Abstract
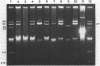
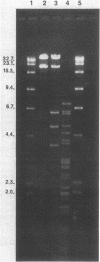
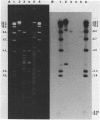
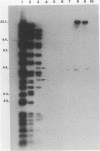
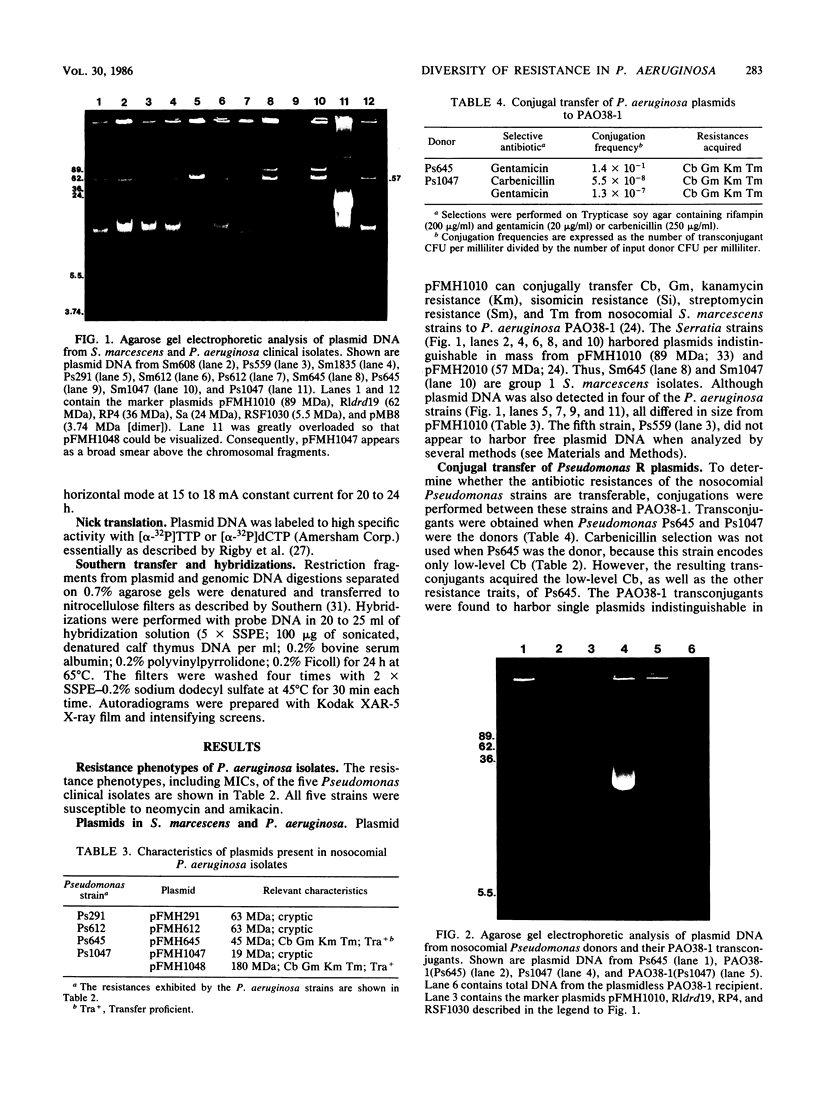
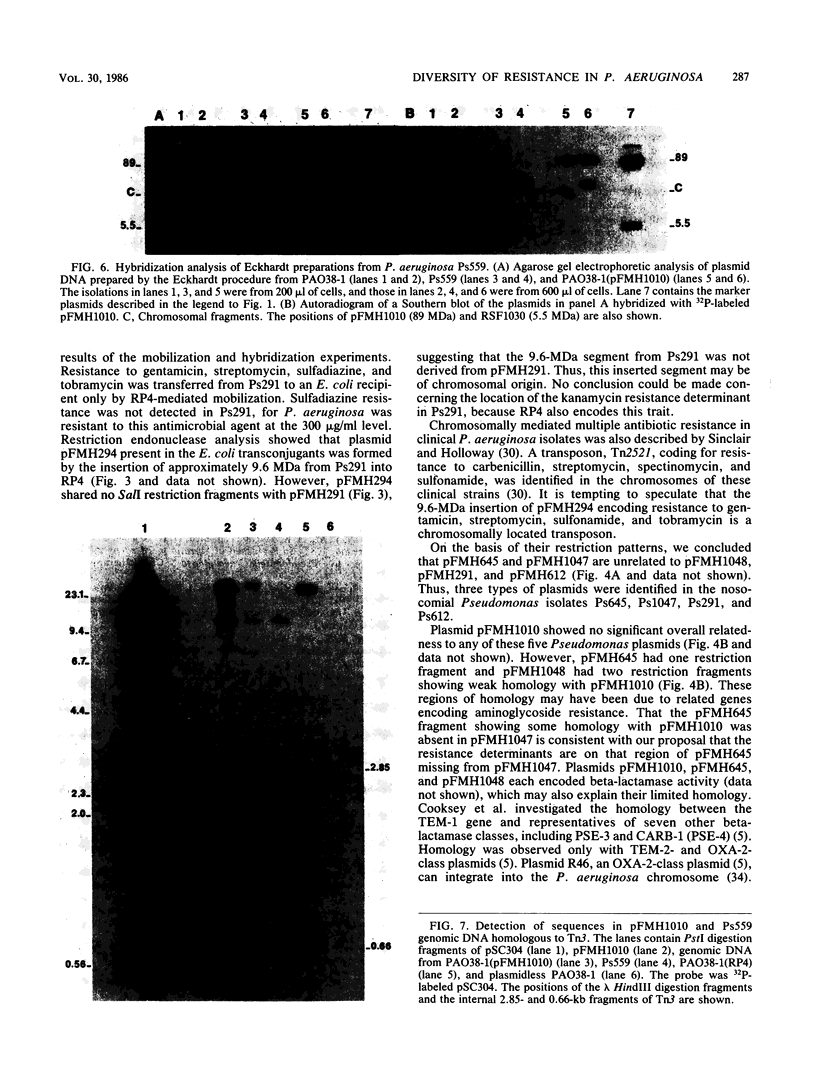
Plasmid pFMH1010, an 89-megadalton R plasmid, is endemic among members of the family Enterobacteriaceae at Hines Veterans Administration Hospital, Hines, Ill. It encodes resistance to nine antibiotics, including resistance to carbenicillin (Cb), gentamicin (Gm), and tobramycin (Tm). Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains resistant to carbenicillin, gentamicin, and tobramycin were isolated from five patients at Hines Veterans Administration Hospital from whom Serratia marcescens strains harboring pFMH1010 were also obtained. The P. aeruginosa strains were investigated to determine whether their Cb, Gm, and Tm characteristics derived from pFMH1010. One of the isolates, Ps559, was shown by Southern hybridization to contain approximately 76% of pFMH1010. Several lines of evidence suggested that the pFMH1010 sequences in Ps559 are integrated in the chromosome. Southern hybridization also demonstrated that the beta-lactam resistance of pFMH1010 is most probably due to the presence of sequences homologous with Tn3 and that these sequences are retained in Ps559. In two other Pseudomonas isolates, resistance to carbenicillin, gentamicin, tobramycin, and kanamycin was encoded by R plasmids unrelated to pFMH1010. In the last two isolates, resistance to gentamicin and tobramycin and several other antibiotics appeared to be chromosomally encoded, and it was rescuable from one of these strains by RP4-mediated mobilization.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Mylroie J. R., Friello D. A., Vacca J. G. Transformation of Pseudomonas putida and Escherichia coli with plasmid-linked drug-resistance factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3647–3651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey R. C., Clark N. C., Thornsberry C. A gene probe for TEM type beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):154–156. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curiale M. S., Mills D. Integration and partial excision of a cryptic plasmid in Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):797–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.797-802.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depicker A., De Block M., Inzé D., Van Montagu M., Schell J. IS-like element IS8 in RP4 plasmid and its involvement in cointegration. Gene. 1980 Sep;10(4):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Weiss P., Fekety F. R., Jr Application of microtitration techniques to bacteriostatic and bactericidal antibiotic susceptibility testing. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Sep;72(3):511–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., McCarthy B. J., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. DNA sequence analysis of the transposon Tn3: three genes and three sites involved in transposition of Tn3. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfhagen T. R., Ferrel J. A., Menefee C. L., Loper J. C. Resistance plasmids of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: change from conjugative to nonconjugative in a hospital population. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):810–816. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer P. J., Cohen S. N. Selected translocation of plasmid genes: frequency and regional specificity of translocation of the Tn3 element. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):888–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.888-899.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Veazey J. M., Jr, Macrina F. L., Mayhall C. G., Lamb V. A. Sequential outbreaks of infection due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in a neonatal intensive care unit: implication of a conjugative R plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):106–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer A. A., Loutit J. S. Transformation and transfection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: effects of metal ions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.37-42.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. F., Ross D. G., Guzman M. A., Medeiros A. A., Hedges R. W., Botstein D. Dissemination of an antibiotic resistance plasmid in hospital patient flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):537–543. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexy V. M., Bird T. J., Grieble H. G., Farrand S. K. Hospital isolates of Serratia marcescens transferring ampicillin, carbenicillin, and gentamicin resistance to other gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):93–100. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexy V. M., Mucha D. K., Bird T. J., Grieble H. G., Farrand S. K. An R plasmid of Serratia marcescens transferable to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chemotherapy. 1982;28(1):6–17. doi: 10.1159/000238054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A. M., Paul G. C., Jacoby G. A. Properties of PSE-2 beta-lactamase and genetic basis for its production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):362–369. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Farrar W. E., Jr, McGee Z. A., Schaffner W. Evolution of a plasmid mediating resistance to multiple antimicrobial agents during a prolonged epidemic of nosocomial infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):170–181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. L., Peterson B. C., Gerding D. N., Cleary P. P. Physical characterization of ten R plasmids obtained from an outbreak of nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):616–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair M. I., Holloway B. W. A chromosomally located transposon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):569–579. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.569-579.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo L. J., Mills D. Characterization of eight excision plasmids of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):90–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00332729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantulavanich S., Olexy V. M., Prasad T. R., Bird T. J., Talanda-Fath C., Grieble H. G., Farrand S. K. An R plasmid of broad host-range, coding for resistance to nine antimicrobial agents endemic in Gram-negative nosocomial isolates. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):371–380. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardif G., Grant R. B. Transfer of IncN plasmids to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):142–144. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardif G., Grant R. B. Transfer of plasmids from Escherichia coli to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant with enhanced recipient ability for enterobacterial plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):201–208. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Plorde J. J., Falkow S. Molecular analysis of R-factors from multiresistant nosocomial isolates. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):625–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Grinsted J. Physical and genetic analysis of the Inc-W group plasmids R388, Sa, and R7K. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]