Abstract
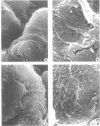
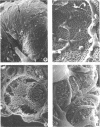
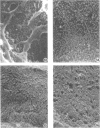
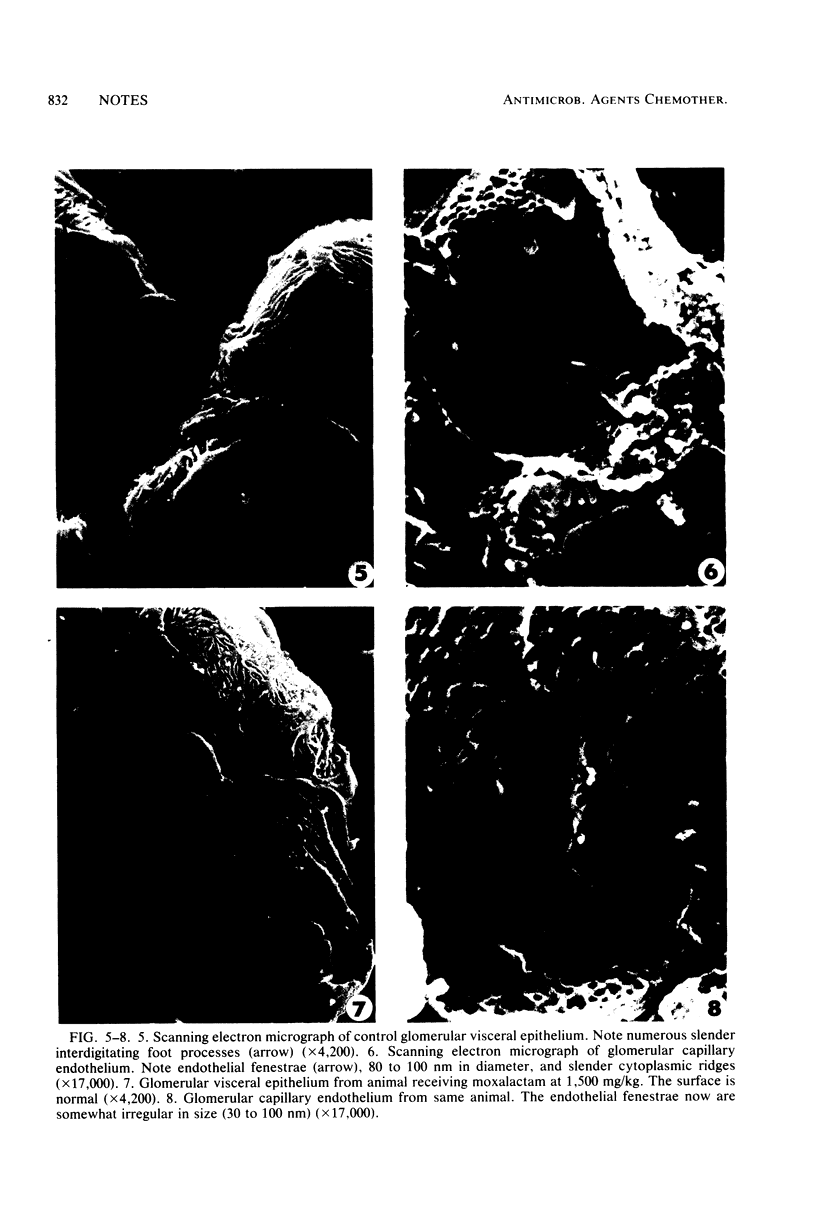
To determine and compare the effects of moxalactam and cefotaxime on kidneys, we gave these drugs in doses of 750 and 1,500 mg/kg to rabbits for 7 days. Cephaloridine was included as a positive control. Neither moxalactam nor cefotaxime at either dose caused lysosomal enzymuria, changes visible by light microscopy or increased plasma creatine. Both drugs caused minor alterations in glomerular ultrastructure at the higher dose. Cephaloridine, on the other hand, caused widespread renal functional and morphological damage. We conclude that in rabbits, both moxalactam and cefotaxime are remarkably nonnephrotoxic.
Full text
PDF
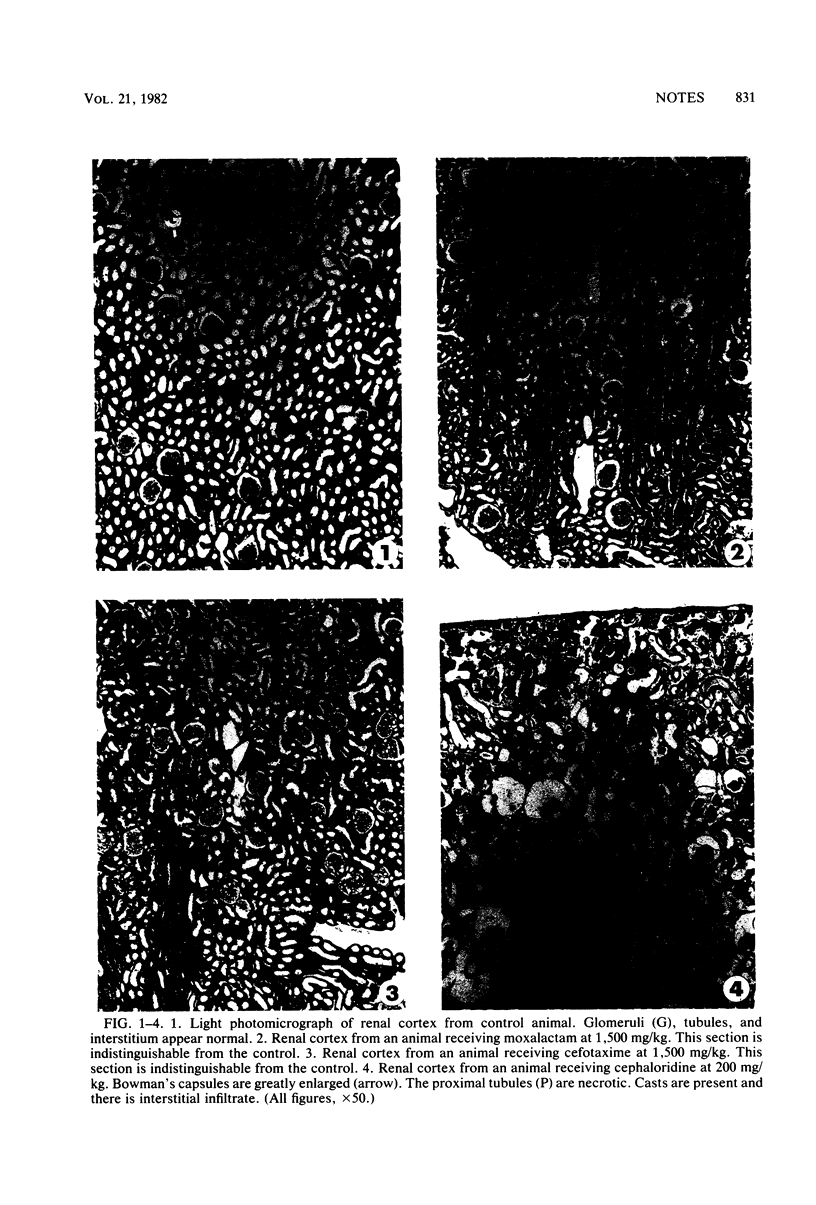

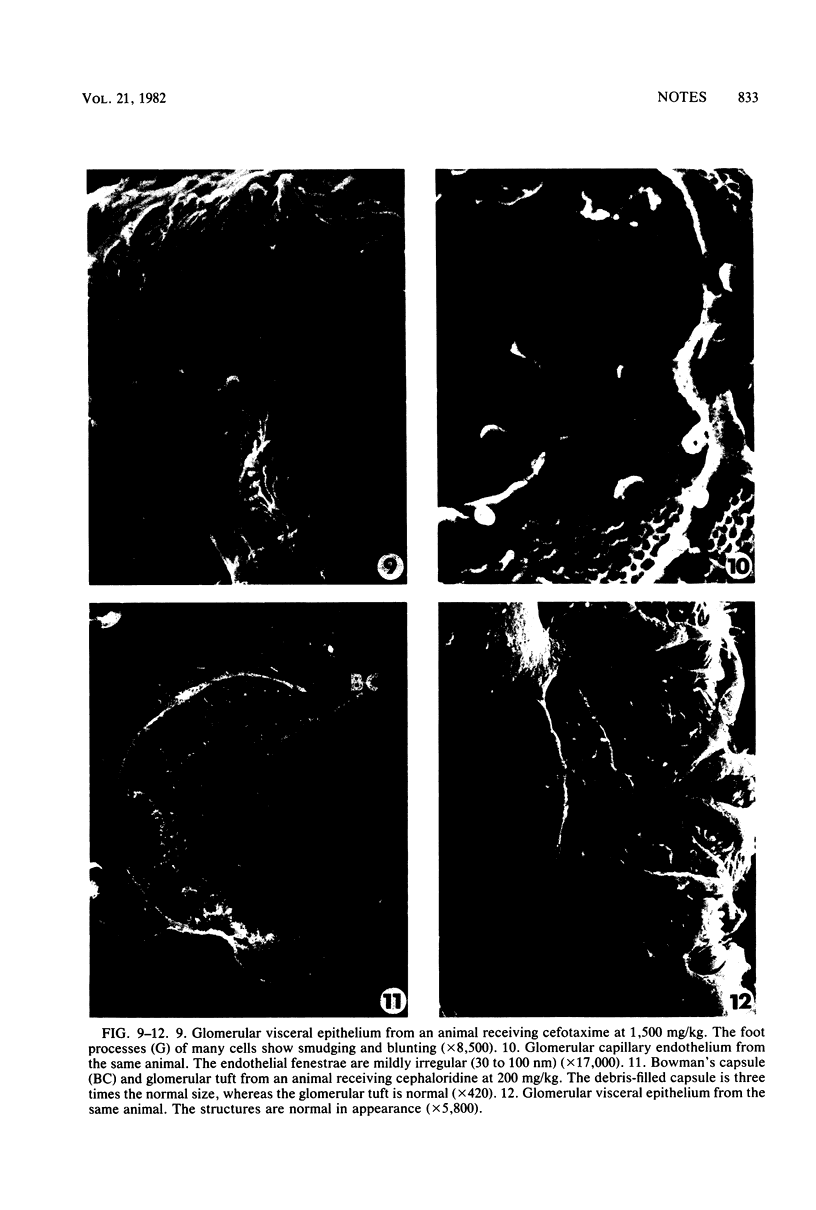


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avasthi P. S., Evan A. P., Huser J. W., Luft F. C. Effect of gentamicin on glomerular ultrastructure. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Sep;98(3):444–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerr B. I., Glomot R., Kief H., Kramer M., Sakaguchi T. Toxicology of cefotaxime in comparison to other cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6 (Suppl A):79–82. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.suppl_a.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P., Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Kung K. Comparative activity and beta-lactamase stability of cefoperazone, a piperazine cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):150–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel V., Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Patel B., Zeman W., Kleit S. A. Enzymuria in gentamicin-induced kidney damage. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):364–369. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tune B. M., Fravert D. Mechanisms of cephalosporin nephrotoxicity: a comparison of cephaloridine and cephaloglycin. Kidney Int. 1980 Nov;18(5):591–600. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]