Abstract
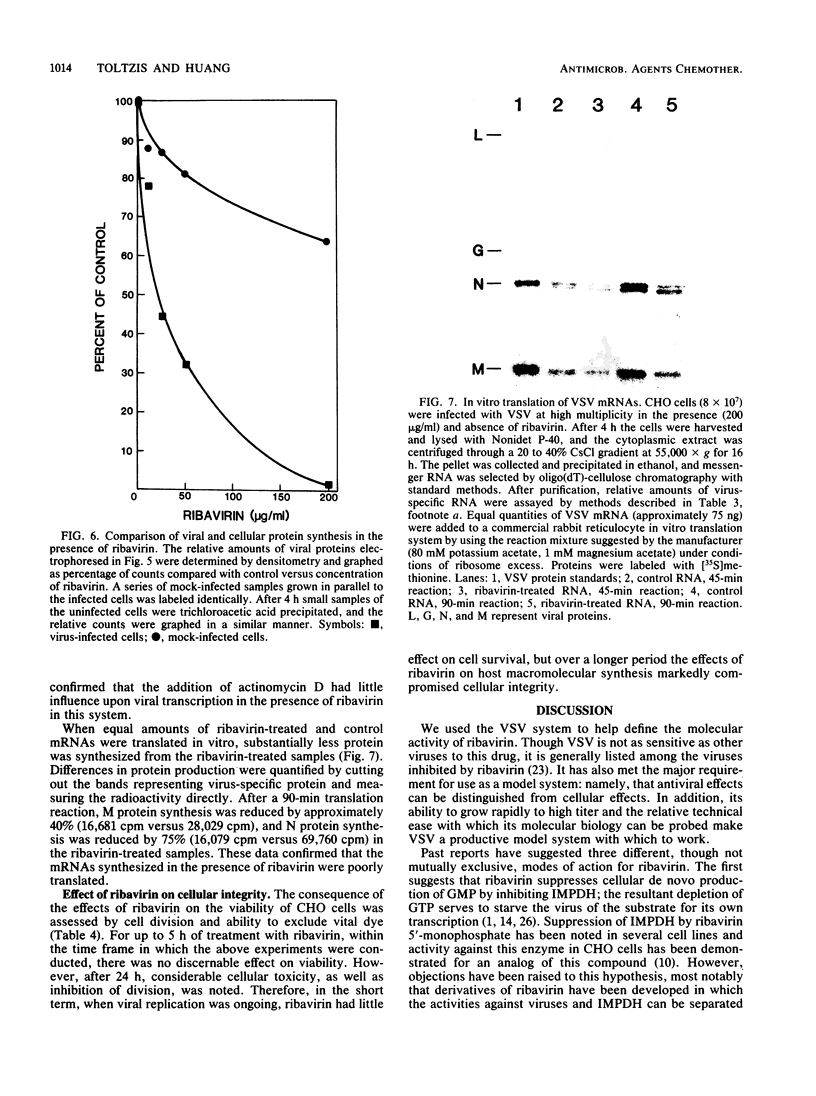
Ribavirin at 200 micrograms/ml inhibited vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) growth in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells by 2.5 logs. To determine the mechanism of this inhibition, viral macromolecular synthesis was examined. VSV primary transcription remained unaffected, but overall VSV RNA synthesis decreased by 40 to 60%. When ribavirin was added 1.5 h after infection, inhibition of progeny production was partially lost, indicating that the antiviral effect was on an early stage after primary transcription. Inhibition of RNA polymerization by premature chain termination was not evident. Viral translation, on the other hand, was reduced by 95% with an inhibition of every protein species. Furthermore, viral RNA synthesized in the presence of ribavirin did not translate well in an in vitro translation system. In contrast, uninfected CHO cells treated with ribavirin showed a greater sensitivity in RNA synthesis than in protein synthesis. This suggests that the cellular translational machinery was not directly affected. Short-term treatment of cells resulted in negligible toxicity, but after 24 h there was marked alteration of cellular integrity. These results, taken together with data on other viruses, suggest that in the presence of ribavirin, dysfunctional VSV mRNA was synthesized, resulting in its failure to be translated. The selective antiviral effects of ribavirin and its relative lack of toxicity for host cells may be predicted on the basis of mRNA turnover and the requirements for de novo functional mRNA.
Full text
PDF
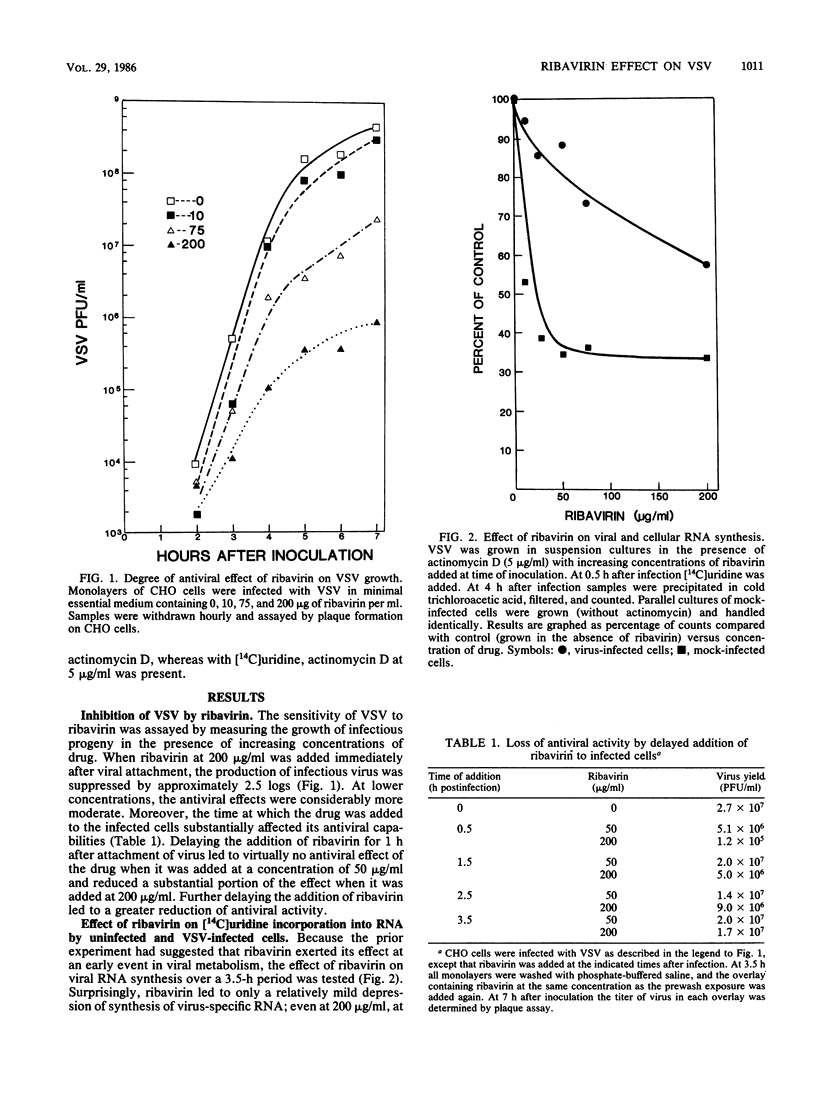
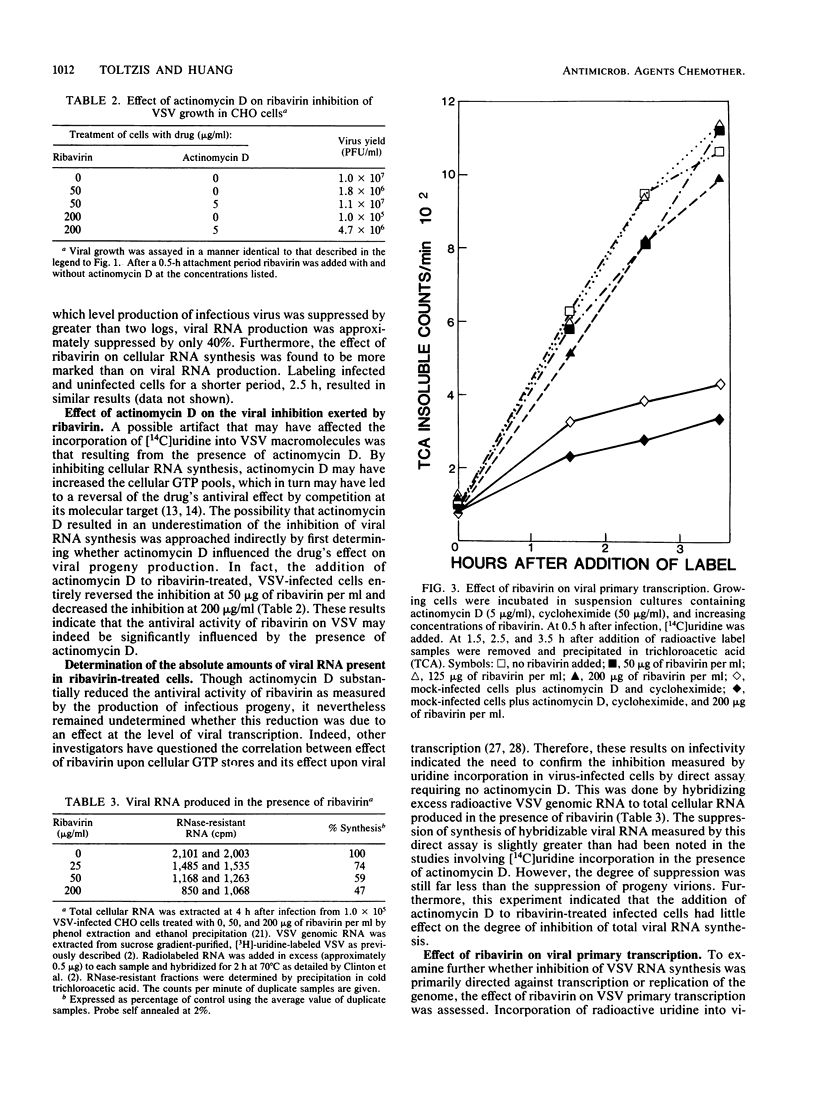
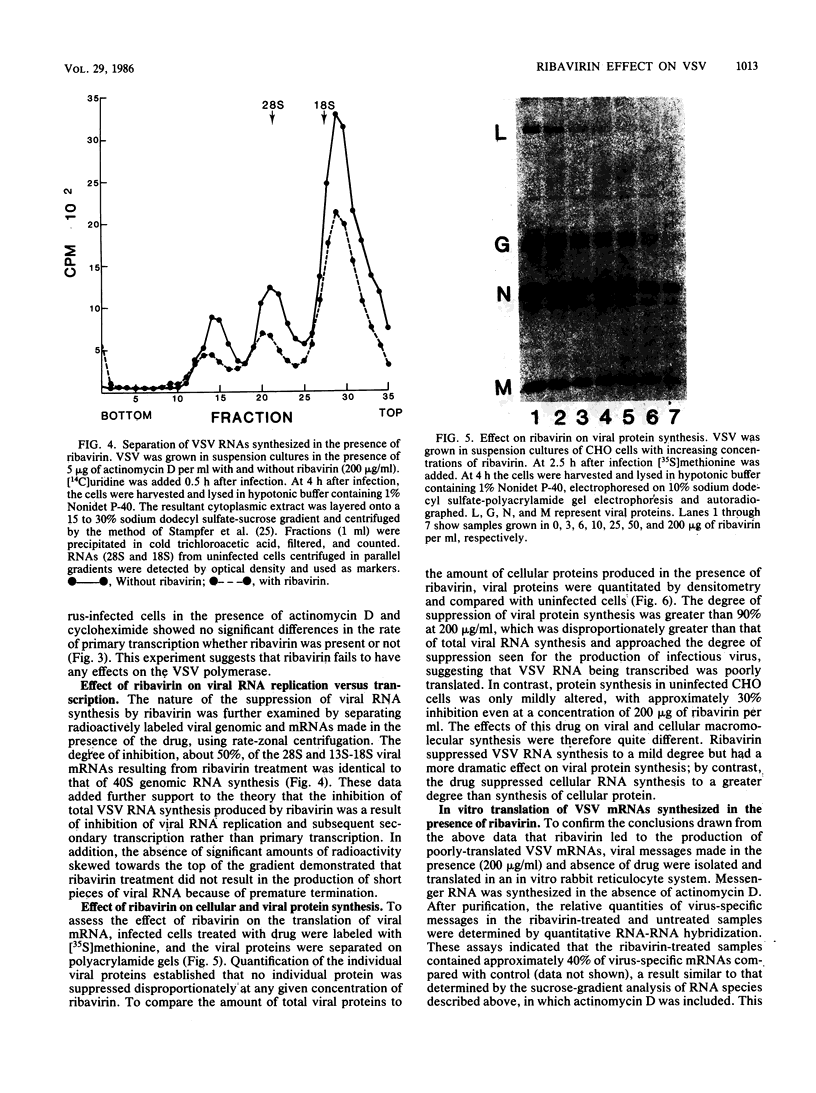


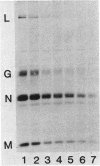
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Browne M. J. Mechanism and specificity of action of ribavirin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):747–753. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton G. M., Little S. P., Hagen F. S., Huang A. S. The matrix (M) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus regulates transcription. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1455–1462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Helgstrand E., Johansson N. G., Larsson A., Misiorny A., Norén J. O., Philipson L., Stenberg K., Stening G., Stridh S. Inhibition of influenza virus ribonucleic acid polymerase by ribavirin triphosphate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):946–951. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami B. B., Borek E., Sharma O. K., Fujitaki J., Smith R. A. The broad spectrum antiviral agent ribavirin inhibits capping of mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91853-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., McBride J. T., Walsh E. E., Bell D. M., Gala C. L., Hildreth S., Ten Eyck L. G., Hall W. J. Aerosolized ribavirin treatment of infants with respiratory syncytial viral infection. A randomized double-blind study. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 16;308(24):1443–1447. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306163082403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Multiple complementary messenger RNA molecules. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):946–957. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffman J. H., Sidwell R. W., Khare G. P., Witkowski J. T., Allen L. B., Robins R. K. In vitro effect of 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (virazole, ICN 1229) on deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid viruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):235–241. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight V., Wilson S. Z., Alling D. W., Moore R. V., Longoria R. M. Lack of interference of guanosine with ribavirin aerosol treatment of influenza A infection in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):477–480. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuttan R., Robins R. K., Saunders P. P. Inhibition of inosinate dehydrogenase by metabolites of 2-beta-D-ribofuranosyl thiazole-4-carboxamide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):862–868. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Stenberg K., Oberg B. Reversible inhibition of cellular metabolism by ribavirin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):154–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinoski F., Stollar V. Inhibition of Sindbis virus replication in Aedes albopictus cells by virazole (ribavirin) and its reversal by actinomycin: a correction. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):473–476. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinoski F., Stollar V. Inhibitors of IMP dehydrogenase prevent sindbis virus replication and reduce GTP levels in Aedes albopictus cells. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClung H. W., Knight V., Gilbert B. E., Wilson S. Z., Quarles J. M., Divine G. W. Ribavirin aerosol treatment of influenza B virus infection. JAMA. 1983 May 20;249(19):2671–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Maidhof A., Taschner H., Zahn R. K. Virazole (1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide; a cytostatic agent. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jun 1;26(11):1071–1075. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patki S. A., Gupta P. Evaluation of ribavirin in the treatment of acute hepatitis. Chemotherapy. 1982;28(4):298–303. doi: 10.1159/000238094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman S. M., Huang A. S. RNA synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. V. Interactions between transcription and replication. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1395–1400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1395-1400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner P., Sundaralingam M. A new class of synthetic nucleoside analogues with broad-spectrum antiviral properties. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 25;244(134):116–118. doi: 10.1038/newbio244116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Knipe D. Nucleotide sequence complexities, molecular weights, and poly(A) content of the vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA species. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):994–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.994-1003.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H., Khare G. P., Allen L. B., Witkowski J. T., Robins R. K. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of Virazole: 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):705–706. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Robins R. K., Hillyard I. W. Ribavirin: an antiviral agent. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;6(1):123–146. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter D. G., Witkowski J. T., Khare G. P., Sidwell R. W., Bauer R. J., Robins R. K., Simon L. N. Mechanism of action of 1- -D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (Virazole), a new broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. K., Gilbert B. E., Knight V. Effect of ribavirin triphosphate on primer generation and elongation during influenza virus transcription in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1985 Feb;5(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. K., Gilbert B. E., Noall M. W., Knight V. Mode of action of ribavirin: effect of nucleotide pool alterations on influenza virus ribonucleoprotein synthesis. Antiviral Res. 1985 Feb;5(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J. N., Cochran B. H., Huang A. S., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and double-stranded ribonucleic acids stimulate expression of the same genes in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]