Abstract
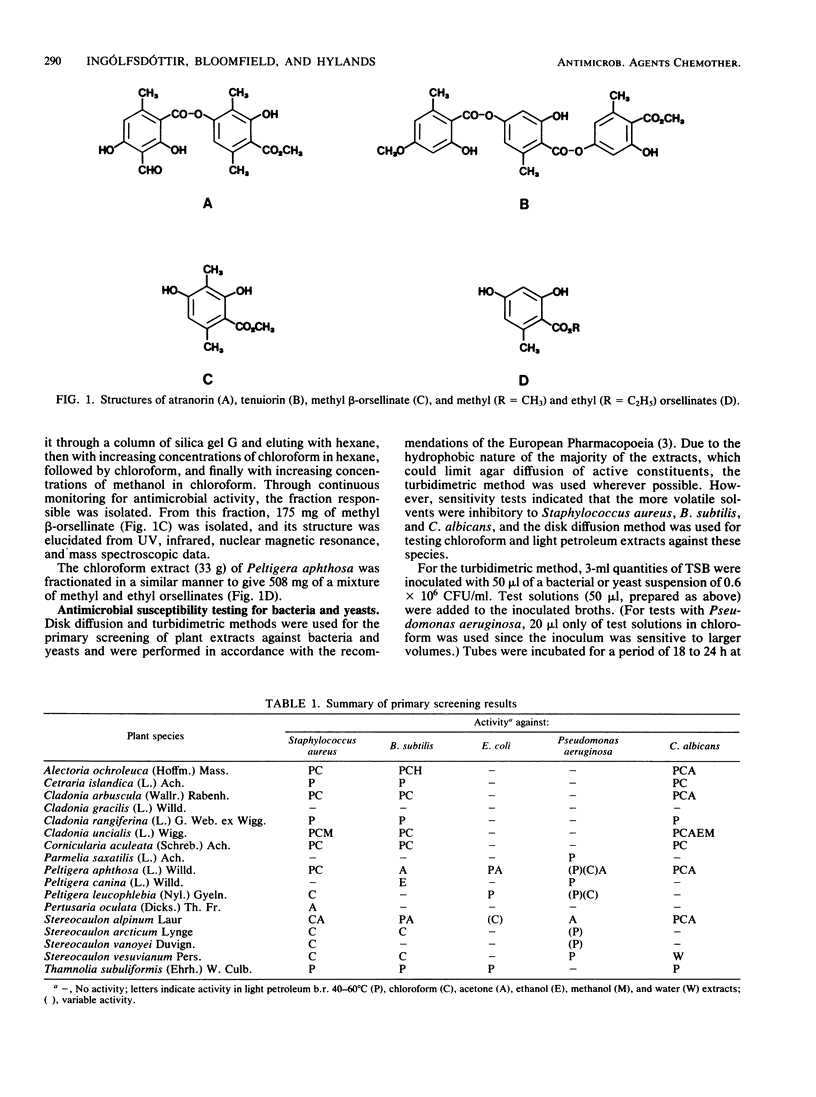
Antimicrobial screening of several lichen species and subsequent isolation and structure elucidation of active compounds revealed that the hydrolysis products of certain lichen metabolites, i.e., depsides, were active against gram-negative bacteria and fungi as well as gram-positive bacteria. The active constituents isolated from Stereocaulon alpinum and Peltigera aphthosa were identified, respectively, as methyl beta-orsellinate and a mixture of methyl and ethyl orsellinates. MIC determinations indicated that activity of these compounds was superior to that of the commonly used preservative agents methyl and propyl p-hydroxybenzoates and was of the same order as that of chlorocresol.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fujikawa F., Hirayama T., Nakamura Y., Suzuki M., Doi M., Niki C. [Studies on antispetics for foodstuff. LXXI. Studies on orsellinic acid ester, beta-orcinolcarboxylic acid ester and olivetonide as a preservative for sake]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1970 Dec;90(12):1517–1519. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.90.12_1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


