Abstract
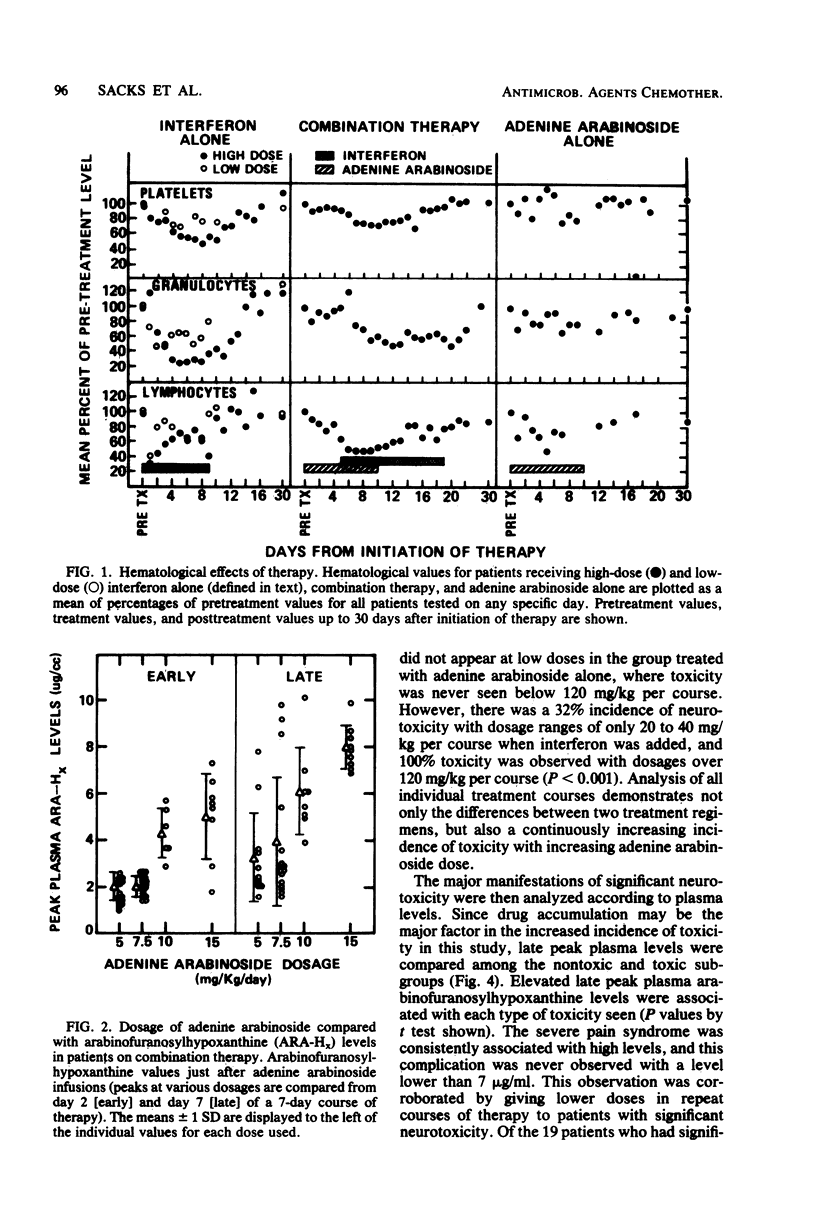
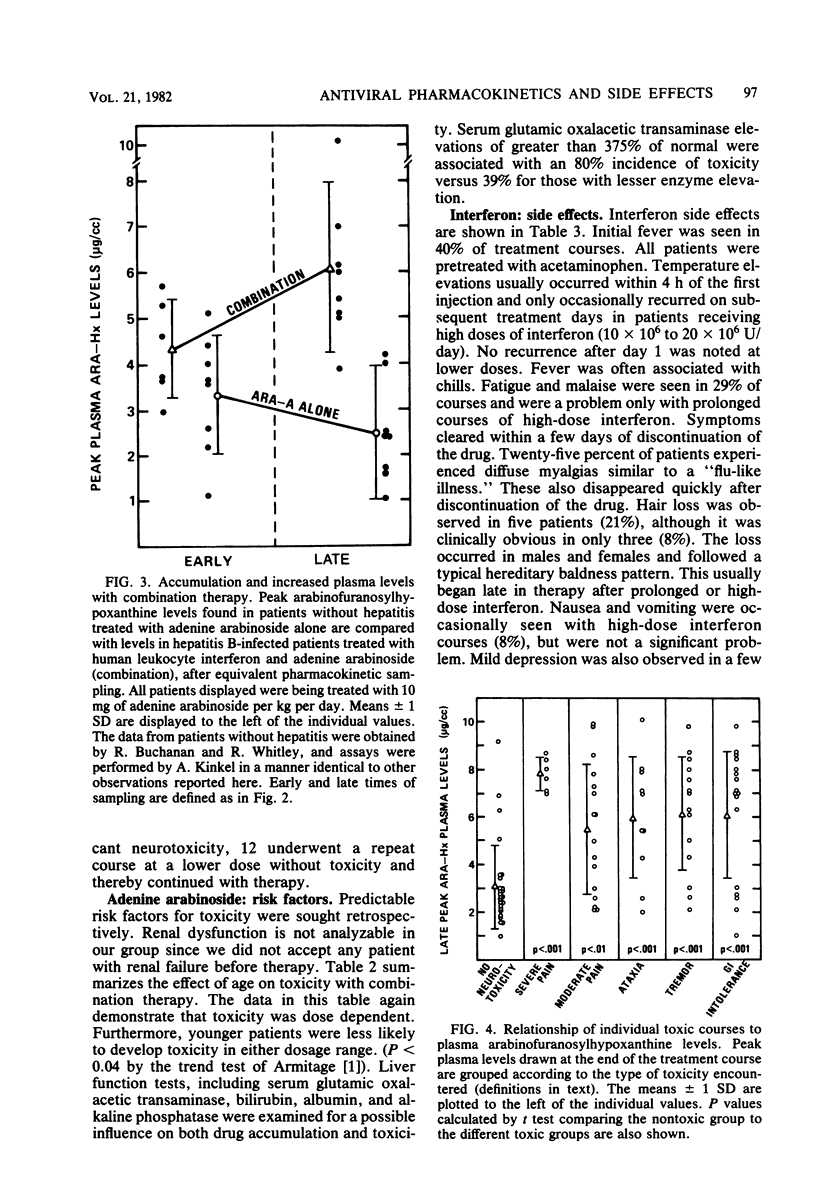
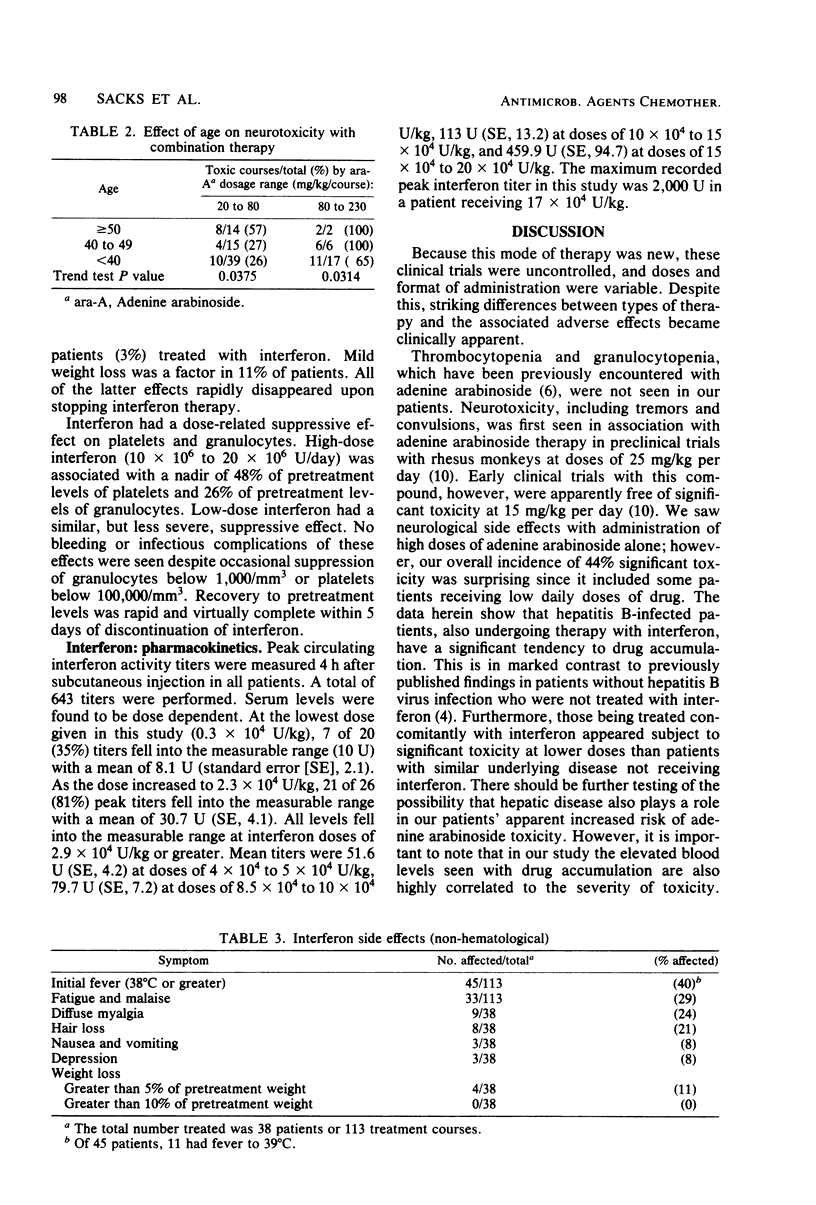
In an uncontrolled trial, 29 patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection were treated with 93 courses of adenine arabinoside at doses ranging from 2.5 to 15 mg/kg per day. Most patients were treated concomitantly with human leukocyte interferon. Significant, but transient, neurotoxicity was seen with adenine arabinoside therapy in 44% of all courses. Manifestations of toxicity were mainly neurological and ranged from pain syndromes to tremors and, rarely, seizures. Suppression of numbers of lymphocytes was also noted. All effects were reversible with time. The extent of toxicity was dependent upon the dosage of adenine arabinoside. Treatment with interferon appeared to potentiate the occurrence of toxicity with adenine arabinoside. Arabinofuranosylhypoxanthine serum levels increased in a dose-dependent manner and tended to accumulate in interferon-treated hepatitis patients during a course of therapy. Elevated blood levels and drug accumulation were associated with toxicity in a significant fashion. Human leukocyte interferon was administered to 38 patients in 113 separate courses. Interferon side effects were rapidly reversible upon cessation of therapy. These included initial fever, myalgias, and hair loss as well as suppression of granulocytes, platelets, and lymphocytes in the blood.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A., De Somers P., Edy V. G., De Clercq E., Heremans H. Human fibroblast interferon for clinical trials: pharmacokinetics and tolerability in experimental animals and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jul;16(1):56–63. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan R. A., Kinkel A. W., Alford C. A., Jr, Whitley R. J. Plasma levels and urinary excretion of vidarabine after repeated dosing. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 May;27(5):690–696. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb J. A., Bodey G. P., Sr Letter: Possible bone-marrow depression by Ara-A therapy for disseminated herpes zoster. N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 18;290(16):914–914. doi: 10.1056/nejm197404182901625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Pollard R. B., Lutwick L. I., Gregory P. B., Robinson W. S., Merigan T. C. Effect of human leukocyte interferon on hepatitis B virus infection in patients with chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 2;295(10):517–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609022951001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingimarsson S., Cantell K., Strander H. Side effects of long-term treatment with human leukocyte interferon. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):560–563. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koplan J. P., Monsur K. A., Foster S. O., Huq F., Rahaman M. M., Huq S., Buchanan R. A., Ward N. A. Treatment of variola major with adenine arabinoside. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jan;131(1):34–39. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauter C. B., Bailey E. J., Lerner A. M. Microbiologic assays and neurological toxicity during use of adenine arabinoside in humans. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):75–79. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Gregory D. F., Petralli J. K. Physical properties of human interferon prepared in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1966 Aug;29(4):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C. Pharmacokinetics and side effects of interferon in man. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos E., Timmons R. F., Schimpff S. C. Inappropriate antidiuretic hormone following adenine arabinoside administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):142–144. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. H., Julia A., Balakrishnan C. Toxicity of adenine arabinoside in humans. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A192–A198. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks S. L., Smith J. L., Pollard R. B., Sawhney V., Mahol A. S., Gregory P., Merigan T. C., Robinson W. S. Toxicity of vidarabine. JAMA. 1979 Jan 5;241(1):28–29. doi: 10.1001/jama.1979.03290270020010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scullard G. H., Pollard R. B., Smith J. L., Sacks S. L., Gregory P. B., Robinson W. S., Merigan T. C. Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. I. Changes in viral markers with interferon combined with adenine arabinoside. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):772–783. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Soong S. J., Dolin R., Galasso G. J., Ch'ien L. T., Alford C. A. Adenine arabinoside therapy of biopsy-proved herpes simplex encephalitis. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases collaborative antiviral study. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 11;297(6):289–294. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708112970601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


