Abstract
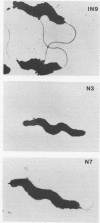
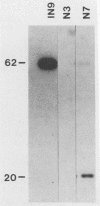
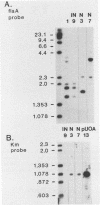
Campylobacter jejuni, an important cause of human gastrointestinal infection, is a major food-borne pathogen in the United States and worldwide. Since poultry becomes colonized and/or contaminated during the early stages of production and is a major food-borne source for this organism, we studied the role of C. jejuni flagella on the ability of the bacterium to colonize the chicken gastrointestinal tract. Three-day-old chicks were orally challenged with a motile wild-type strain of C. jejuni IN9 or with flagellar mutants created from IN9 by disrupting the flagellin genes with a kanamycin resistance cassette by using shuttle mutagenesis (A. Labigne-Roussel, P. Courcoux, and L. Tompkins, J. Bacteriol. 170:1704-1708, 1988). One mutant, IN9-N3, lacked flagella and was nonmotile. The other, IN9-N7, produced a truncated flagellum and was partially motile. Three-day-old chicks were orally challenged with different doses of the wild-type strain and the two mutants. At challenge doses ranging from 3.0 x 10(4) to 6.6 x 10(8) CFU per chick, only the fully motile, wild-type strain colonized the chick ceca. Our results show that intact and motile flagella are important colonization factors for C. jejuni in chicks.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguero-Rosenfeld M. E., Yang X. H., Nachamkin I. Infection of adult Syrian hamsters with flagellar variants of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2214–2219. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2214-2219.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Guerry P., Lee E. C., Burans J. P., Walker R. I. Reversible expression of flagella in Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):941–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.941-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deming M. S., Tauxe R. V., Blake P. A., Dixon S. E., Fowler B. S., Jones T. S., Lockamy E. A., Patton C. M., Sikes R. O. Campylobacter enteritis at a university: transmission from eating chicken and from cats. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Sep;126(3):526–534. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S. H., Nachamkin I. Common and variable domains of the flagellin gene, flaA, in Campylobacter jejuni. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1151–1158. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. A., Hoffman P. S., Smibert R. M., Krieg N. R. Improved media for growth and aerotolerance of Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.36-41.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., Alm R. A., Power M. E., Logan S. M., Trust T. J. Role of two flagellin genes in Campylobacter motility. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4757–4764. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4757-4764.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., Logan S. M., Thornton S., Trust T. J. Genomic organization and expression of Campylobacter flagellin genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1853–1860. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1853-1860.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris N. V., Weiss N. S., Nolan C. M. The role of poultry and meats in the etiology of Campylobacter jejuni/coli enteritis. Am J Public Health. 1986 Apr;76(4):407–411. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.4.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Courcoux P., Tompkins L. Gene disruption and replacement as a feasible approach for mutagenesis of Campylobacter jejuni. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1704–1708. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1704-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Harel J., Tompkins L. Gene transfer from Escherichia coli to Campylobacter species: development of shuttle vectors for genetic analysis of Campylobacter jejuni. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5320–5323. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5320-5323.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H., Woodward D. L., Edgar J. A., Laroche L. J., Gill P. Serotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):761–768. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.761-768.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinersmann R. J., Rigsby W. E., Stern N. J., Kelley L. C., Hill J. E., Doyle M. P. Comparative study of colonizing and noncolonizing Campylobacter jejuni. Am J Vet Res. 1991 Sep;52(9):1518–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morooka T., Umeda A., Amako K. Motility as an intestinal colonization factor for Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myszewski M. A., Stern N. J. Influence of Campylobacter jejuni cecal colonization on immunoglobulin response in chickens. Avian Dis. 1990 Jul-Sep;34(3):588–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., McBride H., Dolby J. M. Investigations on the role of flagella in the colonization of infant mice with Campylobacter jejuni and attachment of Campylobacter jejuni to human epithelial cell lines. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):217–227. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijten P. J., van Asten F. J., Gaastra W., van der Zeijst B. A. Structural and functional analysis of two Campylobacter jejuni flagellin genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17798–17804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Rollins D. M., Haberberger R. L., Jr, Green A. E., Habash L., Strocko S., Walker R. I. Significance of flagella in colonization resistance of rabbits immunized with Campylobacter spp. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2259–2264. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2259-2264.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern N. J., Bailey J. S., Blankenship L. C., Cox N. A., McHan F. Colonization characteristics of Campylobacter jejuni in chick ceca. Avian Dis. 1988 Apr-Jun;32(2):330–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern N. J., Bailey J. S., Meinersmann R. J., Cox N. A., Blankenship L. C. Simultaneous colonization of Campylobacter jejuni and Salmonella typhimurium in day-old chicks. Poult Sci. 1991 Apr;70(4):790–795. doi: 10.3382/ps.0700790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern N. J., Meinersmann R. J., Dickerson H. W. Influence of antibody treatment of Campylobacter jejuni on the dose required to colonize chicks. Avian Dis. 1990 Jul-Sep;34(3):595–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Taylor D. E. Natural transformation in Campylobacter species. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):949–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.949-955.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassenaar T. M., Bleumink-Pluym N. M., van der Zeijst B. A. Inactivation of Campylobacter jejuni flagellin genes by homologous recombination demonstrates that flaA but not flaB is required for invasion. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2055–2061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]