Abstract
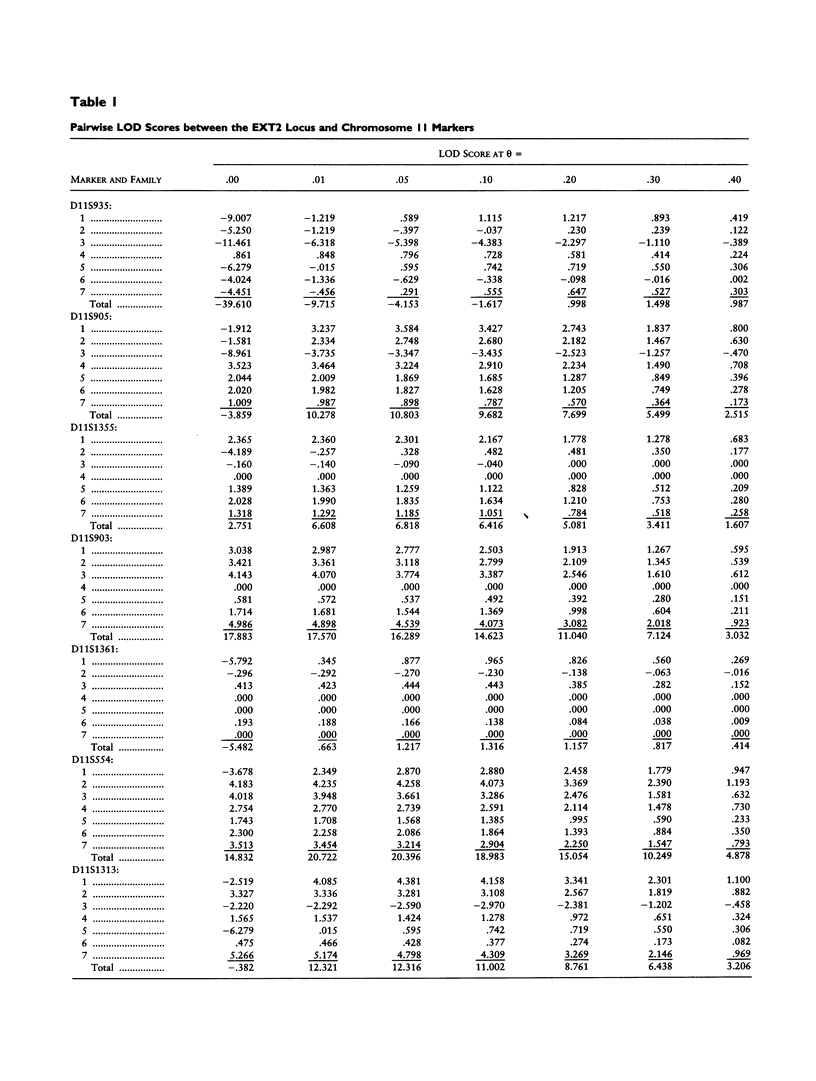
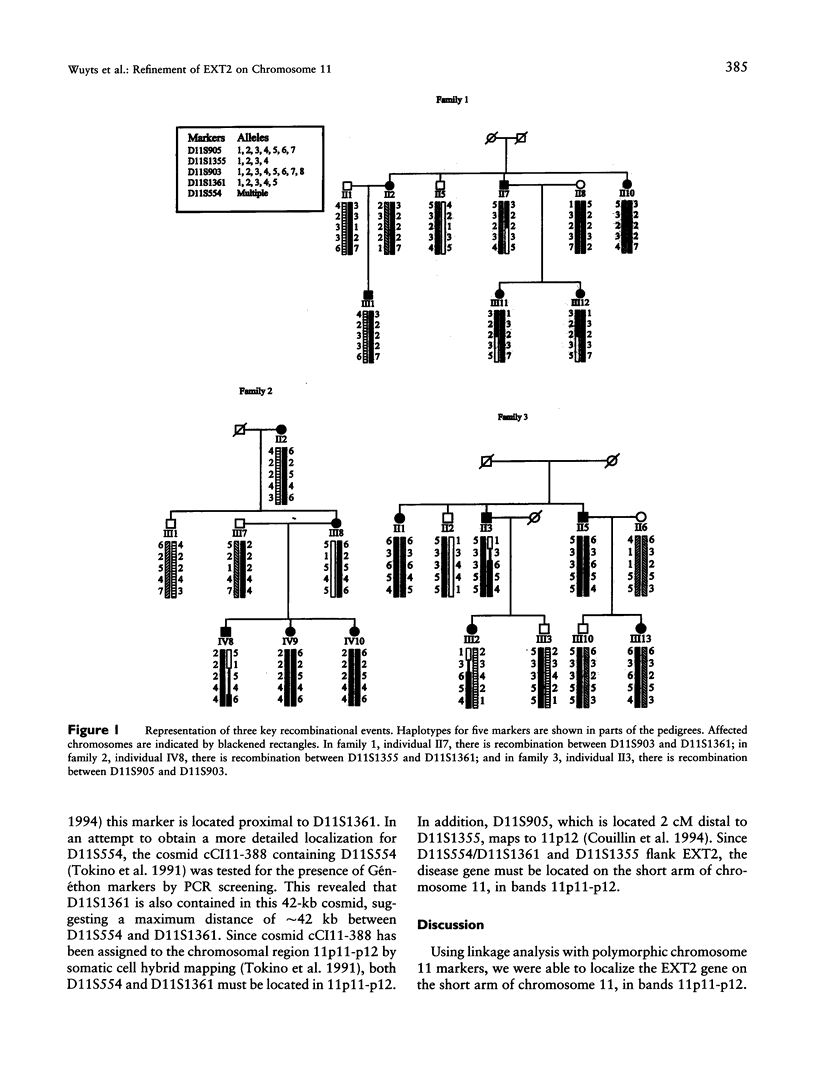
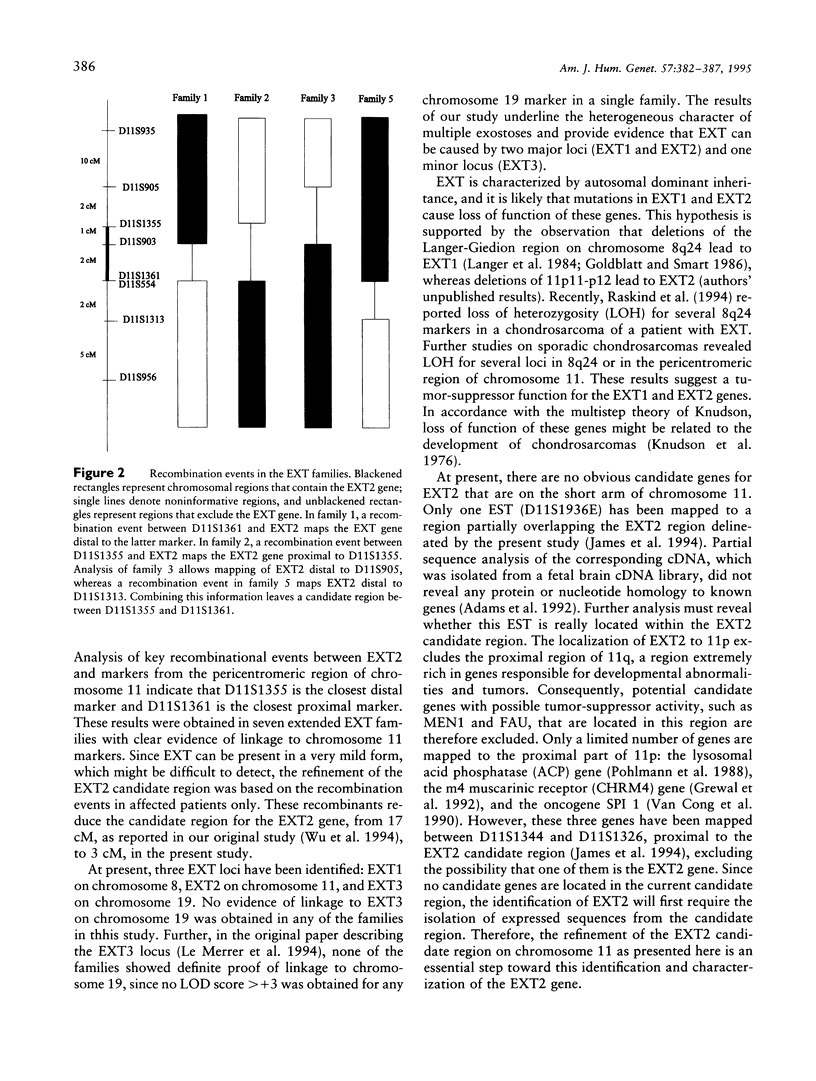
Hereditary multiple exostoses (EXT) is an autosomal dominant skeletal disorder characterized by the formation of multiple exostoses on the long bones. EXT is genetically heterogeneous, with at least three loci involved: one (EXT1) in the Langer-Giedion region on 8q23-q24, a second (EXT2) in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 11, and a third (EXT3) on chromosome 19p. In this study, linkage analysis in seven extended EXT families, all linked to the EXT2 locus, refined the localization of the EXT2 gene to a 3-cM region flanked by D11S1355 and D11S1361/D11S554. This implies that the EXT2 gene is located at the short arm of chromosome 11, in band 11p11-p12. The refined localization of EXT2 excludes a number of putative candidate genes located in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 11 and facilitates the process of isolating the EXT2 gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Dubnick M., Kerlavage A. R., Moreno R., Kelley J. M., Utterback T. R., Nagle J. W., Fields C., Venter J. C. Sequence identification of 2,375 human brain genes. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):632–634. doi: 10.1038/355632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler E. M., Malik N. J. The tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome(s): chromosome 8 long arm deletion: is there a shortest region of overlap between reported cases? TRP I and TRP II syndromes: are they separate entities? Am J Med Genet. 1984 Sep;19(1):113–119. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A., Raskind W., Blanton S. H., Pauli R. M., Gregg R. G., Francomano C. A., Puffenberger E., Conrad E. U., Schmale G., Schellenberg G. Genetic heterogeneity in families with hereditary multiple exostoses. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):71–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couillin P., Le Guern E., Vignal A., Fizames C., Ravisé N., Delportes D., Reguigne I., Rosier M. F., Junien C., van Heyningen V. Assignment of 112 microsatellite markers to 23 chromosome 11 subregions delineated by somatic hybrids: comparison with the genetic map. Genomics. 1994 May 15;21(2):379–387. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eder H. G., Oberbauer R. W., Ranner G. Cervical cord compression in hereditary multiple exostoses. J Neurosurg Sci. 1993 Mar;37(1):53–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt J., Smart R. D. Tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome without exostoses, wih an interstitial deletion of 8q23. Clin Genet. 1986 May;29(5):434–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal R. P., Martinez M., Hoehe M., Bonner T. I., Gershon E. S., Detera-Wadleigh S. Genetic linkage mapping of the m4 human muscarinic receptor (CHRM4). Genomics. 1992 May;13(1):239–240. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90236-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Morissette J., Vignal A., Dib C., Fizames C., Millasseau P., Marc S., Bernardi G., Lathrop M., Weissenbach J. The 1993-94 Généthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):246–339. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennekam R. C. Hereditary multiple exostoses. J Med Genet. 1991 Apr;28(4):262–266. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.4.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. R., Richard C. W., 3rd, Schott J. J., Yousry C., Clark K., Bell J., Terwilliger J. D., Hazan J., Dubay C., Vignal A. A radiation hybrid map of 506 STS markers spanning human chromosome 11. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):70–76. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr, Meadows A. T., Nichols W. W., Hill R. Chromosomal deletion and retinoblastoma. N Engl J Med. 1976 Nov 11;295(20):1120–1123. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197611112952007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer L. O., Jr, Krassikoff N., Laxova R., Scheer-Williams M., Lutter L. D., Gorlin R. J., Jennings C. G., Day D. W. The tricho-rhino-phalangeal syndrome with exostoses (or Langer-Giedion syndrome): four additional patients without mental retardation and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Sep;19(1):81–112. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Merrer M., Legeai-Mallet L., Jeannin P. M., Horsthemke B., Schinzel A., Plauchu H., Toutain A., Achard F., Munnich A., Maroteaux P. A gene for hereditary multiple exostoses maps to chromosome 19p. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 May;3(5):717–722. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.5.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen V. C., Ray D., Gross M. S., de Tand M. F., Frézal J., Moreau-Gachelin F. Localization of the human oncogene SPI1 on chromosome 11, region p11.22. Hum Genet. 1990 May;84(6):542–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00210807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlmann R., Krentler C., Schmidt B., Schröder W., Lorkowski G., Culley J., Mersmann G., Geier C., Waheed A., Gottschalk S. Human lysosomal acid phosphatase: cloning, expression and chromosomal assignment. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2343–2350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03078.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON L. Bone growth in diaphysial aclasis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1961 Nov;43-B:700–716. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.43B4.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale G. A., Conrad E. U., 3rd, Raskind W. H. The natural history of hereditary multiple exostoses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994 Jul;76(7):986–992. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199407000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer L. G., Hecht J. T., Ledbetter D. H., Greenberg F. Familial interstitial deletion 11(p11.12p12) associated with parietal foramina, brachymicrocephaly, and mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Mar 1;45(5):581–583. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokino T., Takahashi E., Mori M., Tanigami A., Glaser T., Park J. W., Jones C., Hori T., Nakamura Y. Isolation and mapping of 62 new RFLP markers on human chromosome 11. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Feb;48(2):258–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D. Y., Bergman T. A., Haines S. J. Acute cervical myelopathy from hereditary multiple exostoses: case report. Neurosurgery. 1989 Sep;25(3):472–475. doi: 10.1097/00006123-198909000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicklund C. L., Pauli R. M., Johnston D., Hecht J. T. Natural history study of hereditary multiple exostoses. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Jan 2;55(1):43–46. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320550113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. Q., Heutink P., de Vries B. B., Sandkuijl L. A., van den Ouweland A. M., Niermeijer M. F., Galjaard H., Reyniers E., Willems P. J., Halley D. J. Assignment of a second locus for multiple exostoses to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 11. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):167–171. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


