Abstract
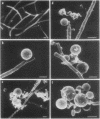
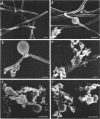
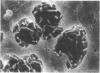
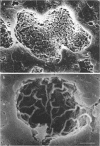
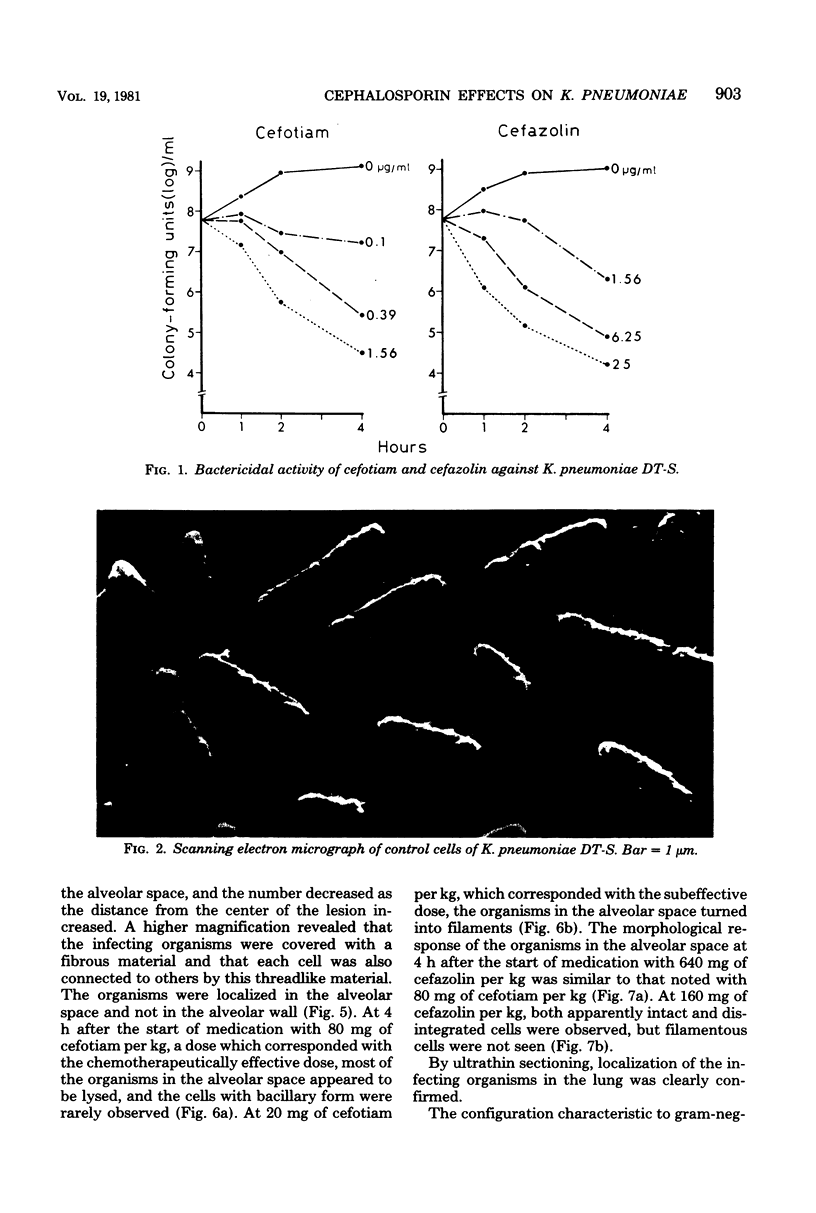
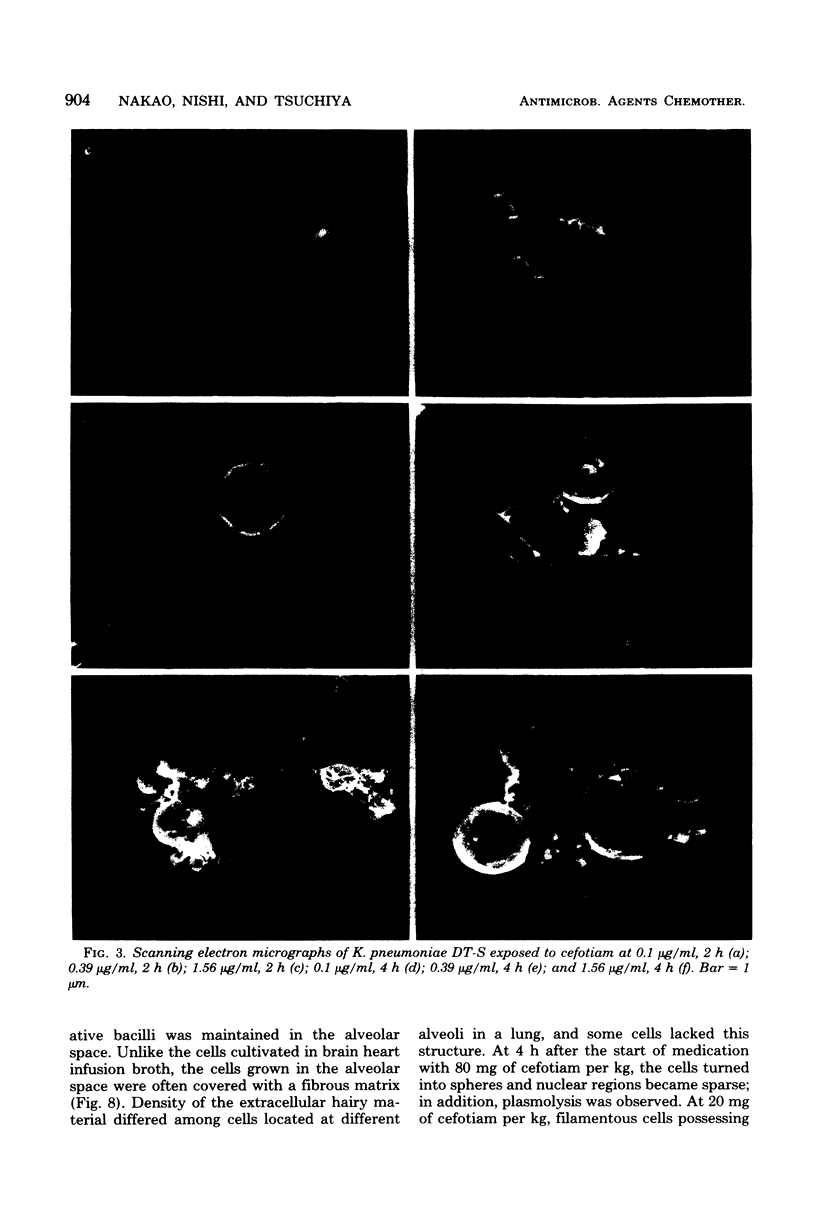
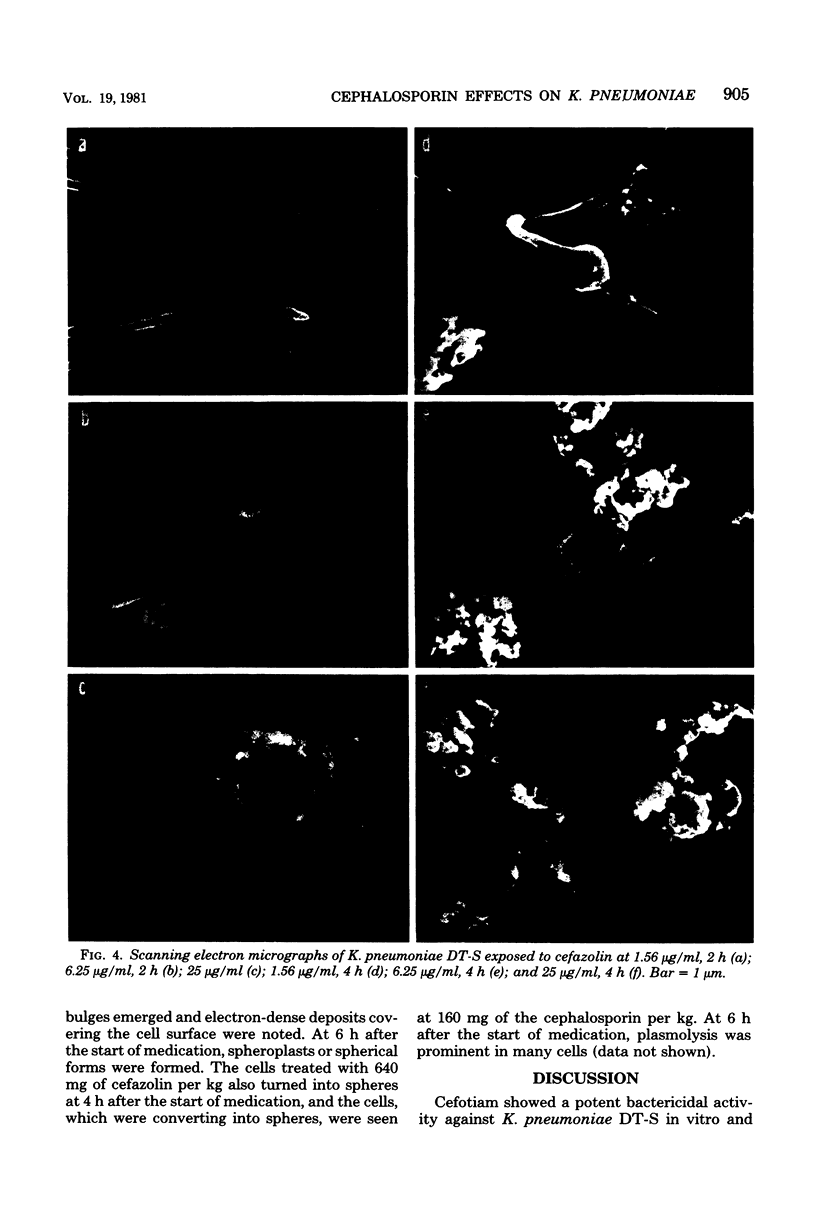
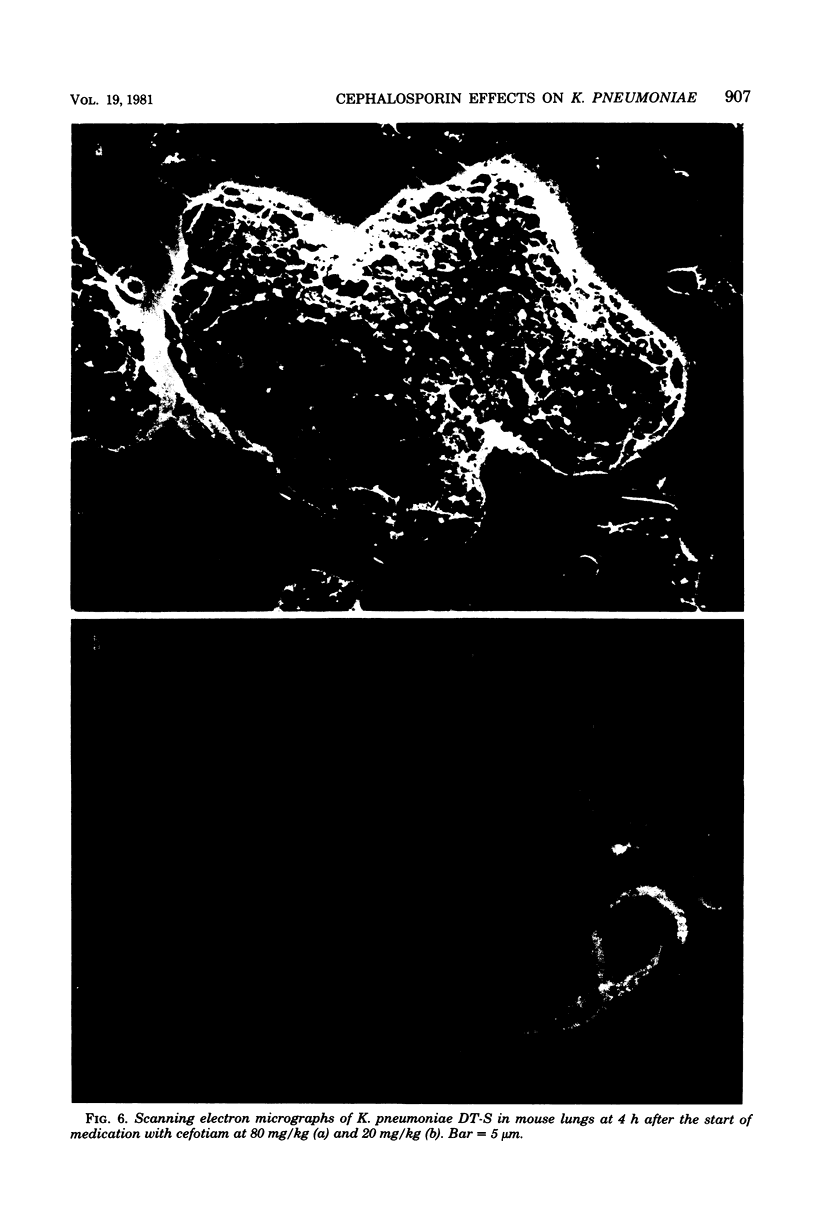
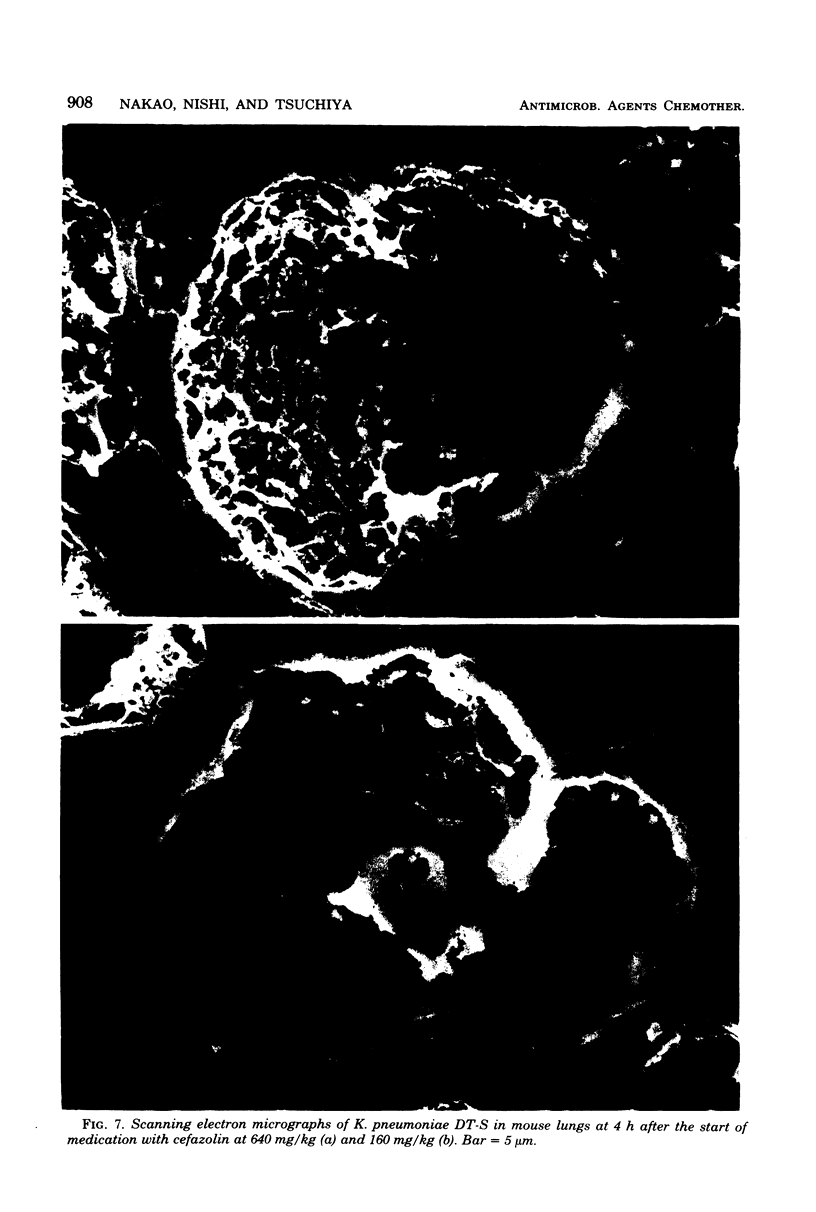
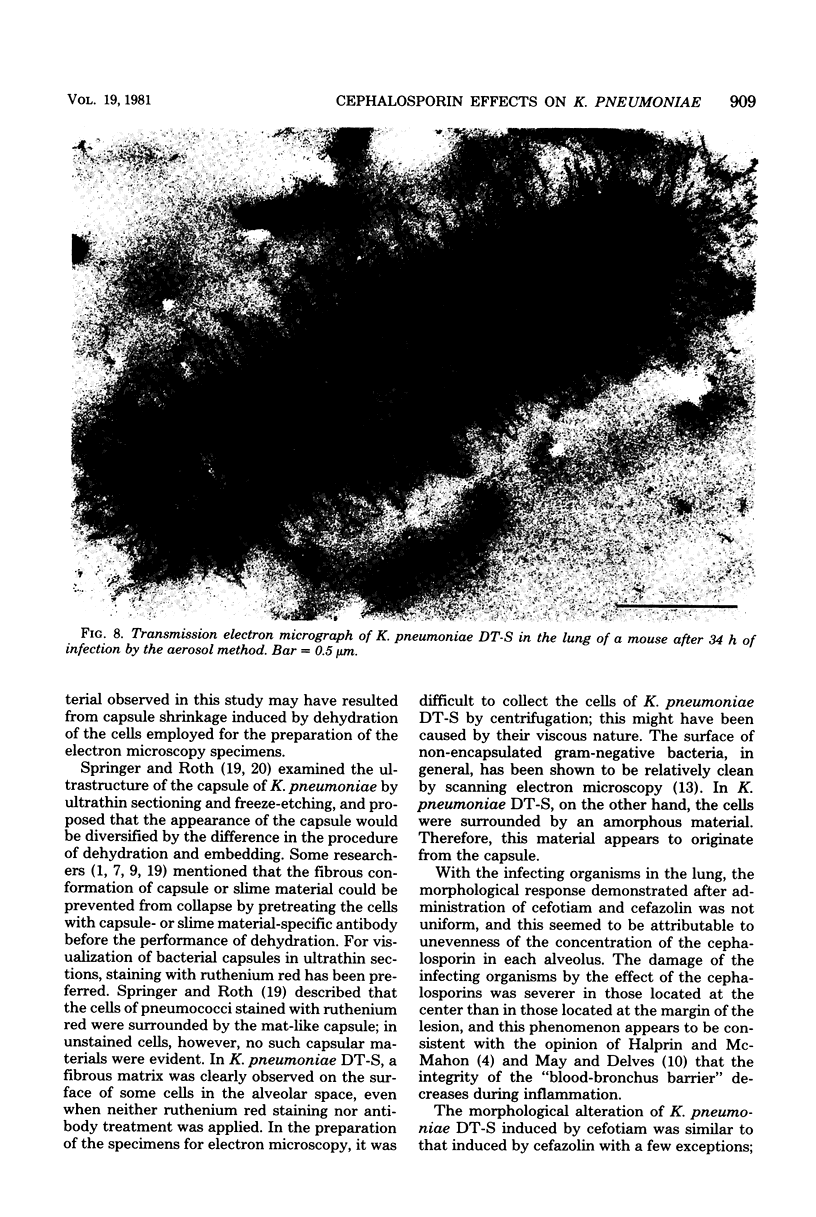
The effect of cefotiam and cefazolin on the ultrastructure of Klebsiella pneumoniae DT-S in vitro and in experimental pneumonia in mice was examined by electron microscopy. The action of both cephalosporins against K. pneumoniae DT-S was bactericidal, and a dose response in the action was definite. At the minimal inhibitory concentration of each cephalosporin, filamentation of the cells was induced and the cytoplasm became sparse during the course of incubation. With elevation of the concentration of the cephalosporins, spheroplasts were formed; they subsequently collapsed. In the lungs of mice, the infecting organisms localized in the alveolar space, and each cell was connected by a threadlike material. A fibrous matrix, located on the cell surface of the infecting organisms, was observed in ultrathin sections. By administration of each cephalosporin to mice, several morphological changes, similar to those noted in vitro, were observed in the infecting organisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendt R. F., Knutsen G. L., Powanda M. C. Nonhuman primate model for the study of respiratory Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):275–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.275-281.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendt R. F., Long G. G., Walker J. S. Treatment of respiratory Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in mice with aerosols of kanamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Nov;8(5):585–590. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.5.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halprin G. M., McMahon S. M. Cephalexin concentrations in sputum during acute respiratory infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):703–707. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno M., Ubukata K., Takahashi H., Sawai M., Saito K. [Morphological studies on antibacterial activities of cefotiam (author's transl)]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1979 May;32(5):583–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAY J. R., DELVES D. M. TREATMENT OF CHRONIC BRONCHITIS WITH AMPICILLIN: SOME PHARMACOLOGICAL OBSERVATION. Lancet. 1965 May 1;1(7392):929–933. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi T., Tsuchiya K. Experimental respiratory tract infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae DT-S in mice: chemotherapy with kanamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):494–505. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Imada A., Yoneda M. SCE-963, a new potent cephalosporin with high affinity for penicillin-binding proteins 1 and 3 of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):20–27. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer E. L., Roth I. L. The ultrastructure of the capsules of Diplococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae stained with ruthenium red. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):21–31. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer E. L., Roth I. L. Ultrastructure of the capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae and slime of Enterobacter aerogenes revealed by freeze etching. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Nov 19;93(4):277–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00427925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kida M., Kondo M., Ono H., Takeuchi M., Nishi T. SCE-963, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):557–568. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]