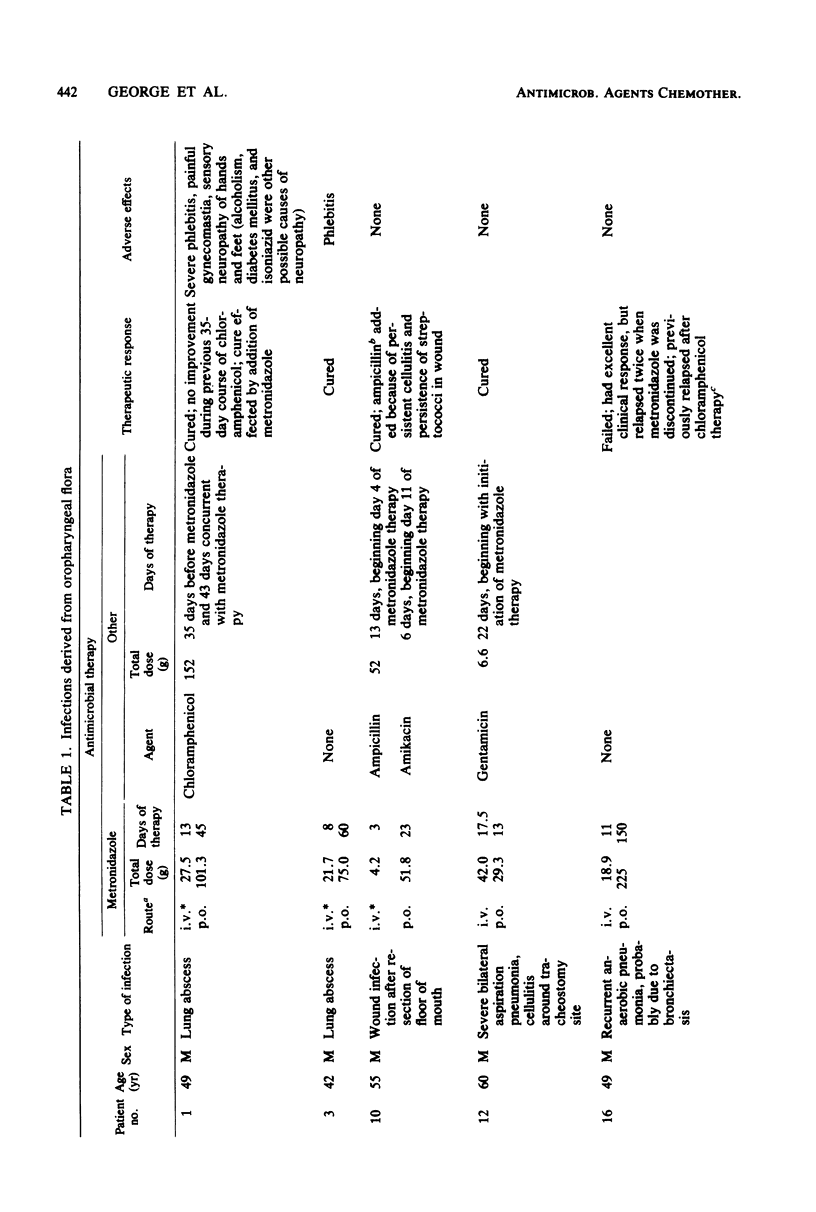
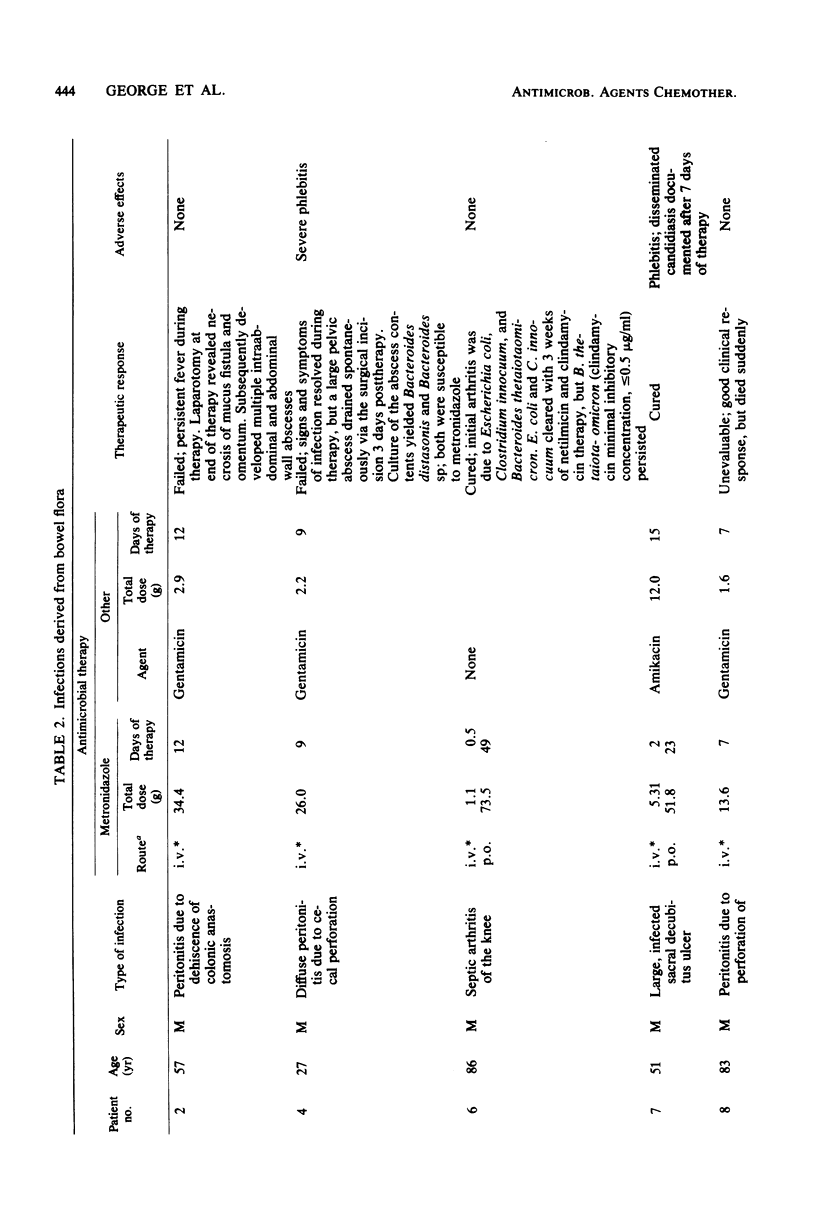
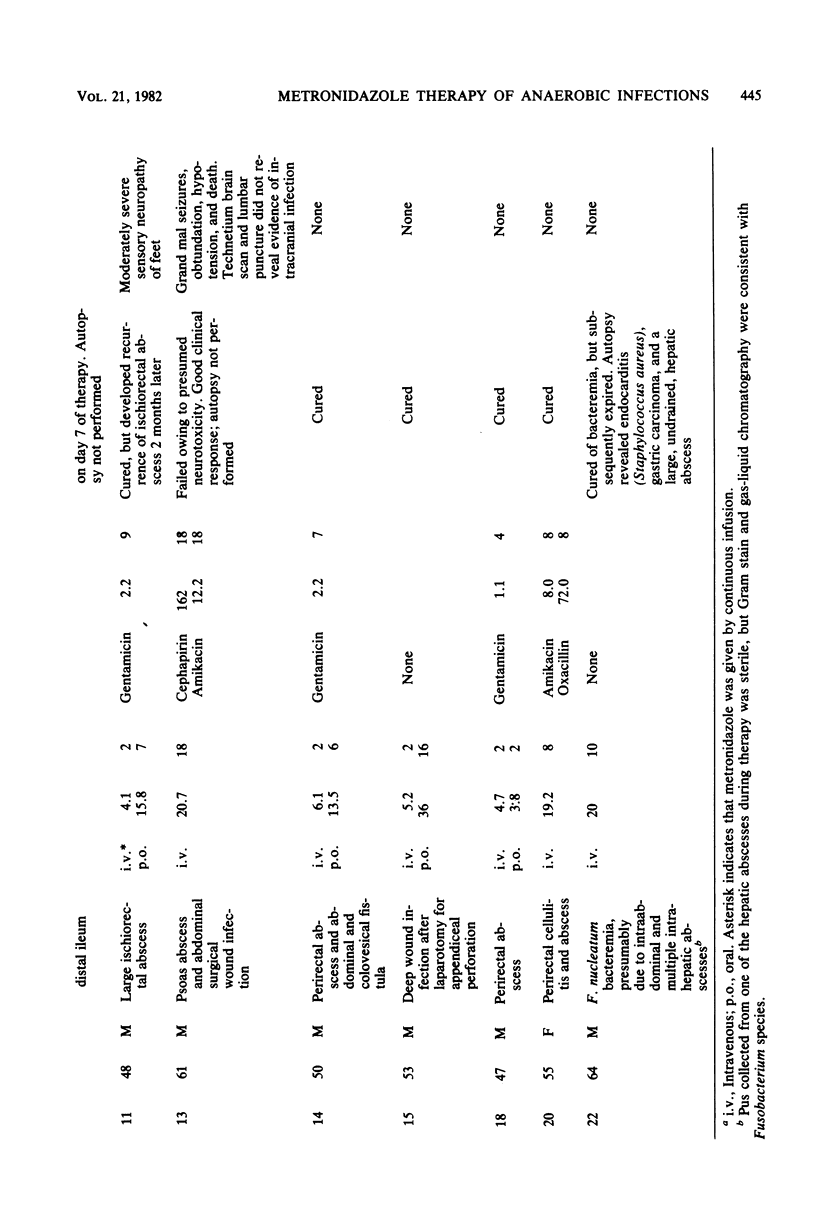
Abstract
Intravenous metronidazole was administered, either by continuous or intermittent infusion, to 20 patients with infections involving anaerobic bacteria; 14 of the 20 patients were changed to oral administration of metronidazole for completion of therapy. Six of eight patients with infections derived from oropharyngeal bacterial flora were cured; the addition of ampicillin was required in one patient, however, because of an incomplete response to metronidazole. Eight of eleven evaluable patients with infections derived from bowel flora were also cured by metronidazole or metronidazole plus an aminoglycoside. Of 93 anaerobic bacteria isolated before therapy, 89 were susceptible to 16 micrograms or less of metronidazole per ml. Mean plasma levels of metronidazole were 27.6 +/- 11.4 micrograms/ml in patients receiving continuous infusions of drug and 19.9 +/- 10.7 micrograms/ml (trough) in patients receiving intermittent infusions. Two patients developed peripheral neuropathy during therapy. Metronidazole is an effective agent for the treatment of anaerobic infections. Because metronidazole is not active against facultative and aerobic bacteria, the addition of a second antimicrobial agent may be required for the treatment of mixed anaerobic-aerobic infections.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brogden R. N., Heel R. C., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Metronidazole in anaerobic infections: a review of its activity, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1978 Nov;16(5):387–417. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197816050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frytak S., Moertel C. H., Childs D. S. Neurologic toxicity associated with high-dose metronidazole therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Mar;88(3):361–362. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-3-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rissing J. P., Newman C., Moore W. L., Jr Artifactual depression of serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase by metronidazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):636–638. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. V., Hanna B. J., Lewis A. C. Metronidazole in the treatment of anaerobic infections. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Aug;120(2):337–343. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.2.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp D. J., Corringham R. E., Nye E. B., Sagor G. R., Noone P. Successful treatment of Bacteroides bacteraemia with metronidazole, after failure with clindamycin and lincomycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 May;3(3):233–237. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Skidmore A. G., Forward A. D., Clarke A. M., Sutherland E. Prospective, randomized, double-blind comparison of metronidazole and tobramycin with clindamycin and tobramycin in the treatment of intra-abdominal sepsis. Ann Surg. 1980 Aug;192(2):213–220. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198008000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to 23 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):736–752. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Metronidazole versus anaerobes. In vitro data and initial clinical observations. Calif Med. 1972 Dec;117(6):22–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler L. A., De Meo M., Halula M., George L., Heseltine P. Use of high-pressure liquid chromatography to determine plasma levels of metronidazole and metabolites after intravenous administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):205–209. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J. P., Hale J. H. Bactericidal activity of metronidazole against Bacteroides fragilis. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jun;26(6):393–395. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.6.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wust J. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to metronidazole, ornidazole, and tinidazole and routine susceptibility testing by standardized methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):631–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


