Abstract
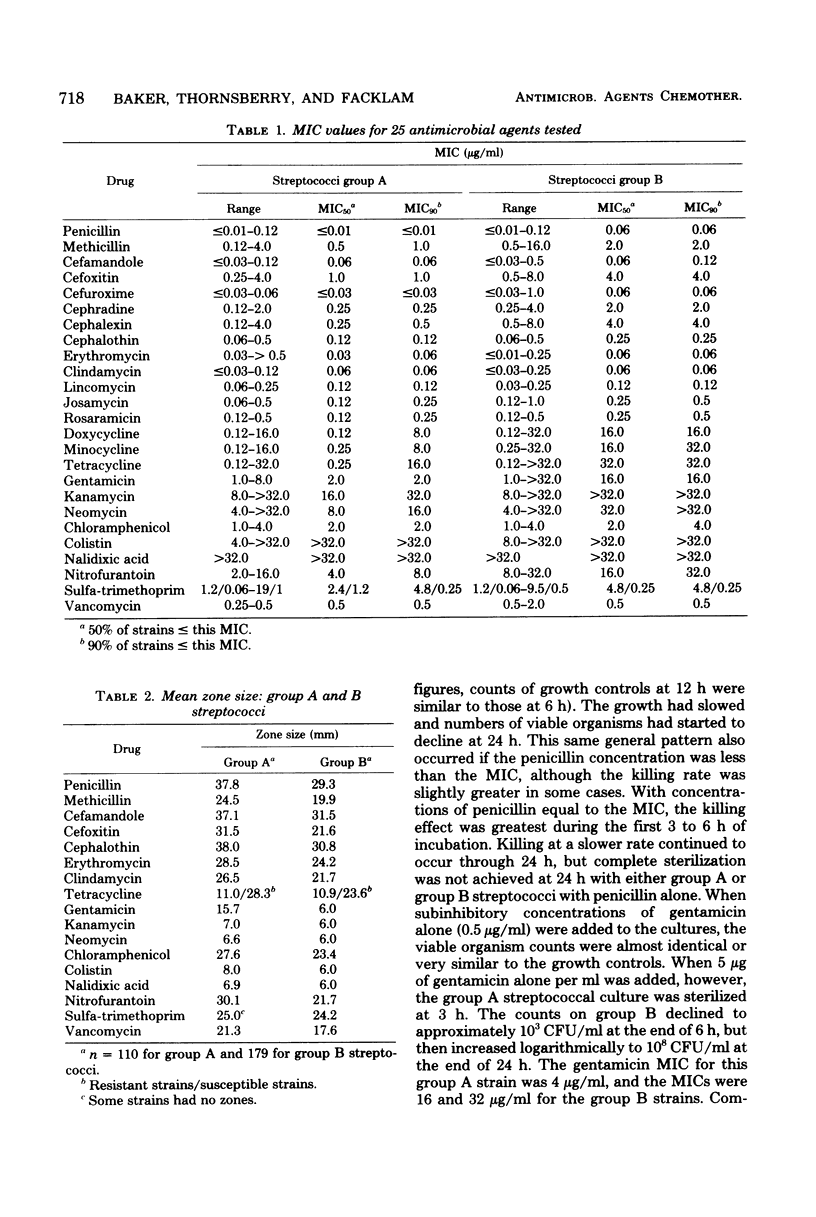
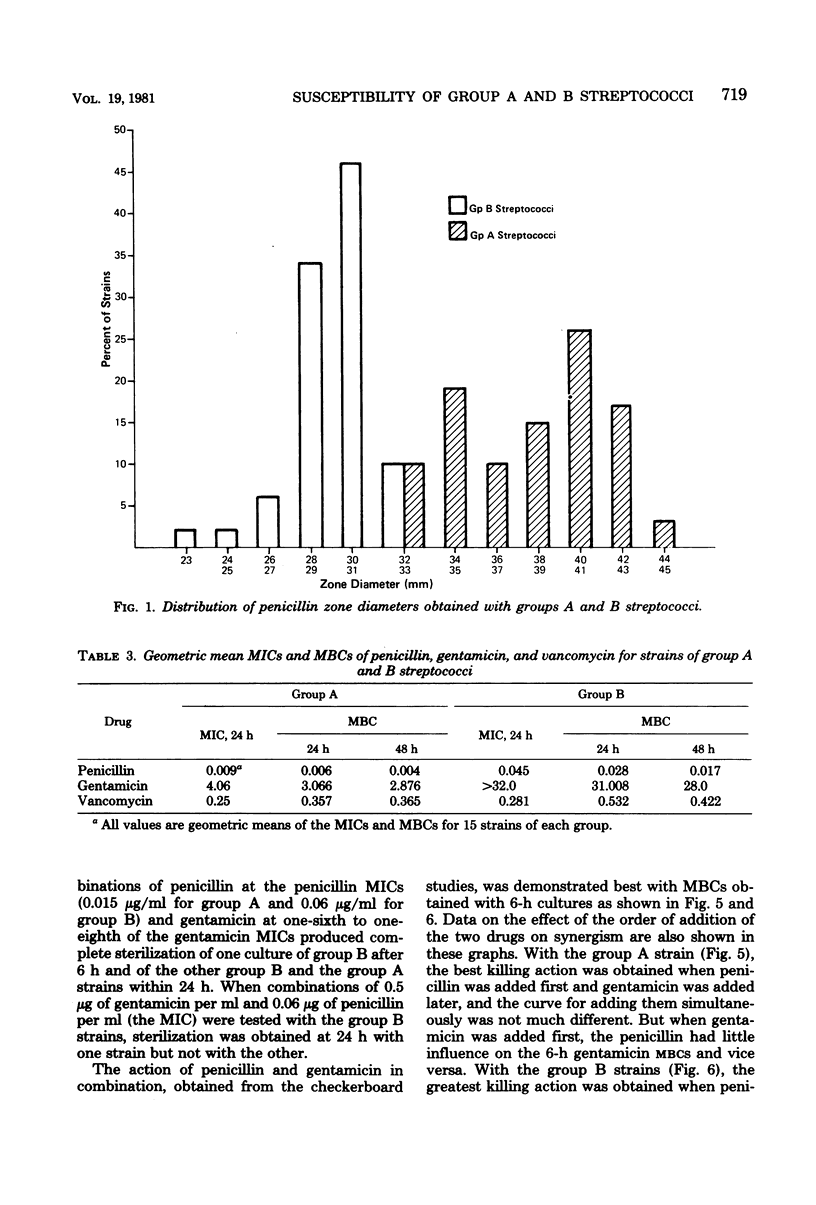
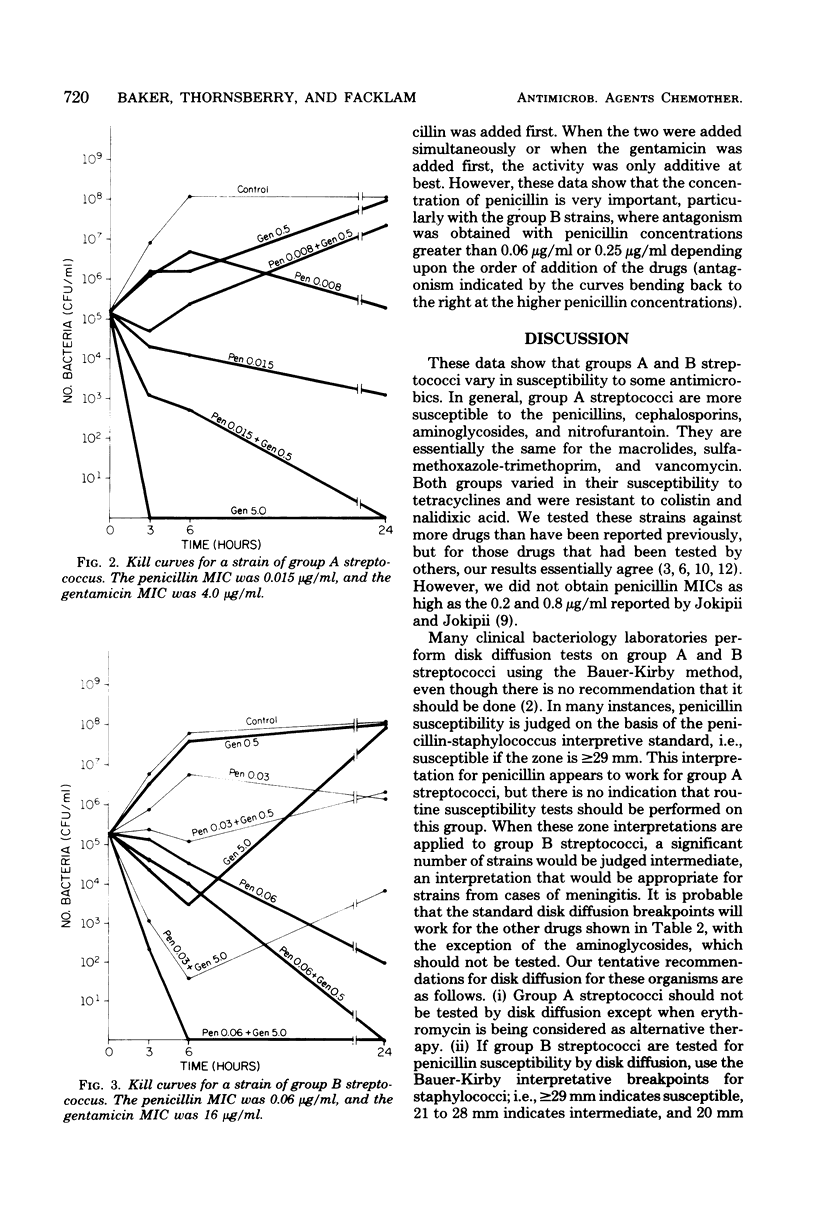
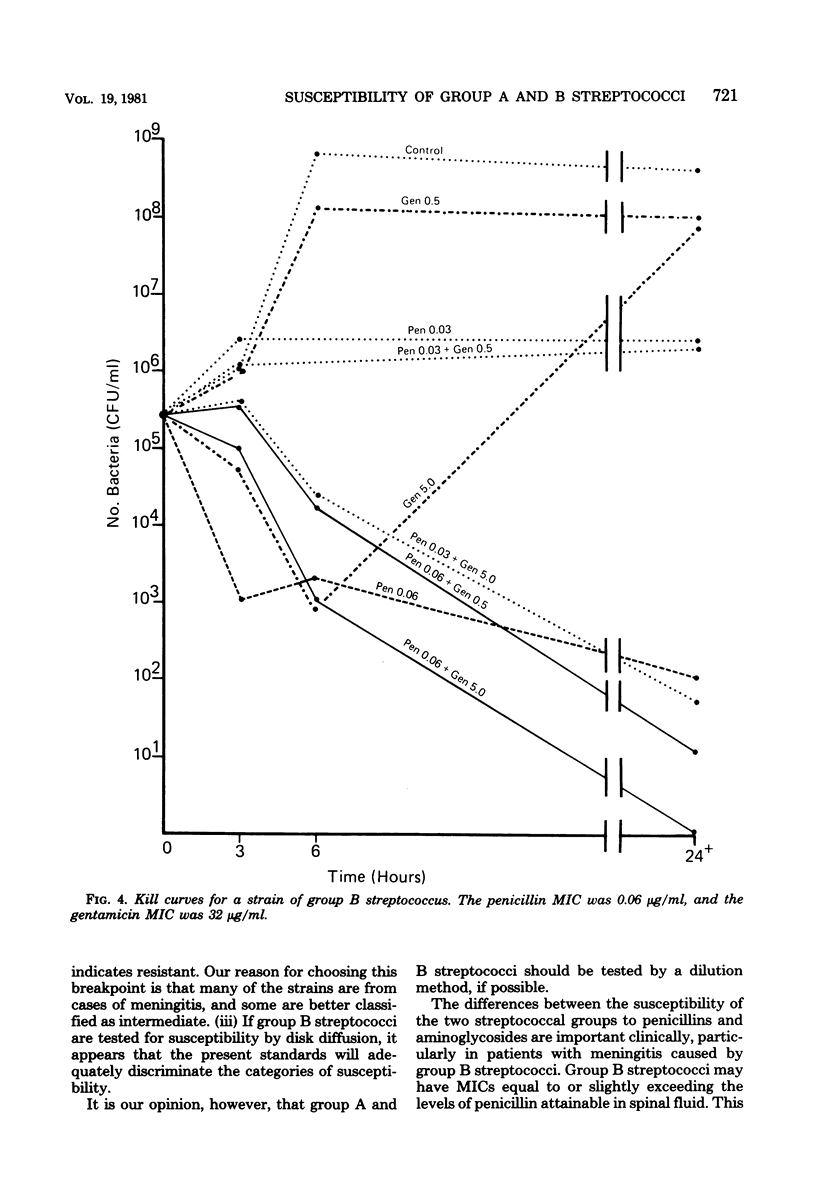
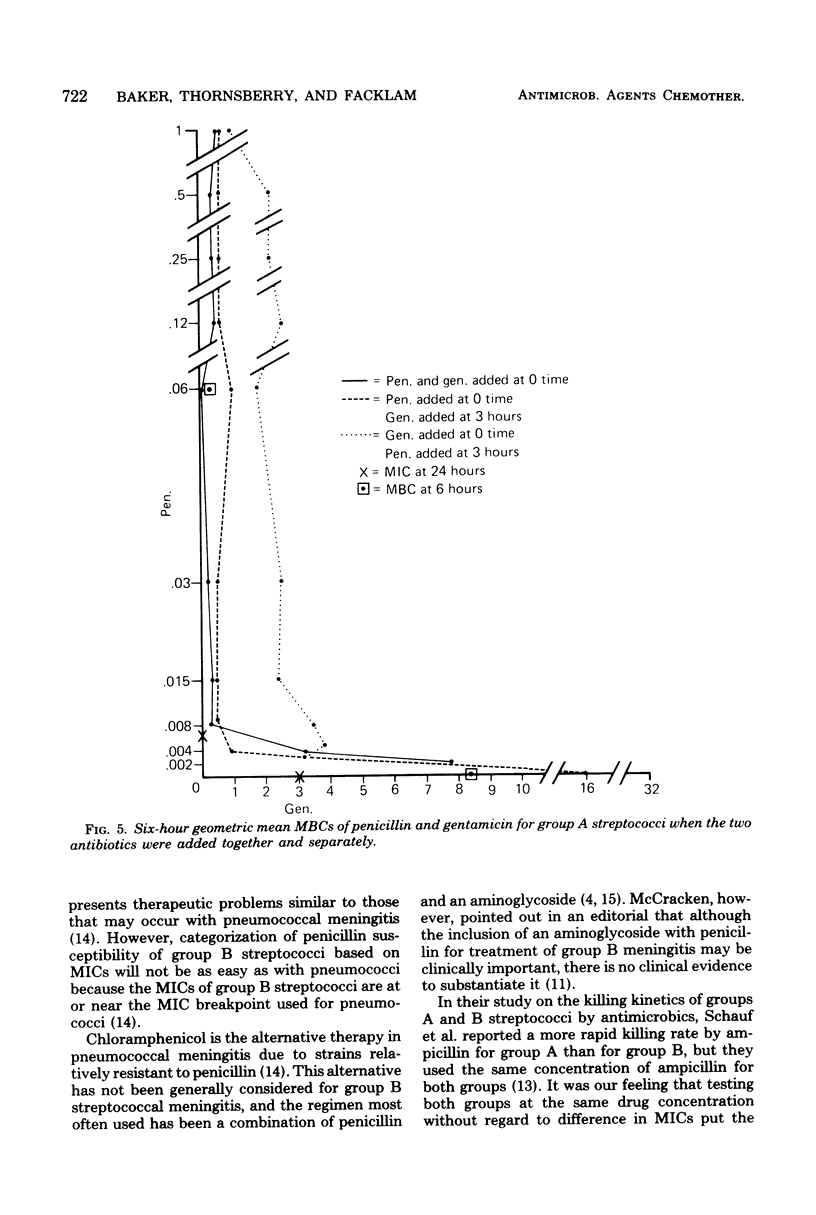
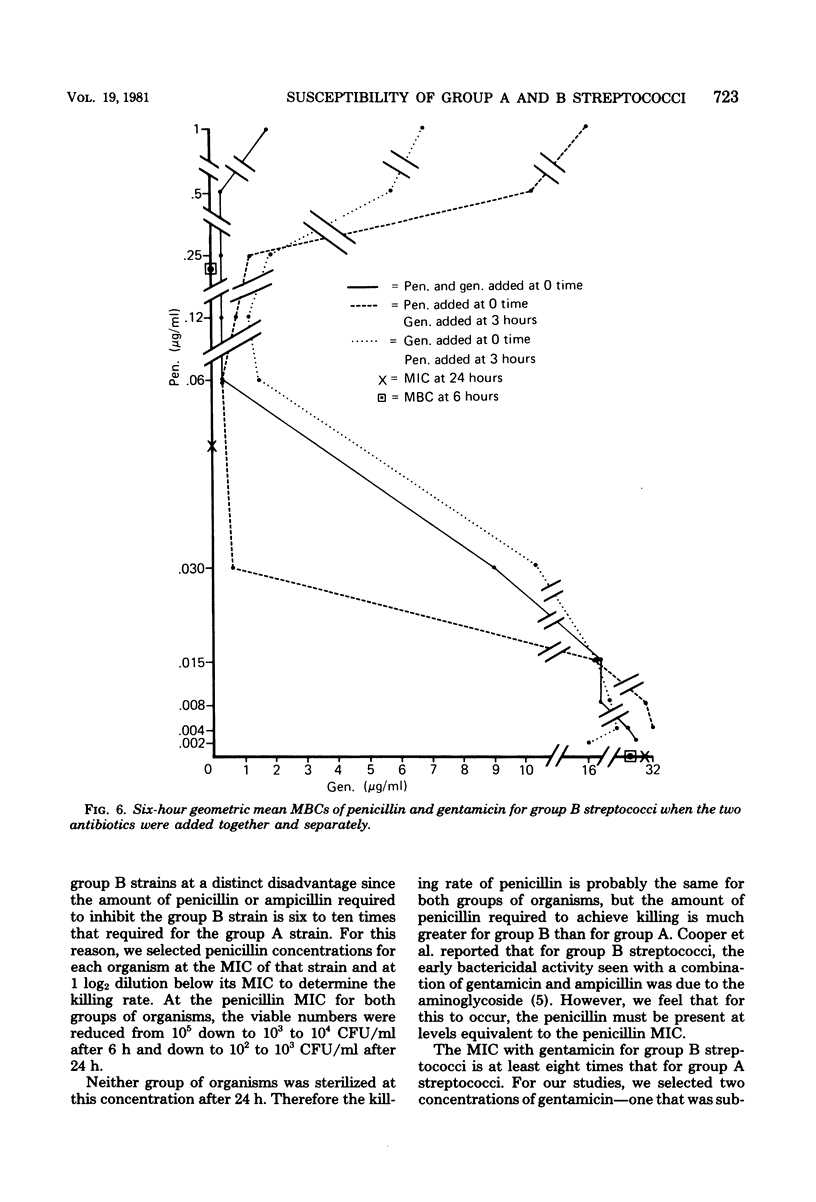
The susceptibility of 110 group A and 179 group B streptococci to 25 antimicrobics was tested by broth microdilution and agar disk diffusion tests. Representative strains were used in killing kinetics, penicillin-gentamicin synergy, and minimal bactericidal concentration tests. Group A streptococci were more susceptible than group B streptococci to 17 of the 25 antimicrobics tested. Group A and B streptococci were killed at the same rate if the amount of penicillin used was equivalent to their respective penicillin minimal inhibitory concentrations. Synergism was demonstrated for both group A and B streptococci when penicillin was used at concentrations equal to each respective minimal inhibitory concentration and subinhibitory concentration of gentamicin. This synergy could be demonstrated best using minimal bactericidal concentrations obtained by culturing 3- and 6-h cultures from the microdilution checkerboard tests rather than from 24-h subcultures. A greater synergistic effect was achieved by adding penicillin first and then adding gentamicin rather than in the reverse order, or simultaneously.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Chow A. W., Anthony B. F., Guze L. B. Serious infections in adults due to group B streptococci. Clinical and serotypic characterization. Am J Med. 1976 Oct;61(4):498–503. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton D. D., Mitchell W. G., Grossman M., Hadley W. K., Cohen M. S. Recurrence of group B streptococcal infection. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):182–185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Keeney R. E., Lyons S. F., Cheatle E. L. Synergistic effects of ampicillin-aminoglycoside combinations on group B streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):484–486. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICKHOFF T. C., KLEIN J. O., DALY A. K., INGALL D., FINLAND M. NEONATAL SEPSIS AND OTHER INFECTIONS DUE TO GROUP B BETA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 10;271:1221–1228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412102712401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutschik E., Jepsen O. B., Mortensen I. Effect of combinations of penicillin and aminoglycosides on Streptococcus faecalis: a comparative study of seven aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):832–836. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokipii A. M., Jokipii L. Presumptive identification and antibiotic susceptibility of group B streptococci. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Aug;29(8):736–739. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.8.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Feldman W. E. Editorial: Neonatal group B streptococcal infection. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):203–204. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M. J., El Batool Hafeez A. Group B streptococci in human disease. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):774–792. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.774-792.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf V., Deveikis A., Riff L., Serota A. Antibiotic-killing kinetics of group B streptococci. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):194–198. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80446-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. H., Santos A. Q., Quintero B. A. Recurrence of group B III streptococcal meningitis. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):187–188. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R. A., Moellering R. C., Jr, Weinberg A. N. Mechanism of resistance to antibiotic synergism in enterococci. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):873–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.873-879.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


