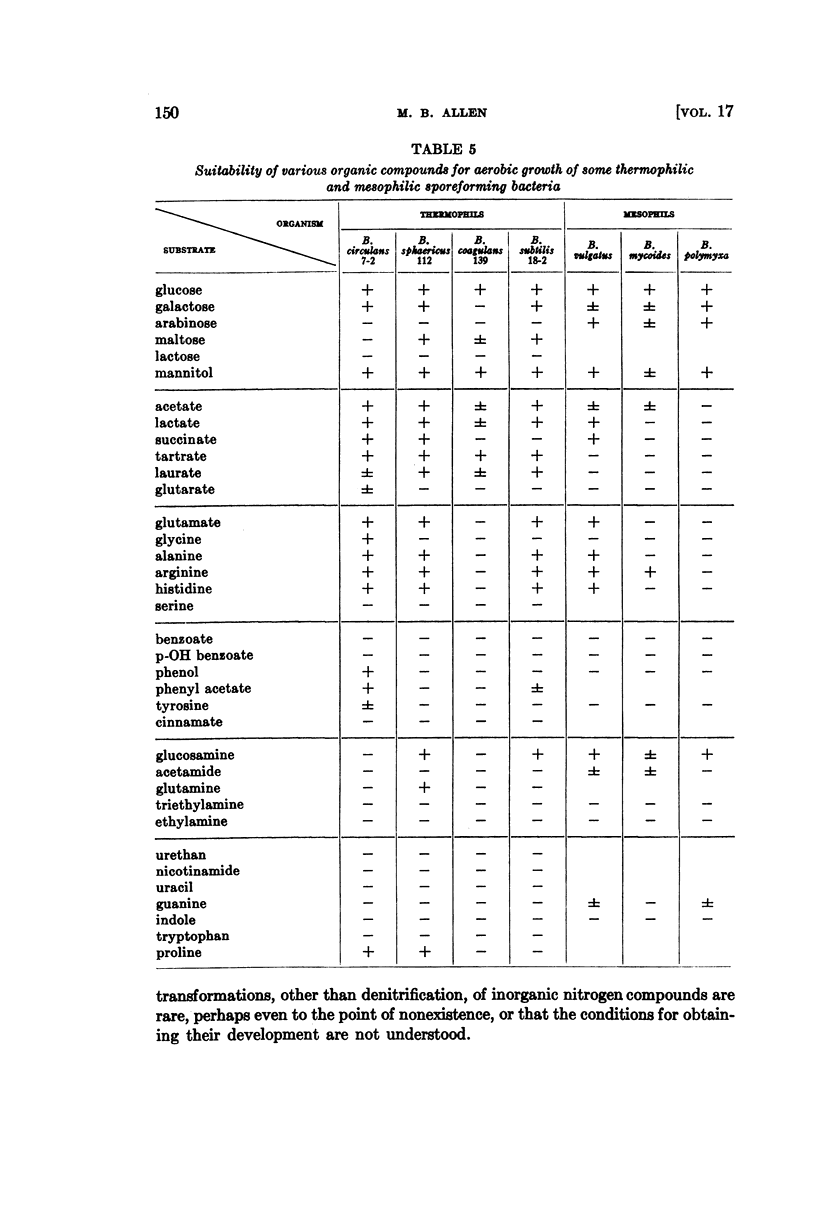
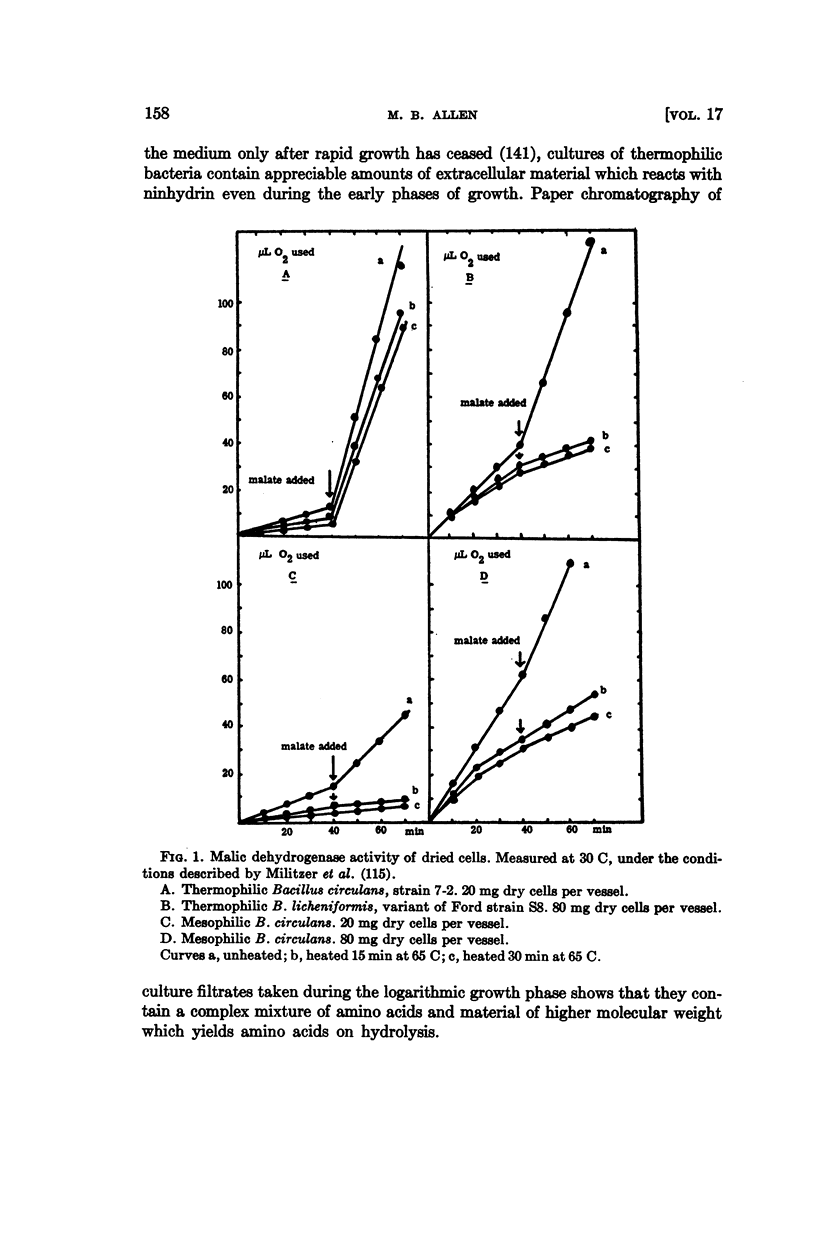
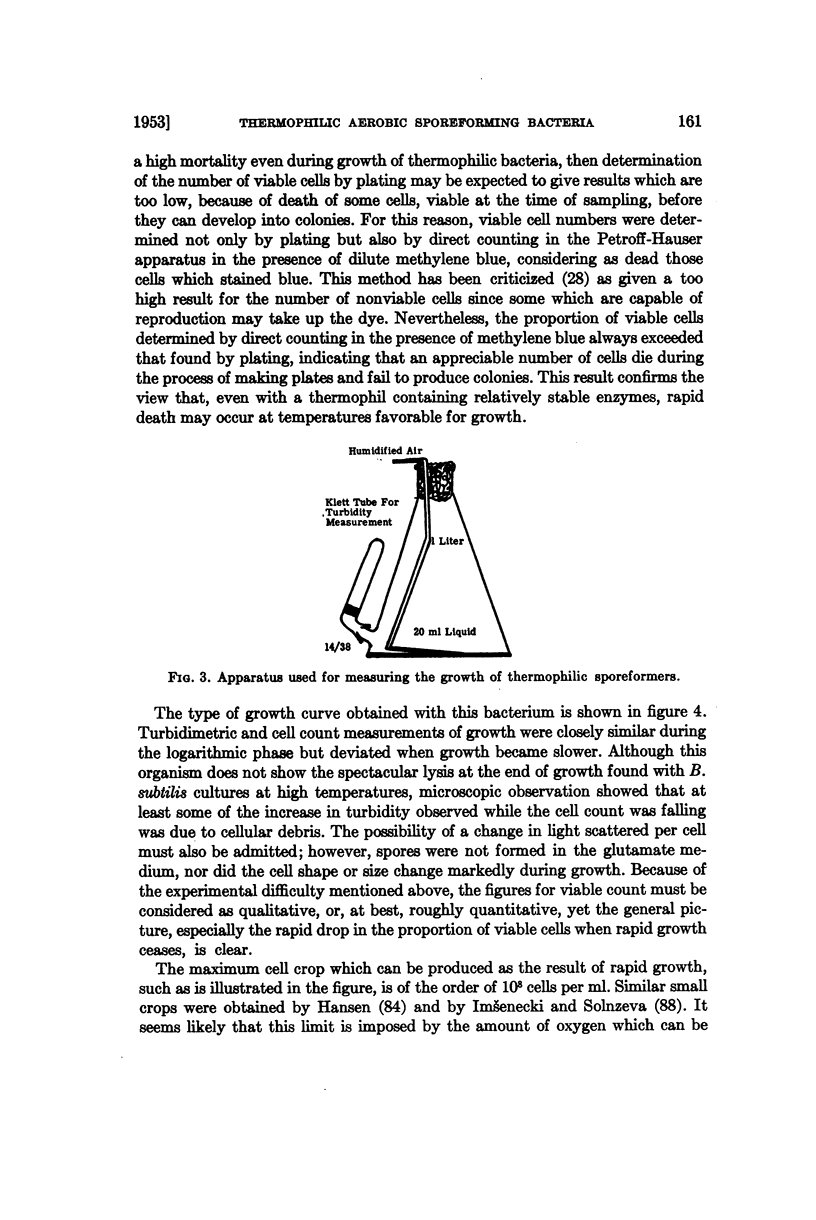
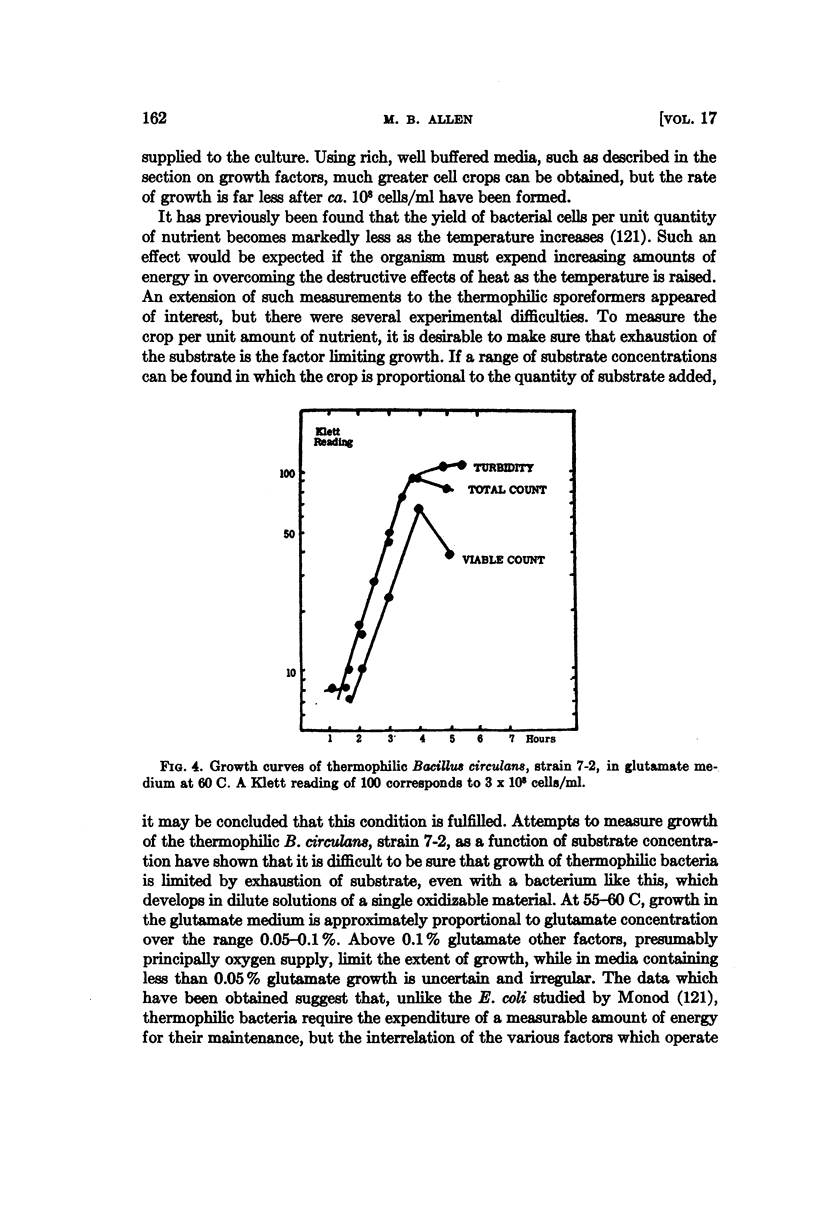
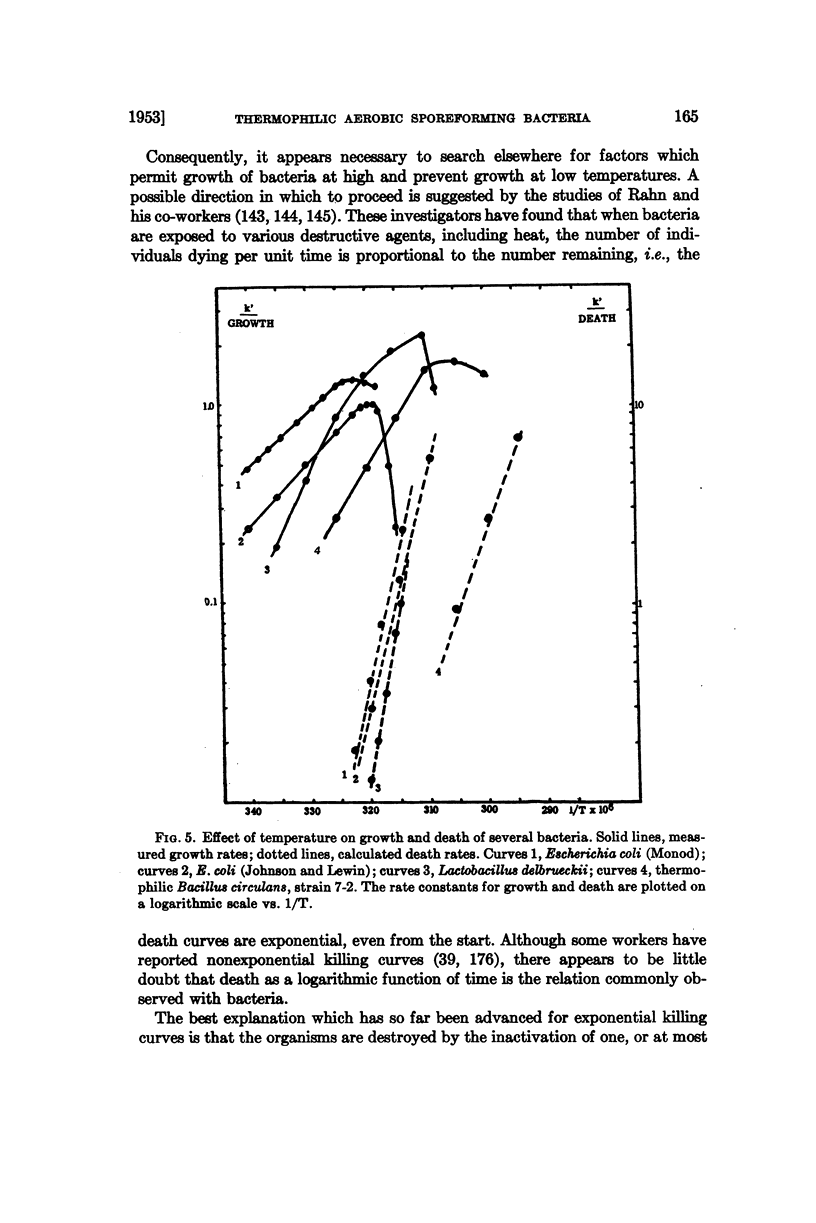
Full text
PDF











































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN M. B. The dynamic nature of thermophily. J Gen Physiol. 1950 Jan 20;33(3):205–214. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON E. E., ESSELEN W. B., Jr, FELLERS C. R. Effect of acids, salt, sugar and other food ingredients on thermal resistance of Bacillus thermoacidurans. Food Res. 1949 Nov-Dec;14(6):499–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1949.tb16261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers S. H., Johnson W. T. STUDIES ON PASTEURIZATION XII. CAUSE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF PIN-POINT COLONIES FROM PASTEURIZED MILK. J Bacteriol. 1924 May;9(3):285–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.9.3.285-300.1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER M. E., PEDERSON C. S. The physiological characters of Bacillus coagulans (Bacillus thermoacidurans). J Bacteriol. 1950 Jun;59(6):717–725. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.6.717-725.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew J. W., Rittenberg S. C. THERMOPHILIC BACTERIA FROM DEEP OCEAN BOTTOM CORES. J Bacteriol. 1949 Jun;57(6):658–658. doi: 10.1128/jb.57.6.658-658.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner J. G. Heat Sterilised Reducing Sugars and Their Effects on the Thermal Resistance of Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1938 Oct;36(4):369–382. doi: 10.1128/jb.36.4.369-382.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergey D. H. Thermophilic Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1919 Jul;4(4):301–306. doi: 10.1128/jb.4.4.301-306.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., Jr, WILLIAMS O. B. The effect of temperature on the nutritional requirements of facultative and obligate thermophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):141–145. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.141-145.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Rettger L. F. Limitation of Bacterial Growth at Higher Temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1933 Jul;26(1):77–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.26.1.77-123.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleverdon R. C., Pelczar M. J., Doetsch R. N. VITAMIN REQUIREMENTS OF BACILLUS COAGULANS. J Bacteriol. 1949 Jul;58(1):113–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleverdon R. C., Pelczar M. J., Jr, Doetsch R. N. THE VITAMIN REQUIREMENTS OF STENOTHERMOPHILIC AEROBIC SPOROGENOUS BACILLI. J Bacteriol. 1949 Oct;58(4):523–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.4.523-526.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran H. R., Brunstetter B. C., Myers A. T. Spectrochemical Analysis of Vegetative Cells and Spores of Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1943 May;45(5):485–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.45.5.485-494.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damon S. R., Feirer W. A. ANAEROBIC SPORULATING THERMOPHILES SOME OBSERVATIONS ON A NEW GROUP OF BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1925 Jan;10(1):37–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.10.1.37-46.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donk P. J. A Highly Resistant Thermophilic Organism. J Bacteriol. 1920 Jul;5(4):373–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.5.4.373-374.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards O. F., Rettger L. F. Relation of Certain Respiratory Enzymes to the Maximum Growth Temperatures of Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1937 Nov;34(5):489–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.34.5.489-515.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel G., Hopf H. S. The physiological action of abnormally high temperatures on poikilothermic animals: Temperature adaptation and the degree of saturation of the phosphatides. Biochem J. 1940 Jul;34(7):1085–1092. doi: 10.1042/bj0341085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGI C. E., MILITZER W., BURNS L., HEOTIS J. On the existence of a cell granule in a thermophilic bacterium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Mar;76(3):598–601. doi: 10.3181/00379727-76-18572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaughran E. R. THE THERMOPHILIC MICROORGANISMS. Bacteriol Rev. 1947 Sep;11(3):189–225. doi: 10.1128/br.11.3.189-225.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. E., Smith N. R. AEROBIC SPOREFORMING BACTERIA CAPABLE OF GROWTH AT HIGH TEMPERATURES. J Bacteriol. 1949 Sep;58(3):327–341. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.3.327-341.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussong R. V., Hammer B. W. A THERMOPHILE COAGULATING MILK UNDER PRACTICAL CONDITIONS. J Bacteriol. 1928 Mar;15(3):179–188. doi: 10.1128/jb.15.3.179-188.1928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imsenecki A., Solnzeva L. The Growth of Aerobic Thermophilic Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1945 Jun;49(6):539–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.49.6.539-546.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT B. C. J. G., PROOM H. A comparative survey of the nutrition and physiology of mesophilic species in the genus Bacillus. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):508–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaysi G., Gunsalus I. C. A Study of the So-Called Marburg and the Lawrence and Ford Strains of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1944 Apr;47(4):381–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.47.4.381-389.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamanna C. Relation Between Temperature Growth Range and Size in the Genus Bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1940 May;39(5):593–596. doi: 10.1128/jb.39.5.593-596.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSH C., MILITZER W. Thermal enzymes. V. Properties of a malic dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Apr;36(2):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILITZER W., TUTTLE L. C., GEORGI C. E. Thermal enzymes. III. Apyrase from a thermophilic Bacterium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 May;31(3):416–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBee R. H. The Culture and Physiology of a Thermophilic Cellulose-fermenting Bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1948 Nov;56(5):653–663. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.5.653-663.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClung L. S. Studies on Anaerobic Bacteria: III. Historical Review and Technique of Culture of Certain Thermophilic Anaerobes. J Bacteriol. 1935 Feb;29(2):173–187. doi: 10.1128/jb.29.2.173-187.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Tanner F. W. Studies on Thermophilic Bacteria: I. Aerobic Thermophilic Bacteria from Water. J Bacteriol. 1922 May;7(3):343–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.7.3.343-366.1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. C. Aerobic decomposition of cellulose by thermophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1944 Feb;47(2):117–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.47.2.117-122.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson L. K., Raper H. S. The Influence of Temperature on the Nature of the Fat formed by Living Organisms. Biochem J. 1927;21(4):875–879. doi: 10.1042/bj0210875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarles W. B., Hammer B. W. Observations on Bacillus coagulans. J Bacteriol. 1932 Apr;23(4):301–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.23.4.301-314.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y. Agar-Decomposing Strains of the Actinomyces Coelicolor Species-Group. J Bacteriol. 1942 Nov;44(5):555–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.44.5.555-570.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner F. W., Wallace G. I. RELATION OF TEMPERATURE TO THE GROWTH OF THERMOPHILIC BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1925 Sep;10(5):421–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.10.5.421-437.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERHOEVEN W. On a sporeforming bacterium causing the swelling of cans containing cured ham. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1950;16(4):269–281. doi: 10.1007/BF02274424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A. I. On the Enzymes of Bacteria and Bacterial Metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1934 Nov;28(5):447–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.28.5.447-460.1934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARE G. C. Nutritional requirements of Bacterium coli at 44 degrees. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Nov;5(5 Suppl):880–884. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-5-880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. H., Winslow C. E. Factors Determining the Rate of Mortality of Bacteria Exposed to Alkalinity and Heat. J Bacteriol. 1932 Sep;24(3):243–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.24.3.243-265.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van HALTEREN P. Effets d'un choc thermique sur le métabolisme des levures. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1950;32(7-8):458–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


