Abstract
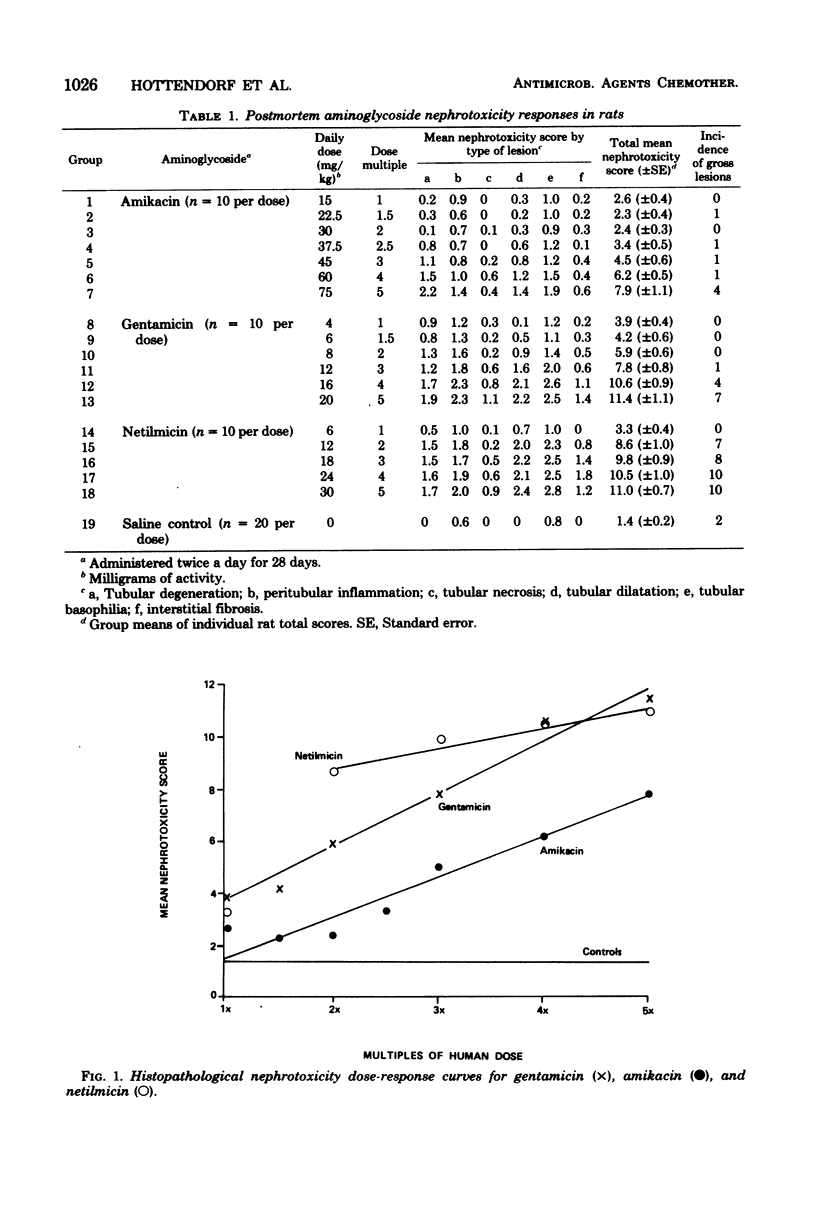
Nephrotoxicity comparisons of aminoglycosides in rats, utilizing large multiples of human doses, have indicated an advantage for netilmicin. However, no nephrotoxicity advantage of netilmicin has been demonstrated at the lower doses used in clinics. Some high-dose studies in rats have also suggested that the slope of the nephrotoxicity dose-response curve of netilmicin was less steep than the slopes of other aminoglycosides. Therefore, the slopes of the nephrotoxicity dose-response curves of gentamicin, amikacin, and netilmicin were compared in 200 rats at low multiples (one to five times) of human clinical doses. Histopathological evaluations of both kidneys from each rat revealed that netilmicin produced equivalent or greater nephrotoxicity as compared with gentamicin and amikacin and that the slope of the nephrotoxicity dose-response curve of netilmicin was approximately one-half as steep as the slopes of amikacin and gentamicin, which were parallel. The distribution of casts excreted in the urine after 2 weeks of dosing and the terminal gross observations corroborated the flatter dose-response slope of netilmicin. Nephrotoxicity advantages predicted by high-dose comparisons with netilmicin in rats are apparently a function of its less steep dose-response slope and therefore may have no relevance to lower doses.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bock B. V., Edelstein P. H., Meyer R. D. Prospective comparative study of efficacy and toxicity of netilmicin and amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):217–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman R. L., Silverblatt F. J., Kaloyanides G. J. Comparison of the nephrotoxicity of netilmicin and gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Oct;12(4):474–478. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.4.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornfield J. Carcinogenic risk assessment. Science. 1977 Nov 18;198(4318):693–699. doi: 10.1126/science.910152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Houghton D. C., Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Reger K., Porter G. A. Reversibility of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats: recovery during continuous drug administration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Jan;160(1):99–103. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hottendorf G. H., Gordon L. L. Comparative low-dose nephrotoxicities of gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):176–181. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton D. C., Hartnett M., Campbell-Boswell M., Porter G., Bennett W. A light and electron microscopic analysis of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):589–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn T., Bosch J., Wiener P., Dikman S. Course of gentamicin nephrotoxicity. Toxicology. 1980;16(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(80)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosek J. C., Mazze R. I., Cousins M. J. Nephrotoxicity of gentamicin. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):48–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Bloch R., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N., Costello R., Maxwell D. R. Comparative nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics in rats. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):541–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Rankin L. I., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N. Recovery from aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity with continued drug administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):284–287. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. H., Chiu P. J., Waitz J. A. Biological activity of SCH 21420, the 1-N-S-alpha-hydroxy-beta-aminopropionyl derivative of gentamicin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Jul;31(7):688–696. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panwalker A. P., Malow J. B., Zimelis V. M., Jackson G. G. Netilmicin: clinical efficacy, tolerance, and toxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. A., Gilbert D. N., Houghton D. C., Porter G. A., Bennett W. M. Comparative nephrotoxicities of high-dose netilmicin and tobramycin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Aug;18(2):346–348. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin L. I., Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Sloan R. S., Dinwiddie C. B., Jr, Isaacs L. L. Comparative nephrotoxicity of SCH 21420 and amikacin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):491–494. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schentag J. J., Gengo F. M., Plaut M. E., Danner D., Mangione A., Jusko W. J. Urinary casts as an indicator of renal tubular damage in patients receiving aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):468–474. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann G. B., Harris S., Henry J. B. An improved technic for examining urinary casts and a review of their significance. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jan;69(1):18–23. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snydman D. R., Tally F. P., Landesman S. H., Barza M., Gorbach S. L. Netilmicin in gram-negative bacterial infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon L., Bowman R. L., Pastoriza-Munoz E., Kaloyanides G. J. Comparative nephrotoxicities of gentamicin, netilmicin and tobramycin in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Sep;210(3):334–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trestman I., Parsons J., Santoro J., Goodhart G., Kaye D. Pharmacology and efficacy of netilmicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):832–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


