Abstract
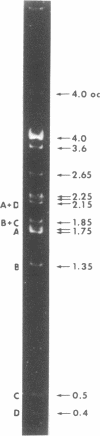
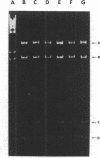
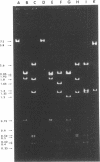
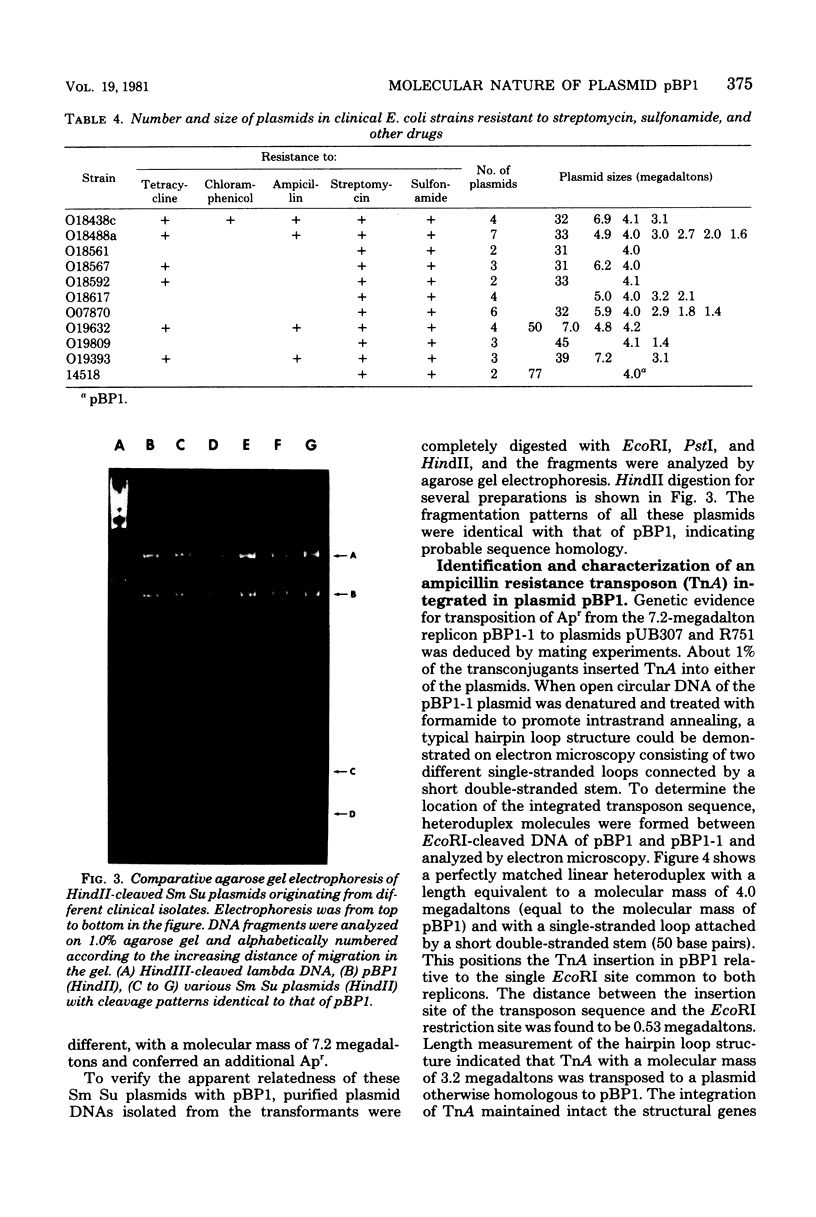
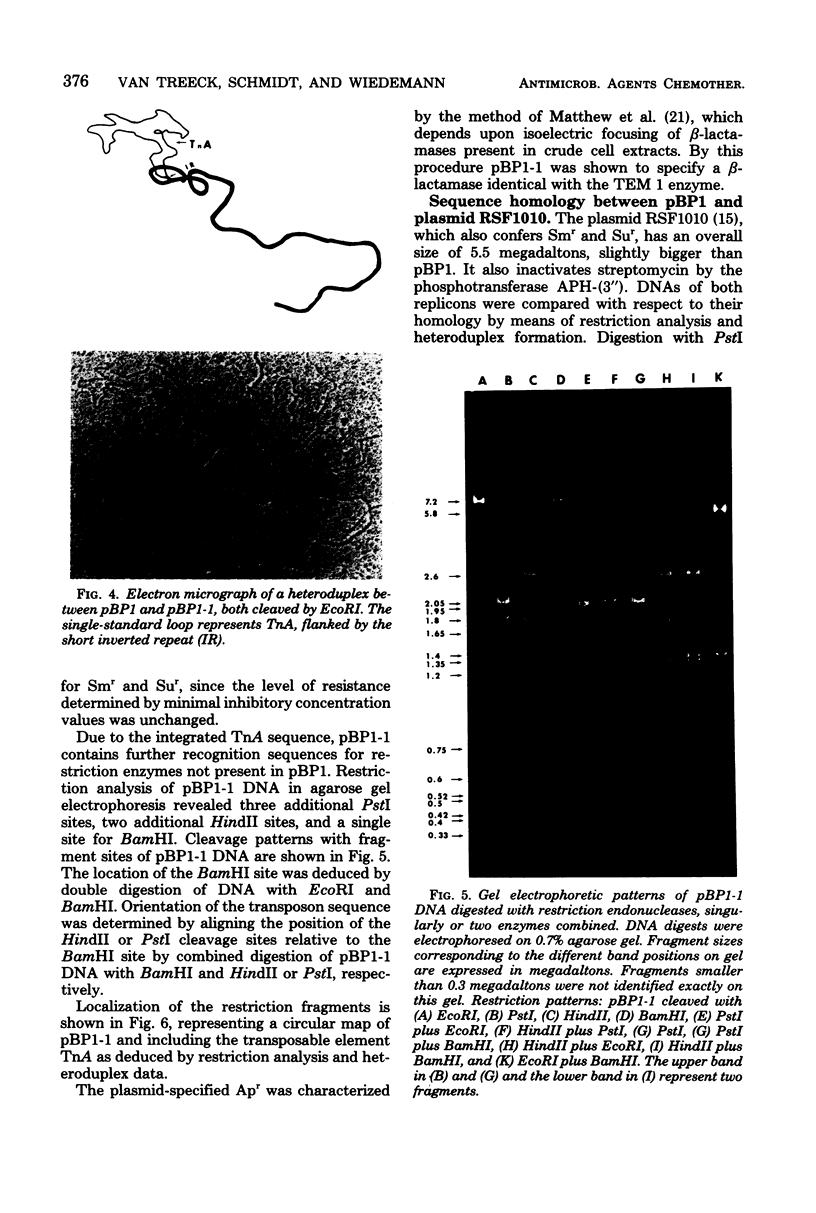
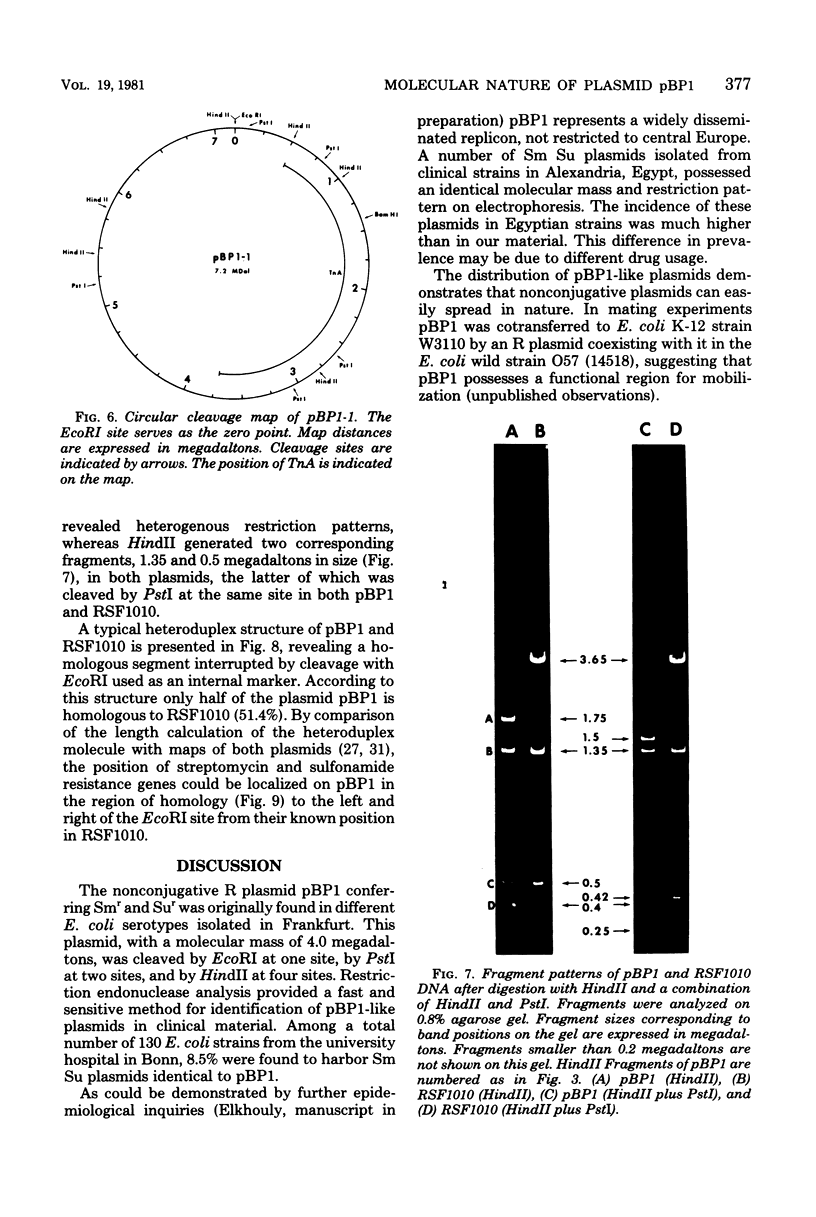
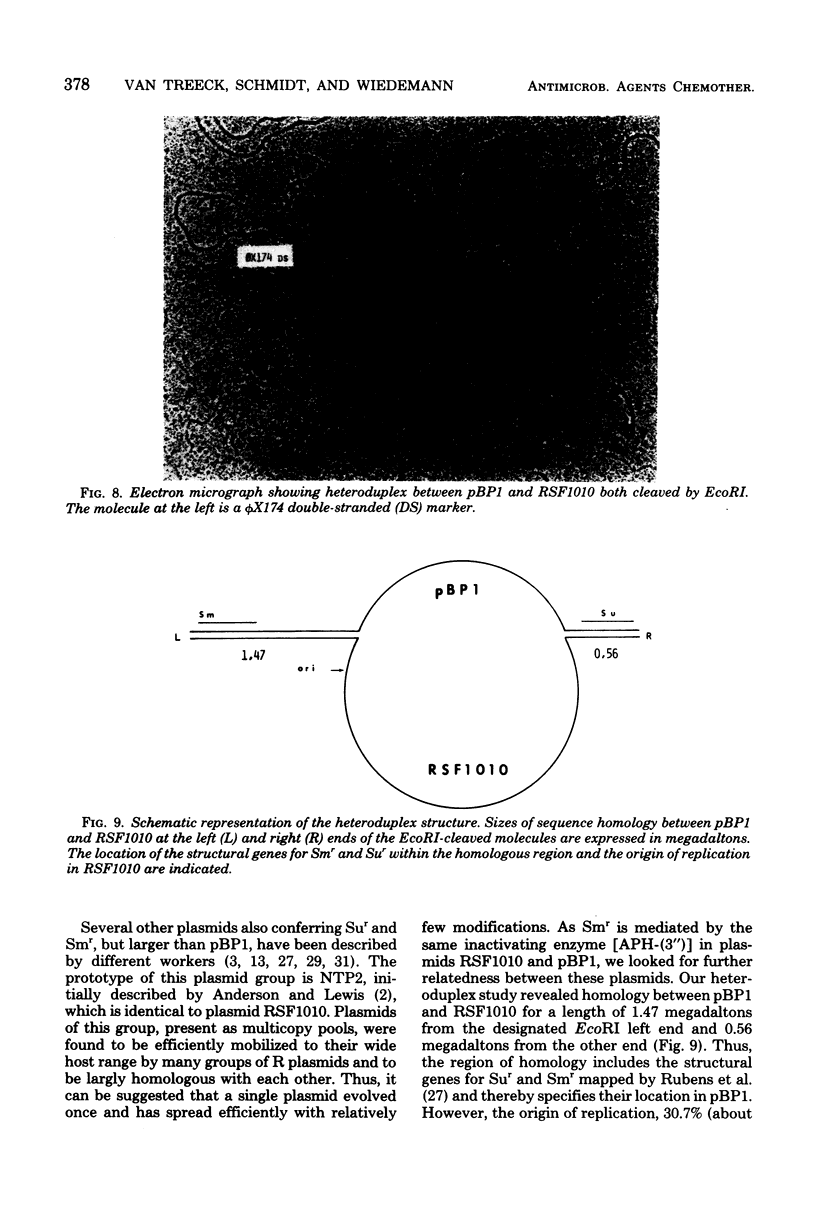
A small, nonconjugative plasmid, designated pBP1, was originally found in different fecal Escherichia coli serotypes isolated from a healthy proband. Of a total number of 130 hospital strains of E. coli subsequently studied, 8.5% yielded plasmid of the pBP1 type. This R plasmid specifies resistance to streptomycin (Sm) and sulfonamides (Su) and has a mass of 4.0 megadaltons. Inactivation of streptomycin is due to the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase APH-(3 "). A physical map was constructed by analysis with restriction endonucleases. Another small plasmid, pBP1-1, was isolated from one of the hospital strains and characterized as an enlarged pBP1 replicon containing an additional deoxyribonucleic acid sequence identified as a transposable element for ampicillin resistance (TnA). Plasmid pBP1-1 was cleaved by restriction enzymes for identification of the transposon sequence which codes for a TEM 1 beta-lactamase. The sequence organizations in the Sm Su plasmids RSF1010 and pBP1 were shown to be identical for regions specifying streptomycin and sulfonamide resistance, but different for the region containing the origin of replication and genes for replicative functions. Thus, RSF1010, which has been considered as the prototype of Sm Su plasmids, and pBP1, which is at least as frequent in clinical isolates as RSF1010, do not have a single common ancestor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Willetts N., Clark A. J. Beginning a genetic analysis of conjugational transfer determined by the F factor in Escherichia coli by isolation and characterization of transfer-deficient mutants. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):529–538. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.529-538.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Lewis M. J. Characterization of a transfer factor associated with drug resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Nature. 1965 Nov 27;208(5013):843–849. doi: 10.1038/208843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. T., Grinter N. J. Comparison of the deoxyribonucleic acid molecular weights and homologies of plasmids conferring linked resistance to streptomycin and sulfonamides. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):618–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.618-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. M., Grinsted J., Richmond M. H. Transposition of TnA does not generate deletions. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jul 20;154(2):205–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00330839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H. Translocation of a discrete piece of deoxyribonucleic acid carrying an amp gene between replicons in Eschericha coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.1-6.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. R-factor mediated gentamicin resistance: A new enzyme which modifies aminoglycoside antibiotics. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Casadaban M. J., Lemaux P. G., Cohen S. N. Identification and characterization of a self-regulated repressor of translocation of the Tn3 element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4020–4024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinsted J., Saunders J. R., Ingram L. C., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Properties of a R factor which originated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1822. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):529–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.529-537.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinter N. J., Barth P. T. Characterization of SmSu plasmids by restriction endonuclease cleavage and compatibility testing. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):394–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.394-400.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., van Embden J., Falkow S. Molecular nature of two nonconjugative plasmids carrying drug resistance genes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):619–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.619-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., Rubens C., Falkow S. Translocation of a plasmid DNA sequence which mediates ampicillin resistance: molecular nature and specificity of insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A., Anderson E. S. A simple method for the preparation of large quantities of pure plasmid DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 2;383(4):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobanputra R. S., Datta N. Trimethoprim R factors in enterobacteria from clinical specimens. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe H., Tanaka T., Mitsuhashi S. Streptomycin and Spectinomycin resistance mediated by plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):1031–1035. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Benveniste R., Tipper D., Davies J. Aminoglycoside antibiotics: inactivation by phosphorylation in Escherichia coli carrying R factors. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1144–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1144-1146.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C., Heffron F., Falkow S. Transposition of a plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid sequence that mediates ampicillin resistance: independence from host rec functions and orientation of insertion. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):425–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.425-434.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Genetic and molecular characterisation of some non-transferring plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Mar 27;129(3):229–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00267915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Calame K. L., Grindley J. N., Nakada D. Location of an ampicillin resistance transposon, Tn1701, in a group of small, nontransferring plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):990–999. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.990-999.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaff J., Crosa J. H., Heffron F., Falkow S. Replication of the nonconjugative plasmid RSF1010 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1117–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1117-1122.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D. Translocation of an ampicillin resistance determinant within an R-factor aggregate in Salmonella panama. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1978;44(2):203–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00643223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]