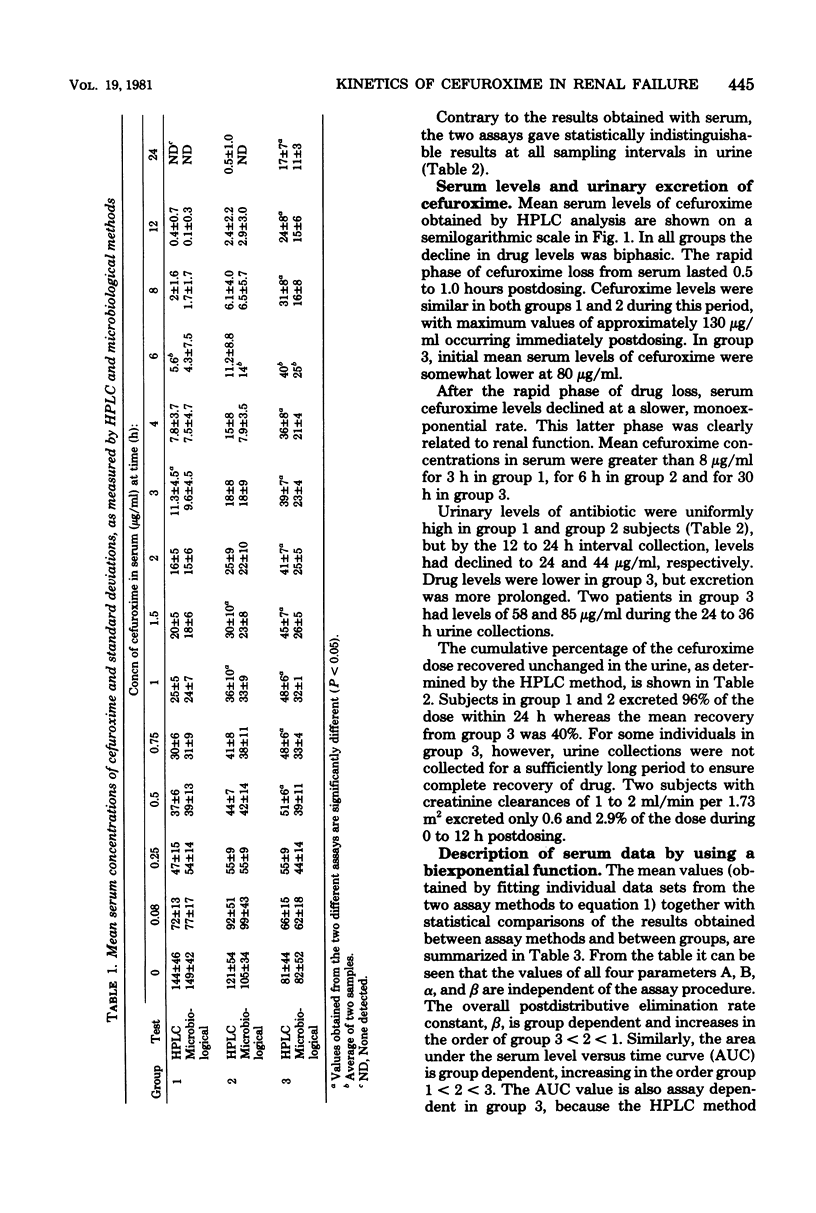
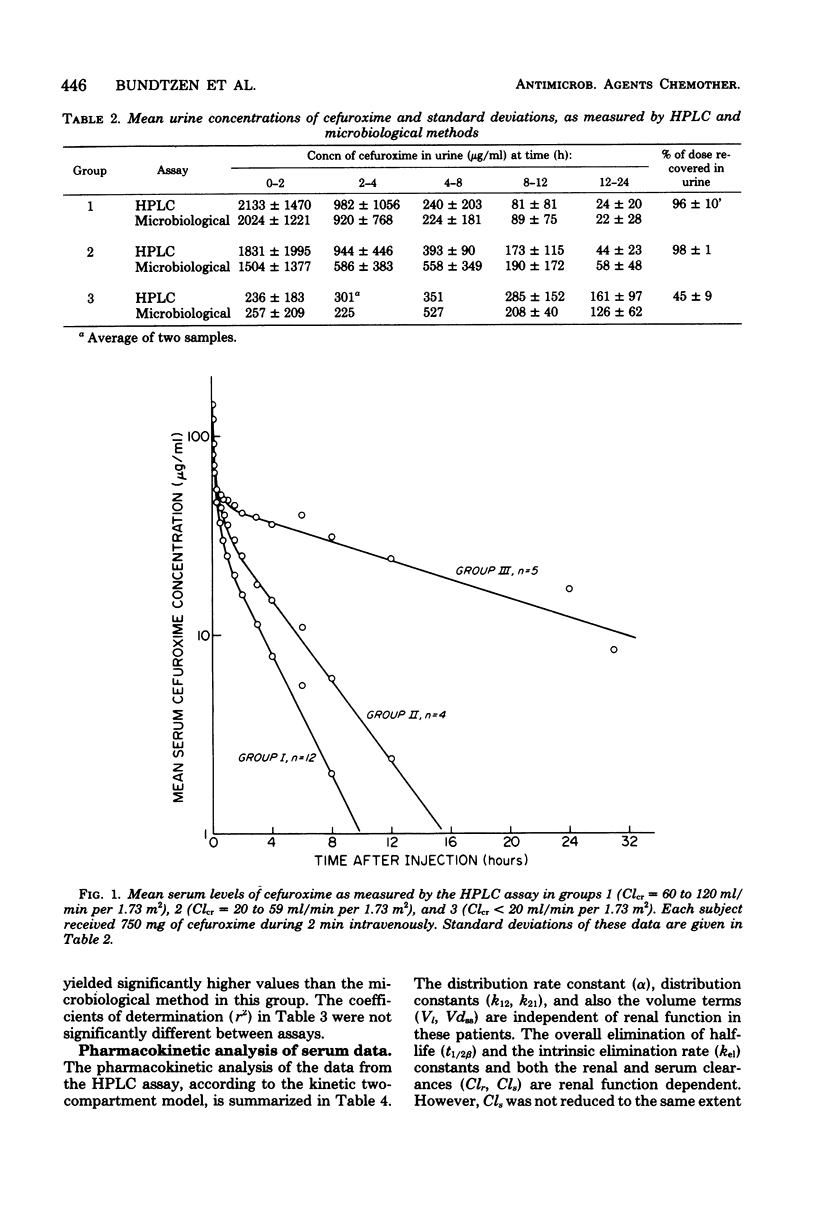
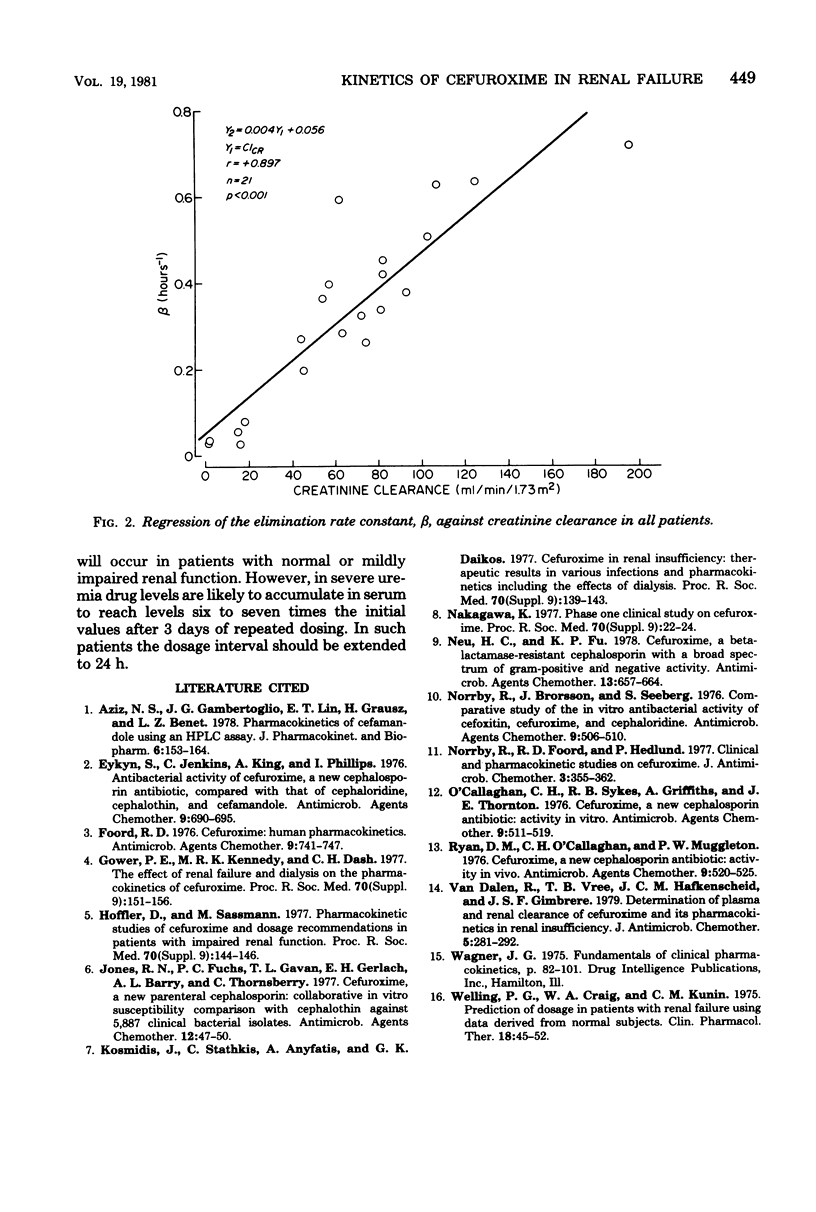
Abstract
The pharmacokinetics of cefuroxime were studied after a single dose of 750 mg was given intravenously to each of 21 male volunteers grouped according to their creatinine clearances; these clearances were 60 to 120, 20 to 59, and less than 20 ml/min per 1.73 m,2 respectively, for groups 1 (12 subjects), 2 (4 subjects), and 3 (5 subjects). Cefuroxime obeyed two-compartment model kinetics in all three groups. Initial serum levels of cefuroxime were approximately 130 microgram/ml in group 1 and 2 and 80 microgram/ml in group 3. the levels then declined rapidly for 0.5 to 1 h after injection. After that time, cefuroxime levels declined more slowly, and the elimination rate became monoexponential. The mean serum half-lives for cefuroxime in groups 2, 2, and 3 were 1.7, 2.4, and 17.6 h, respectively. Mean cefuroxime levels in serum were greater than 8 microgram/ml for 3 h in group 1, for 6 h in group 2, and for 30 h in group 3. Cumulative 24-h urinary excretion accounted for essentially 100% of the dose in group 1 and 2, and for 40% in group 3. Urine levels exceeded the minimal inhibitory concentration for susceptible organisms for more than 12 h in all groups. Cefuroxime distribution characteristics were independent of renal function. In patients with creatinine clearances less than 20 ml/min per 1.73 m2, doses of cefuroxime needs to be reduced. A microbiological disk diffusion assay and a high-pressure liquid chromatography assay for cefuroxime yielded statistically identical results, except for serum levels in uremic patients (group 3).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aziz N. S., Gambertoglio J. G., Lin E. T., Grausz H., Benet L. Z. Pharmacokinetics of cefamandole using a HPLC assay. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Apr;6(2):153–164. doi: 10.1007/BF01117449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eykyn S., Jenkins C., King A., Phillips I. Antibacterial activity of cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic, compared with that of cephaloridine, cephalothin, and cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Apr;9(4):690–695. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.4.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foord R. D. Cefuroxime: human pharmacokinetics.. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):741–747. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower P. E., Kennedy M. R., Dash C. H. The effect of Renal Failure and Dialysis on the Pharmacokinetics of Cefuroxime. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70(Suppl 9):151–157. doi: 10.1177/00359157770700S935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffler D., Sassmann M. Pharmacokinetic studies of cefuroxime and dosage recommendations in patients with impaired renal function. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70(Suppl 9):144–147. doi: 10.1177/00359157770700S933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Fuchs P. C., Gavan T. L., Gerlach E. H., Barry A. L., Thornsberry C. Cefuroxime, a new parenteral cephalosporin: collaborative in vitro susceptibility comparison with cephalothin against 5,887 clinical bacterial isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jul;12(1):47–50. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmidis J., Stathakis C., Anyfantis A., Daikos G. K. Cefuroxime in renal insufficiency: therapeutic results in various infections and pharmacokinetics including the effects of dialysis. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70(Suppl 9):139–143. doi: 10.1177/00359157770700S932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa K. Phase one clinical study on cefuroxime. Proc R Soc Med. 1977;70(Suppl 9):22–24. doi: 10.1177/00359157770700S905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Cefuroxime, a beta-lactamase-resistant cephalosporin with a broad spectrum of gram-positive and -negative activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):657–664. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R., Brorsson J. E., Seeberg S. Comparative study of the in vitro antibacterial activity of cefoxitin, cefuroxine, and cephaloridine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):506–510. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R., Foord R. D., Hedlund P. Clinical and pharmacokinetic studies on cefuroxime. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Jul;3(4):355–362. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. M., O'Callaghan C., Muggleton P. W. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):520–525. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H. Der alloplastische Gelenkflächenersatz am Hüftgelenk. Arch Orthop Unfallchir. 1975;82(2):101–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. G., Craig W. A., Kunin C. M. Prediction of drug dosage in patients with renal failure using data derived from normal subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Jul;18(1):45–52. doi: 10.1002/cpt197518145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dalen R., Vree T. B., Hafkenscheid J. C., Gimbrère J. S. Determination of plasma and renal clearance of cefuroxime and its pharmacokinetics in renal insufficiency. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 May;5(3):281–292. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


