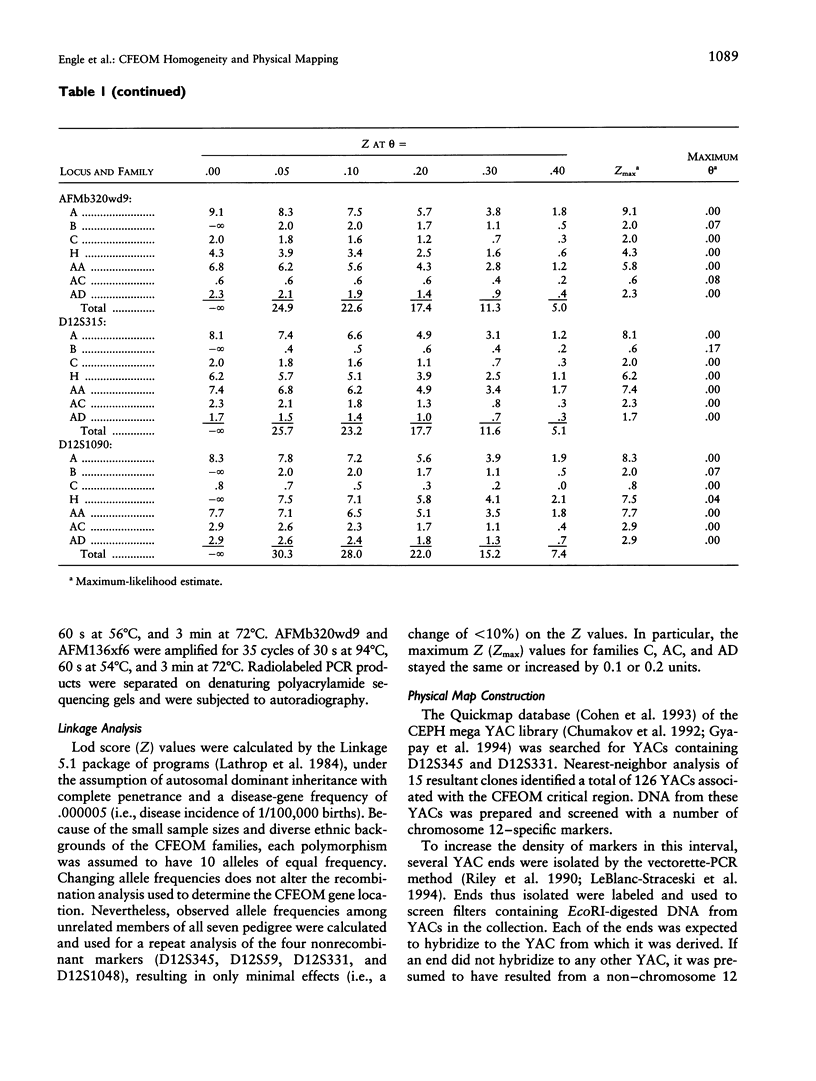
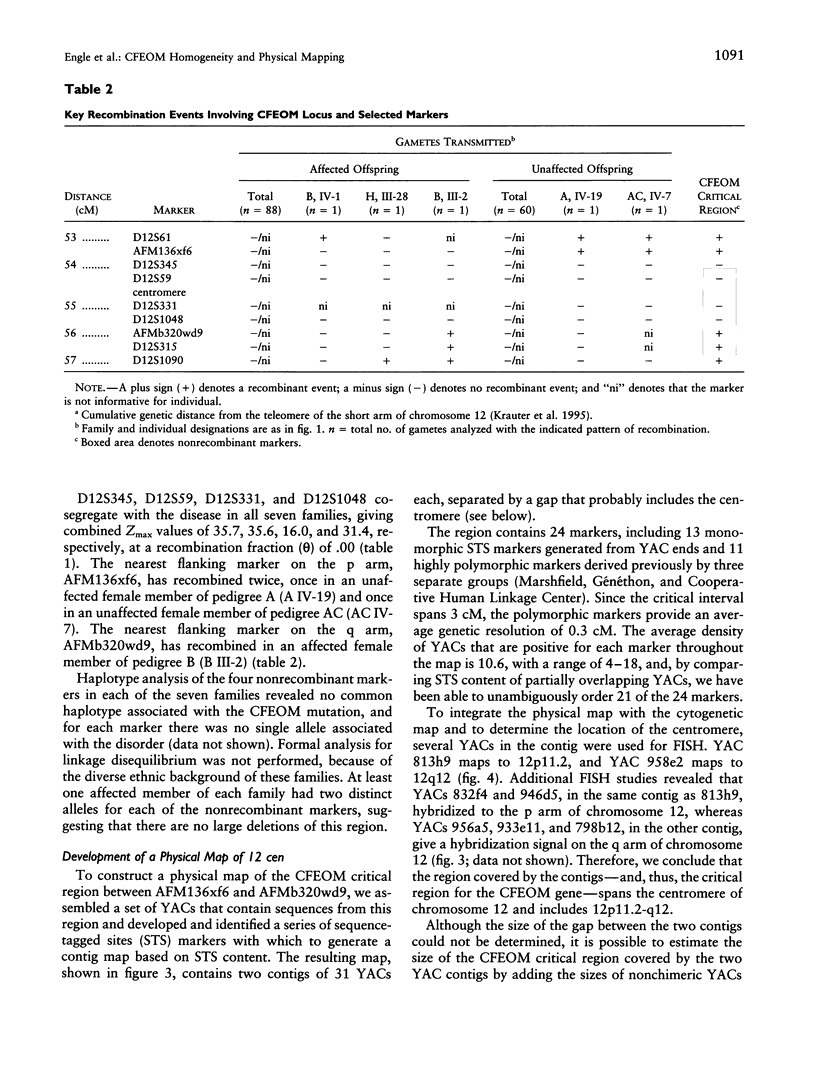
Congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles (CFEOM) is an autosomal dominant syndrome of congenital external ophthalmoplegia and bilateral ptosis. We previously reported linkage of this disorder in two unrelated families to an 8-cM region near the centromere of human chromosome 12. We now present refinement of linkage in the original two families, linkage analysis of five additional families, and a physical map of the critical region for the CFEOM gene. In each of the seven families the disease gene is linked to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 12. D12S345, D12S59, D12S331, and D12S1048 do not recombine with the disease gene and have combined lod scores of 35.7, 35.6, 16.0, and 31.4, respectively. AFM136xf6 and AFMb320wd9 flank the CFEOM locus, defining a critical region of 3 cM spanning the centromere of chromosome 12. These data support the concept that this may be a genetically homogeneous disorder. We also describe the generation of a YAC contig encompassing the critical region of the CFEOM locus. This interval has been assigned cytogenetically to 12p11.2-q12 and spans the centromere of chromosome 12. These results provide the basis for further molecular analyses of the structure and organization of the CFEOM locus and will help in the identification of candidate genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bamshad M., Watkins W. S., Zenger R. K., Bohnsack J. F., Carey J. C., Otterud B., Krakowiak P. A., Robertson M., Jorde L. B. A gene for distal arthrogryposis type I maps to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 9. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Dec;55(6):1153–1158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov I., Rigault P., Guillou S., Ougen P., Billaut A., Guasconi G., Gervy P., LeGall I., Soularue P., Grinas L. Continuum of overlapping clones spanning the entire human chromosome 21q. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):380–387. doi: 10.1038/359380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cibis G. W. Congenital familial external ophthalmoplegia with co-contraction. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet. 1984 Dec;4(3):163–167. doi: 10.3109/13816818409006116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Chumakov I., Weissenbach J. A first-generation physical map of the human genome. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):698–701. doi: 10.1038/366698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engle E. C., Kunkel L. M., Specht L. A., Beggs A. H. Mapping a gene for congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles to the centromeric region of chromosome 12. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):69–73. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houtman W. A., van Weerden T. W., Robinson P. H., de Vries B., Hoogenraad T. U. Hereditary congenital external ophthalmoplegia. Ophthalmologica. 1986;193(4):207–218. doi: 10.1159/000309712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONKERS G. H. Familiaire ptosis congenita, gecombineerd met andere aangeboren defecten in de motiliteit van de bulbusmusculatuur. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1950 May 20;94(20):1471–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorde L. B. Linkage disequilibrium as a gene-mapping tool. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):11–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucherlapati R., Craig I., Marynen P. Report and abstracts of the Second International Workshop on Human Chromosome 12 mapping 1994. New Haven, Connecticut, June 20-22, 1994. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;67(4):245–276. doi: 10.1159/000133868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUGHLIN R. C. Congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles; a report of six cases. Am J Ophthalmol. 1956 Mar;41(3):432–438. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(56)91259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc-Straceski J. M., Montgomery K. T., Kissel H., Murtaugh L., Tsai P., Ward D. C., Krauter K. S., Kucherlapati R. Twenty-one polymorphic markers from human chromosome 12 for integration of genetic and physical maps. Genomics. 1994 Jan 15;19(2):341–349. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looijenga L. H., Oosterhuis J. W., Smit V. T., Wessels J. W., Mollevanger P., Devilee P. Alpha satellite DNAs on chromosomes 10 and 12 are both members of the dimeric suprachromosomal subfamily, but display little identity at the nucleotide sequence level. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1125–1132. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90027-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Ward D. C. Oligonucleotide probes for the analysis of specific repetitive DNA sequences by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Oct;1(7):535–539. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemet P., Godel V., Ron S., Lazar M. Ocular congenital fibrosis syndrome. Metab Pediatr Syst Ophthalmol (1985) 1985;8(4):172–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley J., Butler R., Ogilvie D., Finniear R., Jenner D., Powell S., Anand R., Smith J. C., Markham A. F. A novel, rapid method for the isolation of terminal sequences from yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2887–2890. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Carson N. L., Myers S., Pakstis A. J., Kidd J. R., Castiglione C. M., Anderson L., Hoyle L. S., Genel M., Verdy M. The genetic defect in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A maps next to the centromere of chromosome 10. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):624–630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



