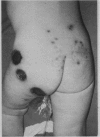
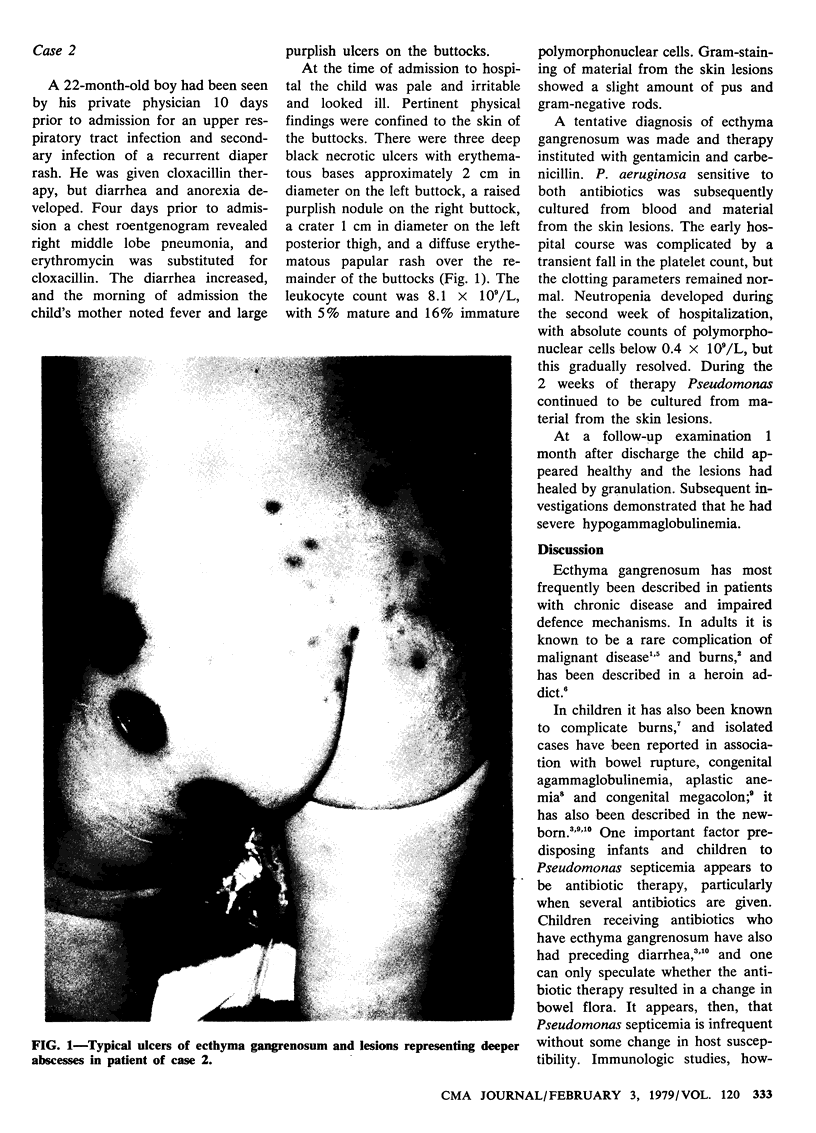
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAZAN A., CHAVEZ P. M., GURMENDI G., MARKLEY K. Fatal Pseudomonas septicemias in burned patients. Ann Surg. 1957 Feb;145(2):175–181. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195702000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D. A. Ecthyma gangrenosum: full thickness nasal slough. Arch Otolaryngol. 1973 Sep;98(3):210–211. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1973.00780020218017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorff G. J., Geimer N. F., Rosenthal D. R., Rytel M. W. Pseudomonas septicemia. Illustrated evolution of its skin lesion. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Oct;128(4):591–595. doi: 10.1001/archinte.128.4.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORKNER C. E., Jr, FREI E., 3rd, EDGCOMB J. H., UTZ J. P. Pseudomonas septicemia; observations on twenty-three cases. Am J Med. 1958 Dec;25(6):877–889. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEPPERT L. J., BAKER H. J., COPPLE B. I., PULASKI E. J. Pseudomonas infections in infants and children. J Pediatr. 1952 Nov;41(5):555–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(52)80102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEFFNER R. W., SMITH G. F. Ecthyma gangrenosum in Pseudomonas septicemia. AMA J Dis Child. 1960 Apr;99:524–528. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1960.02070030526015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebl E. C., Marvin J. A., Curreri P. W., Baxter C. R. Survival with ecthyma gangrenosum, a previously fatal complication of burns. J Trauma. 1974 May;14(5):370–377. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197405000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell I. N., Feiner H. D., Price N. M., Simberkoff M. Pseudomonas cepacia endocarditis and ecthyma gangrenosum. Arch Dermatol. 1977 Feb;113(2):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. K., Larter W. E., Sieber O. F., Jr, John T. J. Peripheral nodular lesions in Pseudomonas sepsis. The importance of incision and drainage. J Pediatr. 1976 Jun;88(6):977–979. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPLITZ C. PATHOGENESIS OF PSEUDOMONAS VASCULITIS AND SEPTIC LEGIONS. Arch Pathol. 1965 Sep;80:297–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]