Abstract
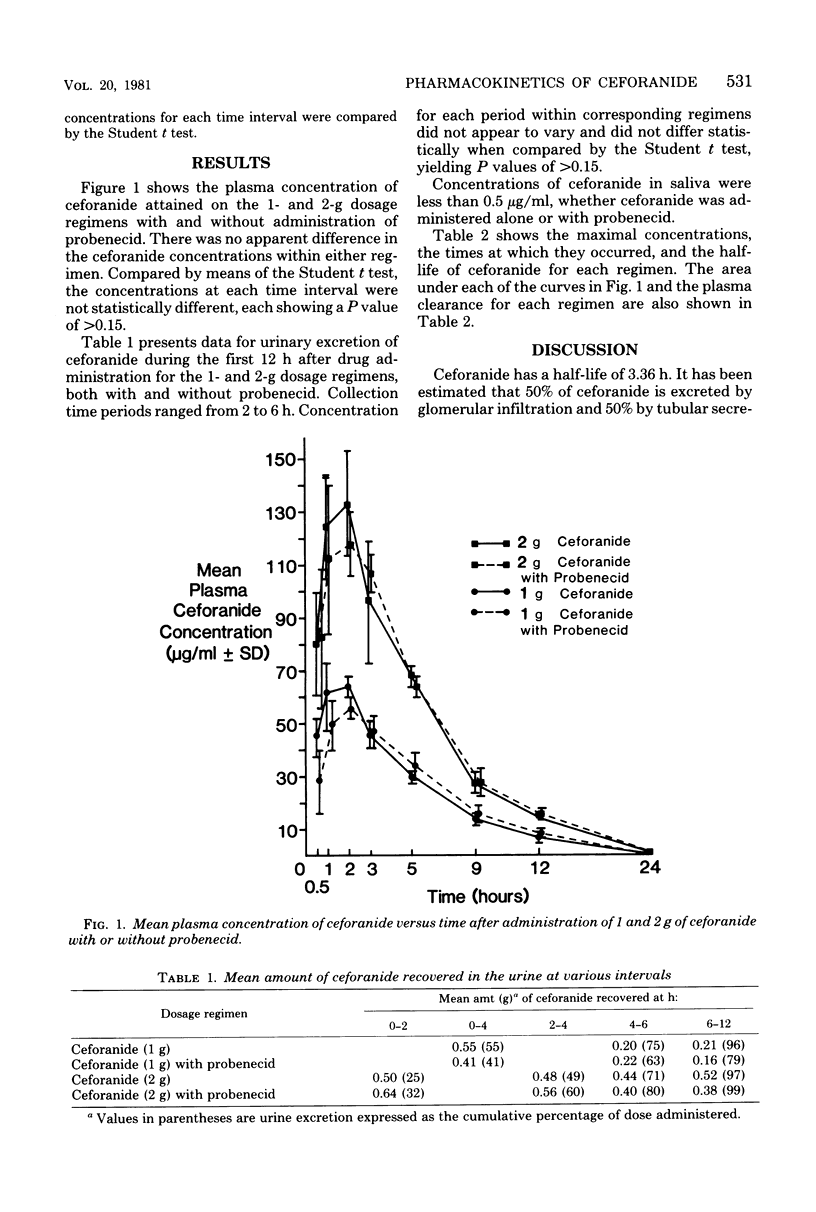
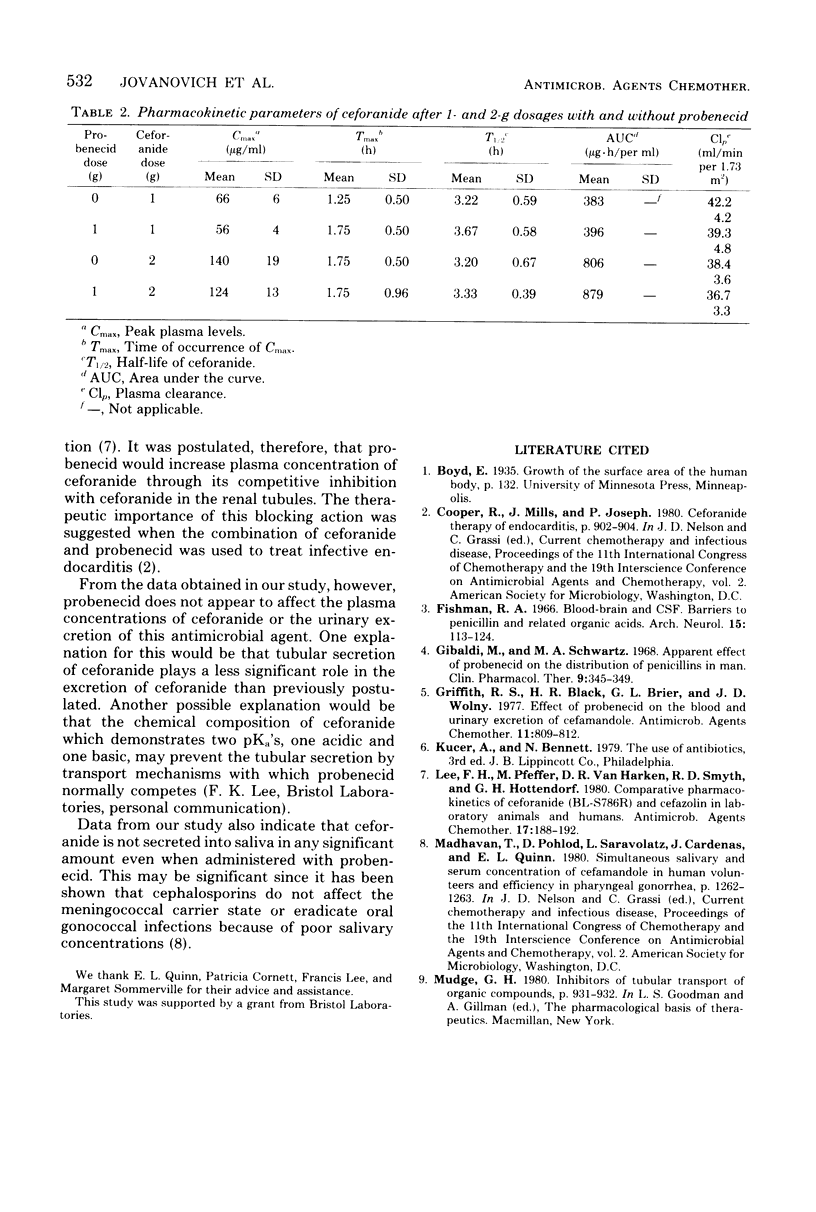
This investigation evaluated the effect of probenecid on ceforanide concentrations in eight healthy volunteers. Each volunteer was given 1 or 2 g of ceforanide either alone or with 1 g of probenecid. Concentrations of ceforanide in plasma, urine, and saliva were then measured. Probenecid did not alter the plasma concentrations of ceforanide, nor did it affect the urinary excretion of this agent. Ceforanide was not secreted into saliva in any detectable amount either when administered alone or with probenecid. It is not clear why probenecid has a negligible effect on ceforanide concentrations in plasma. It may be that tubular secretion plays less of a role in the excretion of ceforanide than expected, or that the physical properties of ceforanide prevent probenecid from affecting its excretion.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fishman R. A. Blood-brain and CSF barriers to penicillin and related organic acids. Arch Neurol. 1966 Aug;15(2):113–124. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470140003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibaldi M., Schwartz M. A. Apparent effect of probenecid on the distribution of penicillins in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1968 May-Jun;9(3):345–349. doi: 10.1002/cpt196893345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. S., Black H. R., Brier G. L., Wolny J. D. Effect of probenecid on the blood levels and urinary excretion of cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):809–812. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. H., Pfeffer M., Van Harken D. R., Smyth R. D., Hottendorf G. H. Comparative pharmacokinetics of ceforanide (BL-S786R) and cefazolin in laboratory animals and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):188–192. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


