Abstract
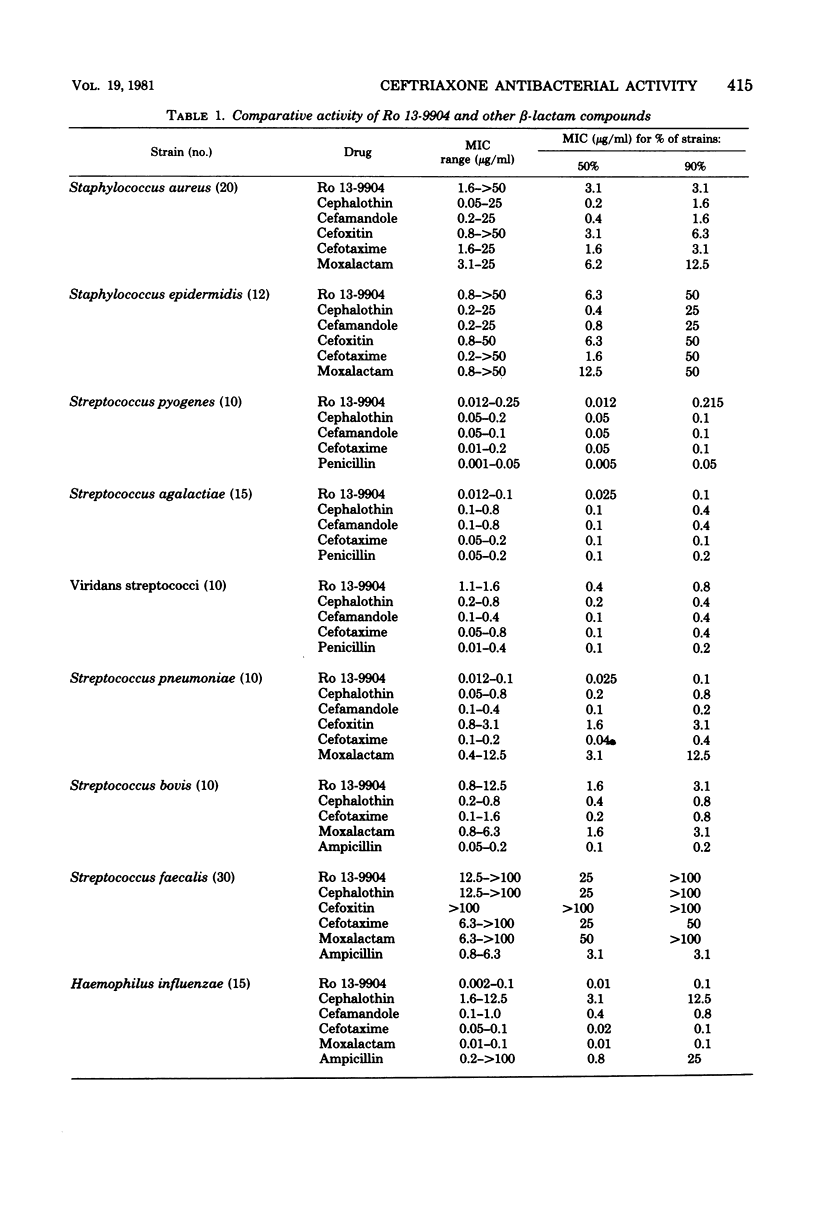
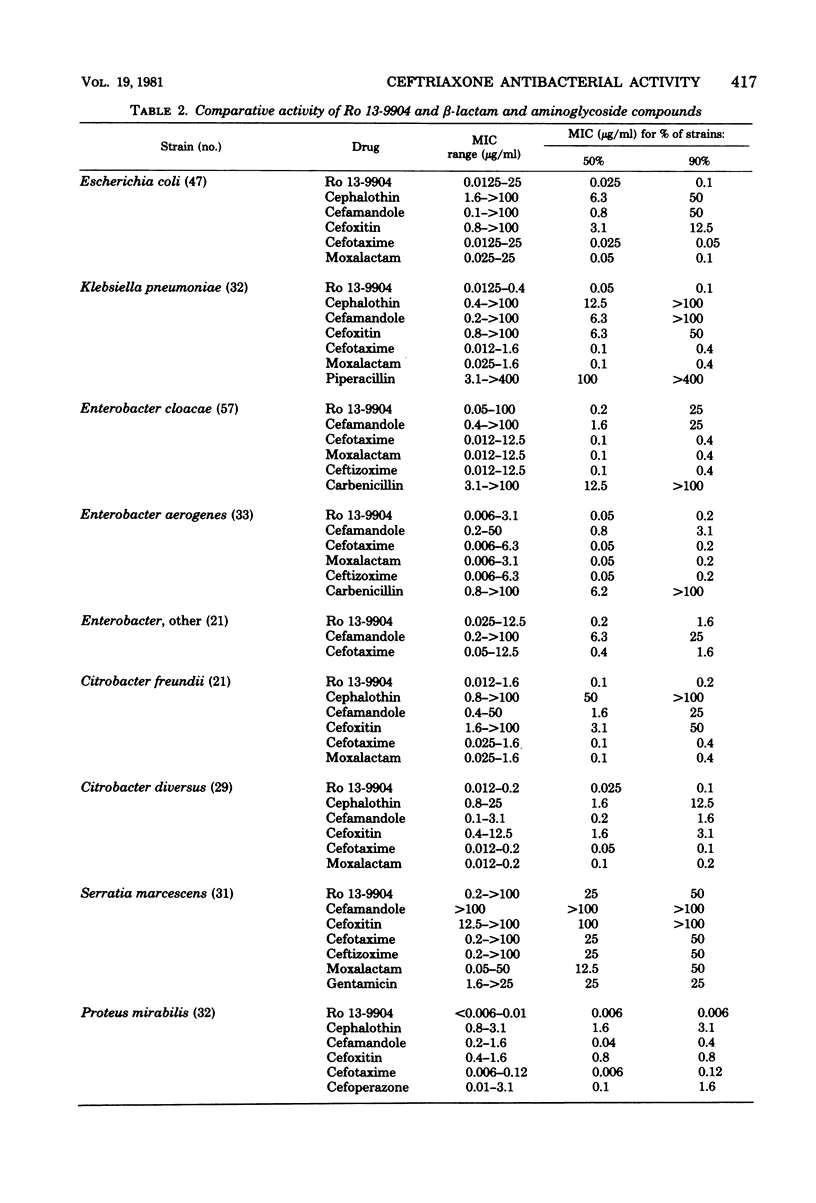
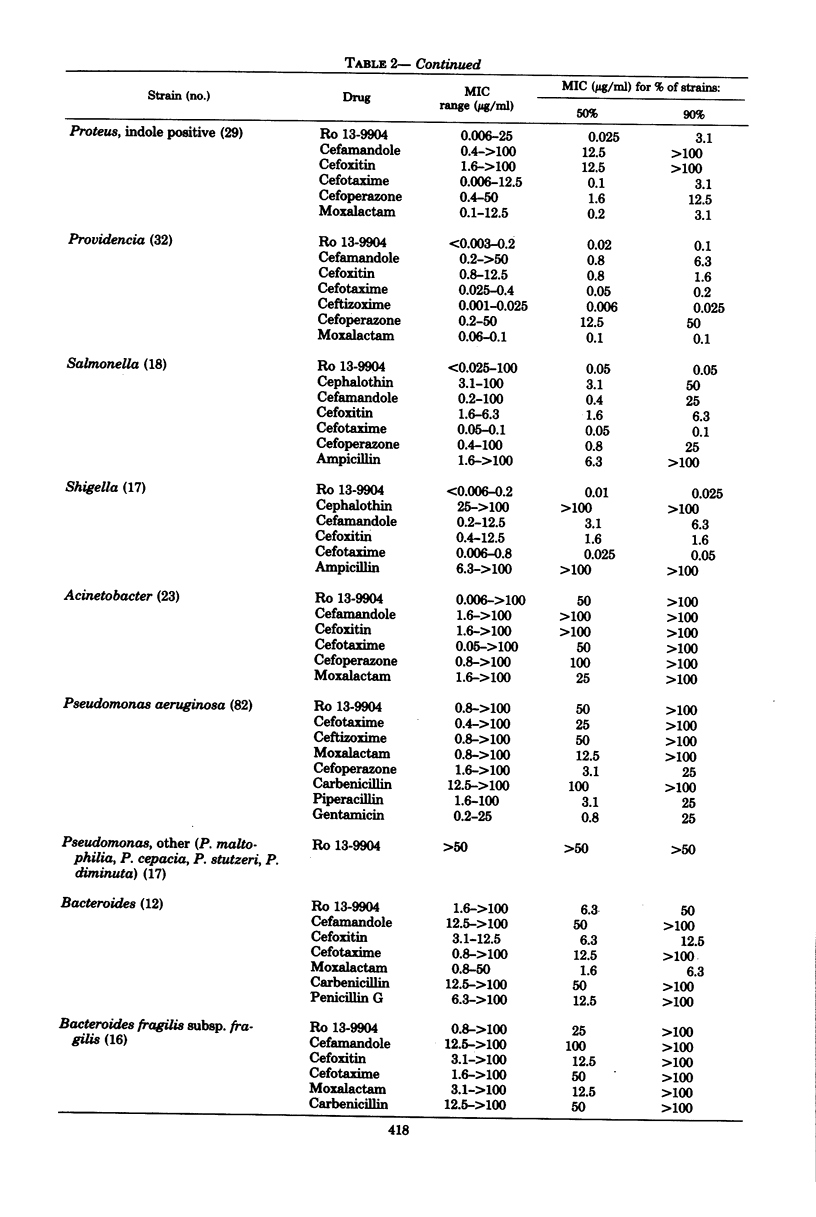
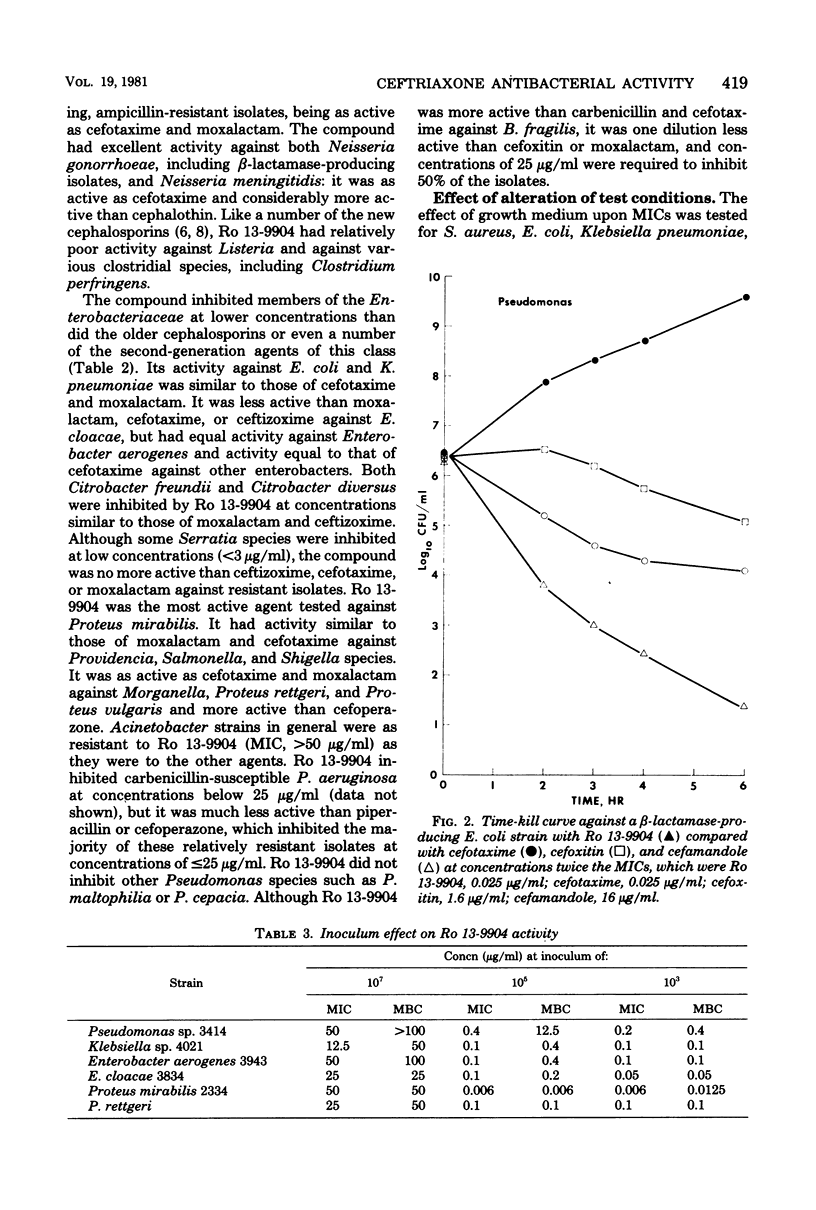
The in vitro activity of ceftriaxone (Ro 13-9904), a parenteral cephalosporin, was compared with that of other beta-lactam antibiotics. the compound was less active against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis than was cephalothin or cefamandole, but it was comparable to cefoxitin, cefotaxime, and moxalactam in inhibiting most isolates of S. aureus at 3.1 microgram/ml. Ro 13-9904 inhibited Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus pneumoniae at concentrations below 0.25 microgram/ml, but Streptococcus faecalis required concentrations above 25 microgram/ml. Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Haemophilus influenzae were inhibited at concentrations similar to those of cefotaxime, less than 0.1 microgram/ml. Ro 13-9904 was as active as cefotaxime and moxalactam against most Enterobacteriaceae and was the most active agent tested against Proteus, inhibiting all strains tested at 0.006 microgram/ml. Ro 13-9904 was slightly less active than moxalactam or cefoxitin against Bacteroides fragilis, requiring more than 100 microgram/ml to inhibit 90% of isolates, and it was less active than cefoperazone against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Presence of serum, alteration of pH, and use of various media did not change the inhibitory levels. Bactericidal concentrations were similar to inhibitory levels. Ro 13-9904 was stable to most plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases, but was hydrolyzed by some Enterobacter, Proteus, and Bacteroides beta-lactamases of chromosomal origin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Antibacterial activity of ceftizoxime, a beta-lactamase-stable cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):583–590. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G., James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XI. Comparison of in vivo and vitro association of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with human neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jan;137(1):38–43. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Fu K. P. HR 756, a new cephalosporin active against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):273–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Fu K. P., Aswapokee P. Antibacterial activity of a new 1-oxa cephalosporin compared with that of other beta-lactam compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):141–149. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: antibacterial spectrum and resistance to hydrolysis by gram-negative beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P., Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Kung K. Comparative activity and beta-lactamase stability of cefoperazone, a piperazine cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):150–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Cefuroxime, a beta-lactamase-resistant cephalosporin with a broad spectrum of gram-positive and -negative activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):657–664. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


