Abstract
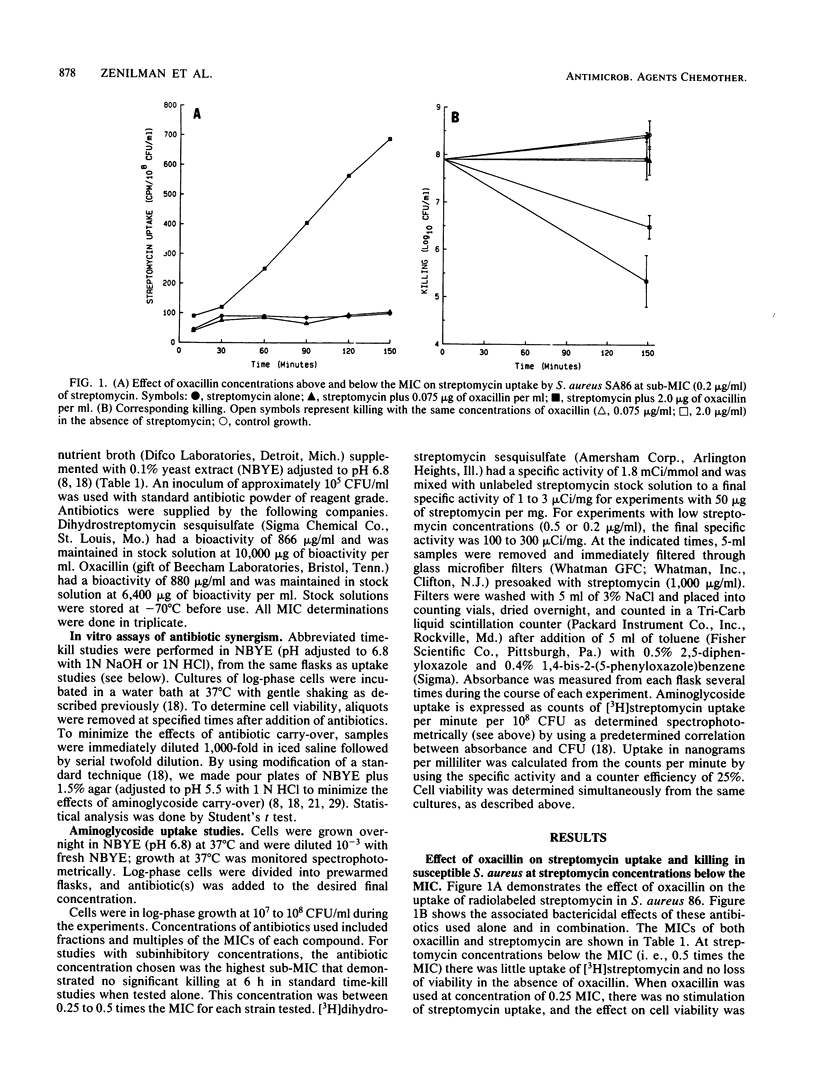
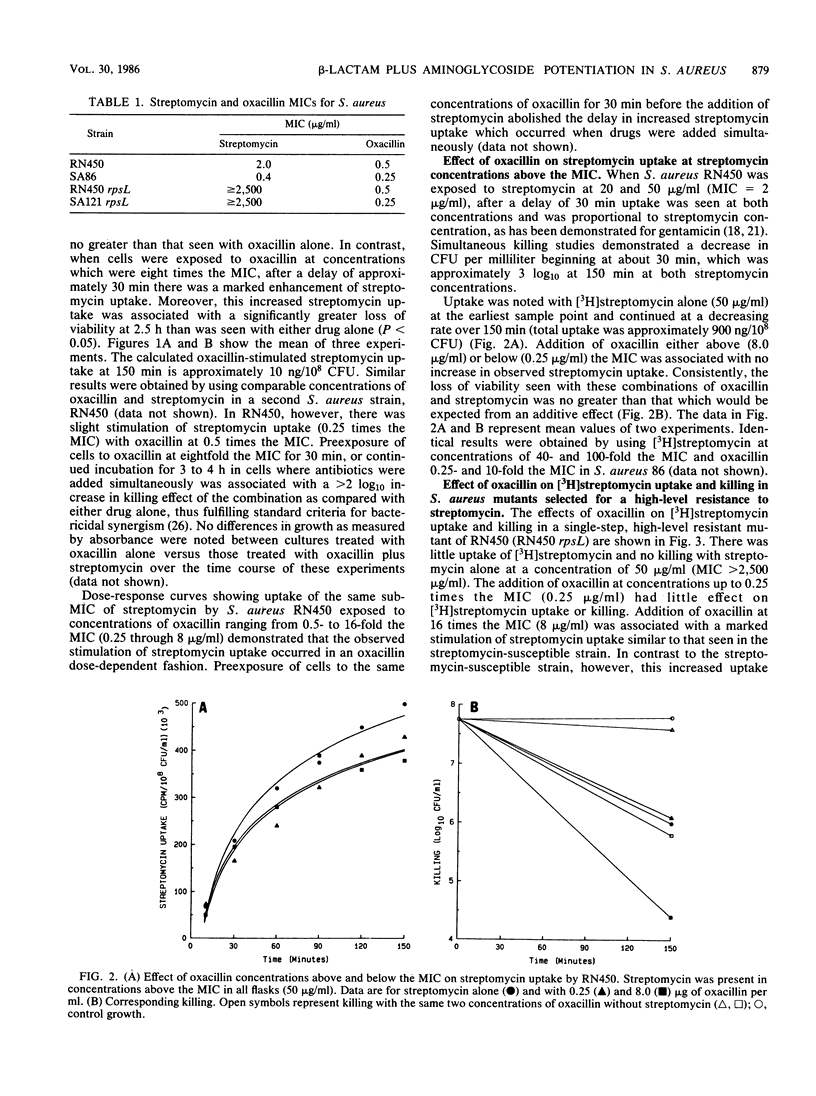
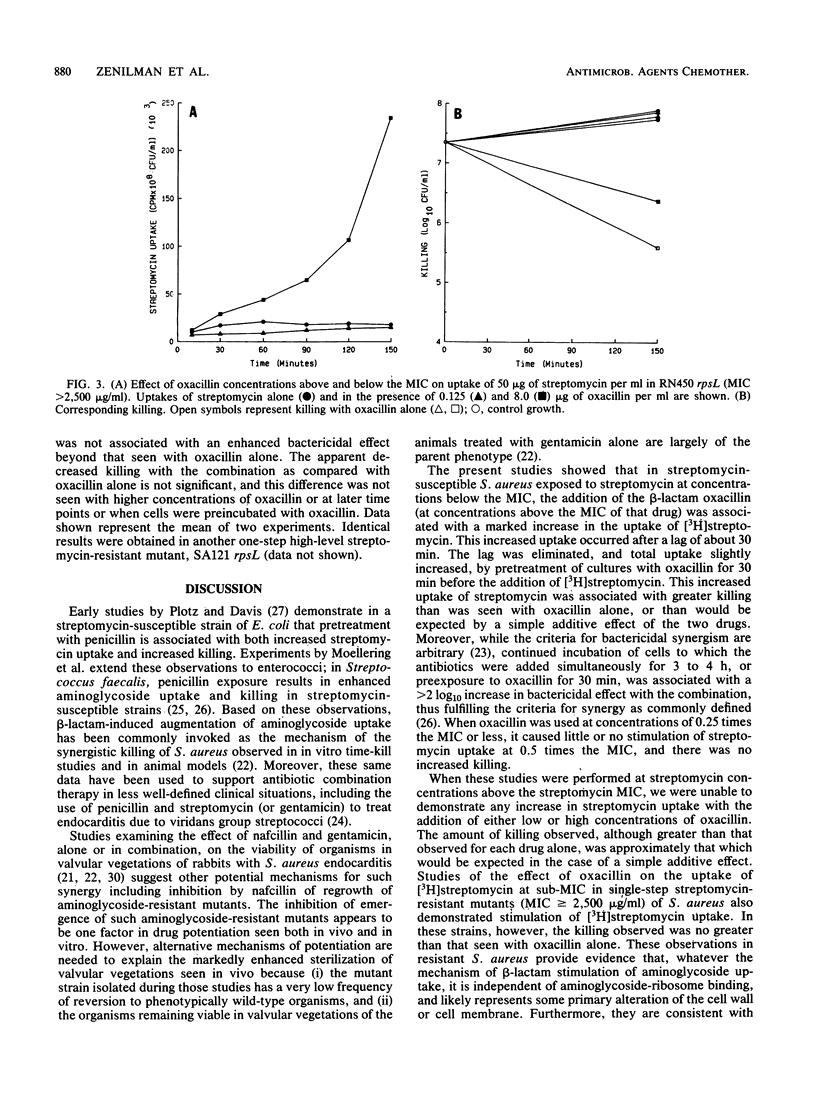
We studied the effects of various concentrations of oxacillin on streptomycin uptake and killing for several strains of Staphylococcus aureus. When streptomycin was present in concentrations below the MIC, addition of oxacillin at concentrations greater than or equal to the MIC was associated with both significantly increased aminoglycoside uptake and killing. In contrast, when streptomycin was present in concentrations above the MIC, no increase of streptomycin uptake was noted with the addition of oxacillin, and killing was no greater than what would have been expected with a simply additive effect. Similar studies in a strain of S. aureus selected for high-level streptomycin resistance also demonstrated increased streptomycin uptake in the presence of concentrations of oxacillin above the MIC; however, killing was no greater than that seen with oxacillin alone. These studies provide data which are potentially important in designing a rational approach to clinical use of combination antibiotic therapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams B., Sklaver A., Hoffman T., Greenman R. Single or combination therapy of staphylococcal endocarditis in intravenous drug abusers. Ann Intern Med. 1979 May;90(5):789–791. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddiley J. Teichoic acids in cell walls and membranes of bacteria. Essays Biochem. 1972;8:35–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Forsberg C. W., Doyle R. J. Major sites of metal binding in Bacillus licheniformis walls. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1438–1448. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1438-1448.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kwan S. Roles of ribosomal binding, membrane potential, and electron transport in bacterial uptake of streptomycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):835–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. D., Kadner R. J. Relation of aerobiosis and ionic strength to the uptake of dihydrostreptomycin in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 5;593(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D. Bactericidal synergism between beta-lactams and aminoglycosides: mechanism and possible therapeutic implications. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):237–245. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Quantitative association between electrical potential across the cytoplasmic membrane and early gentamicin uptake and killing in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):863–867. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.863-867.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Aminoglycoside uptake and mode of action-with special reference to streptomycin and gentamicin. II. Effects of aminoglycosides on cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8(6):429–445. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.6.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano K., Tomasz A. Triggering of autolytic cell wall degradation in Escherichia coli by beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):838–848. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Cappel R., Daneau D. Clinical significance of in vitro synergism between antibiotics in gram-negative infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):470–475. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klastersky J., Zinner S. H. Synergistic combinations of antibiotics in gram-negative bacillary infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):294–301. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniowski O., Sande M. A. Combination antimicrobial therapy for Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in patients addicted to parenteral drugs and in nonaddicts: A prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):496–503. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel L. J., Murphy E., Steigbigel N. H., Miller M. H. Gentamicin uptake in Staphylococcus aureus possessing plasmid-encoded, aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):563–569. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates S. M., Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Patel L., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Membrane potential and gentamicin uptake in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6693–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates S. M., Patel L., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Membrane potential in anaerobically growing Staphylococcus aureus and its relationship to gentamicin uptake. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):526–530. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Edberg S. C., Mandel L. J., Behar C. F., Steigbigel N. H. Gentamicin uptake in wild-type and aminoglycoside-resistant small-colony mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Wexler M. A., Steigbigel N. H. Single and combination antibiotic therapy of Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis: emergence of gentamicin-resistant mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):336–343. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr Antimicrobial synergism--an elusive concept. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):639–641. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Weinberg A. N. Studies on antibiotic syngerism against enterococci. II. Effect of various antibiotics on the uptake of 14 C-labeled streptomycin by enterococci. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2580–2584. doi: 10.1172/JCI106758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Weinberg A. N. Studies on antibiotic synergism against enterococci. I. Bacteriologic studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 May;77(5):821–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ P. H., DAVIS B. D. Synergism between streptomycin and penicillin: a proposed mechanism. Science. 1962 Mar 23;135(3508):1067–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3508.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynor R. H., Scott D. F., Best G. K. Oxacillin-induced lysis of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):134–140. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Casey J. I., Ruch P. A., Stumpf L. L., Finland M. Rapid microassay of gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin, streptomycin, and vancomycin in serum or plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Courtney K. B. Nafcillin-gentamicin synergism in experimental staphylococcal endocarditis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jul;88(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. Teichoic and teichuronic acids: biosynthesis, assembly, and location. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):211–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.211-243.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Glotzbecker C. Synergism with aminoglycosides of penicillin, ampicillin and vancomycin against non-enterococcal group-D streptococci and viridans streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):133–138. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


