Abstract
In the past several years, allelic association has helped map a number of rare genetic diseases in the human genome. A commonly used upper bound on the recombination fraction between the disease gene and an associated marker is known to be biased downward, so there is the possibility that an investigator could be misled. This upper bound is based on a moment equation that can be derived within the context of a Poisson branching process, so its performance can be compared with a recently proposed likelihood bound. We show that the confidence level of the moment upper bound is much lower than expected, while the confidence level of the likelihood bound is in line with expectation. The effects of mutation at either the marker or disease locus on the upper bounds are also investigated. Results indicate that mutation is not an important force for typical mutation rates, unless the recombination fraction between the marker and disease locus is very small or the disease allele is very rare in the general population. Finally, the impact of sample size on the likelihood bound is investigated. The results are illustrated with data on 10 simple genetic diseased in the Finnish population.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltonen J., Björses P., Sandkuijl L., Perheentupa J., Peltonen L. An autosomal locus causing autoimmune disease: autoimmune polyglandular disease type I assigned to chromosome 21. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):83–87. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson B. O., Thomson G. Measuring the strength of associations between HLA antigens and diseases. Tissue Antigens. 1981 Nov;18(5):356–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1981.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haataja L., Schleutker J., Laine A. P., Renlund M., Savontaus M. L., Dib C., Weissenbach J., Peltonen L., Aula P. The genetic locus for free sialic acid storage disease maps to the long arm of chromosome 6. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jun;54(6):1042–1049. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellsten E., Vesa J., Speer M. C., Mäkelä T. P., Järvelä I., Alitalo K., Ott J., Peltonen L. Refined assignment of the infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (INCL, CLN1) locus at 1p32: incorporation of linkage disequilibrium in multipoint analysis. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):720–725. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
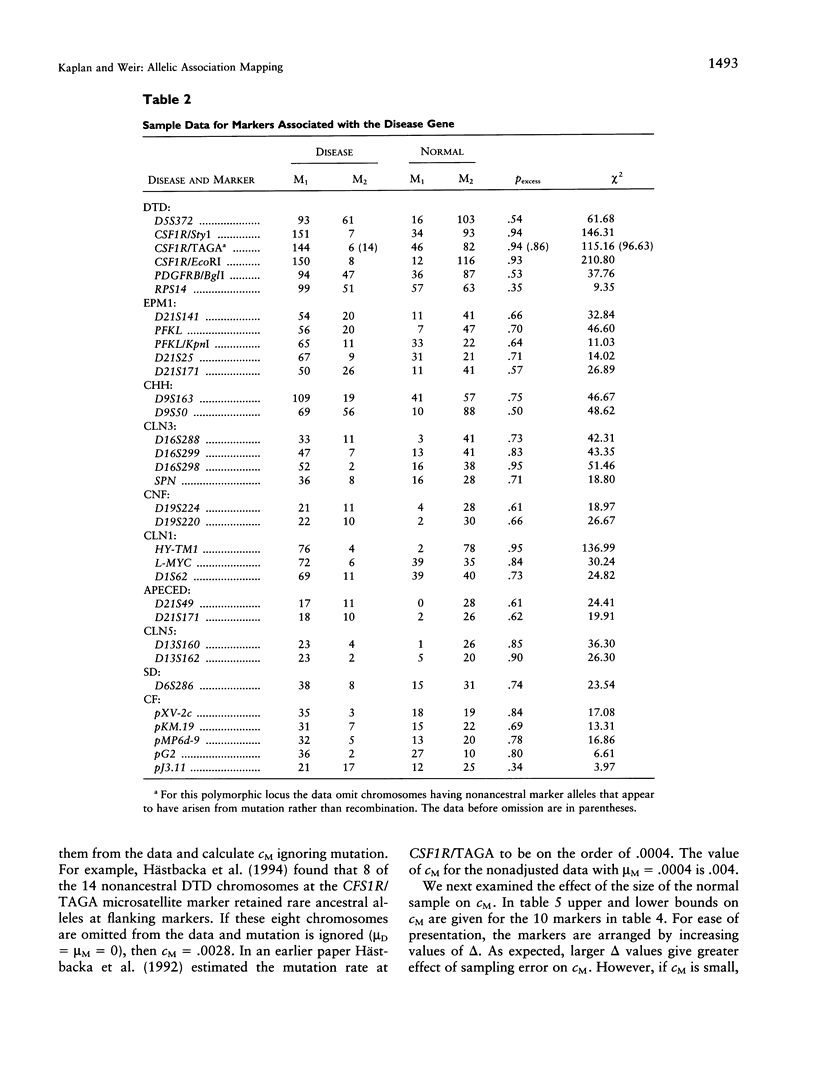
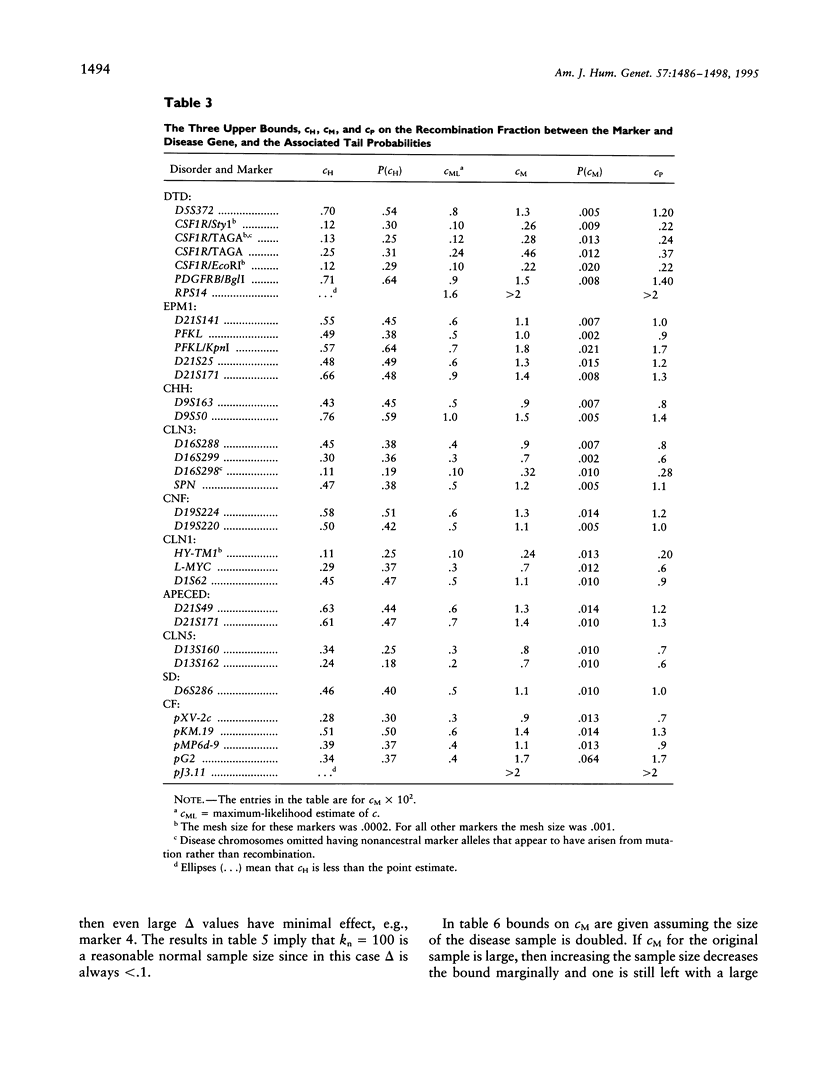
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Mahtani M. M., Clines G., Reeve-Daly M. P., Daly M., Hamilton B. A., Kusumi K., Trivedi B., Weaver A. The diastrophic dysplasia gene encodes a novel sulfate transporter: positional cloning by fine-structure linkage disequilibrium mapping. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1073–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan N. L., Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Likelihood methods for locating disease genes in nonequilibrium populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):18–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestilä M., Männikkö M., Holmberg C., Gyapay G., Weissenbach J., Savolainen E. R., Peltonen L., Tryggvason K. Congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type maps to the long arm of chromosome 19. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):757–764. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Schork N. J. Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2037–2048. doi: 10.1126/science.8091226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehesjoki A. E., Koskiniemi M., Norio R., Tirrito S., Sistonen P., Lander E., de la Chapelle A. Localization of the EPM1 gene for progressive myoclonus epilepsy on chromosome 21: linkage disequilibrium allows high resolution mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1229–1234. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Novelletto A., Lin C., Tagle D., Barnes G., Bates G., Taylor S., Allitto B., Altherr M., Myers R. The Huntington's disease candidate region exhibits many different haplotypes. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):99–103. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison H. M., O'Rawe A. M., Taschner P. E., Sandkuijl L. A., Santavuori P., de Vos N., Breuning M. H., Mole S. E., Gardiner R. M., Järvelä I. E. Batten disease gene, CLN3: linkage disequilibrium mapping in the Finnish population, and analysis of European haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Mar;56(3):654–662. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay M., Williamson R., Estivill X., Wainwright B. J., Ho M. F., Halford S., Kere J., Savilahti E., de la Chapelle A., Schwartz M. Haplotype analysis to determine the position of a mutation among closely linked DNA markers. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):1007–1014. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risch N., de Leon D., Ozelius L., Kramer P., Almasy L., Singer B., Fahn S., Breakefield X., Bressman S. Genetic analysis of idiopathic torsion dystonia in Ashkenazi Jews and their recent descent from a small founder population. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):152–159. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savukoski M., Kestilä M., Williams R., Järvelä I., Sharp J., Harris J., Santavuori P., Gardiner M., Peltonen L. Defined chromosomal assignment of CLN5 demonstrates that at least four genetic loci are involved in the pathogenesis of human ceroid lipofuscinoses. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;55(4):695–701. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirugo G., Keats B., Fujita R., Duclos F., Purohit K., Koenig M., Mandel J. L. Friedreich ataxia in Louisiana Acadians: demonstration of a founder effect by analysis of microsatellite-generated extended haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulisalo T., Klockars J., Mäkitie O., Francomano C. A., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P. High-resolution linkage-disequilibrium mapping of the cartilage-hair hypoplasia gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Nov;55(5):937–945. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A. Disease gene mapping in isolated human populations: the example of Finland. J Med Genet. 1993 Oct;30(10):857–865. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.10.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


