Abstract
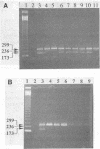
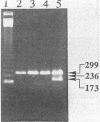
Three sets of oligonucleotide primers were used in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay to detect Salmonella species. phoP primers specific to the phoP/phoQ loci of coliform pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella, Shigella, Escherichia coli, and Citrobacter species served as presumptive indicators of enteric bacteria. In addition to the phoP primers, the Hin and the H-1i primers, which targeted a 236-bp region of hin/H2 and a 173-bp region of the H-1i flagellin gene, respectively, were used. Both Hin and H-1i primers are specific to motile Salmonella species and are not present in Shigella, E. coli, or Citrobacter species. Thus, by multiplex PCR amplification, Salmonella species including Salmonella typhi, Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella paratyphi A, and Salmonella enteritidis can be specifically detected. Optimal reaction conditions have been described to demonstrate this specific, sensitive detection of Salmonella species. By using agarose gel electrophoresis for detection of the PCR-amplified products, the sensitivity of detection was 10(2) CFU after 25 cycles of PCR and 1 (10(0)) CFU after a 50-cycle double PCR. The efficacy of these primers was demonstrated on environmental isolates which had previously been confirmed as Salmonella species by the use of conventional cultural techniques. In addition, positive amplifications resulted from Salmonella species in environmental samples including soil and water.
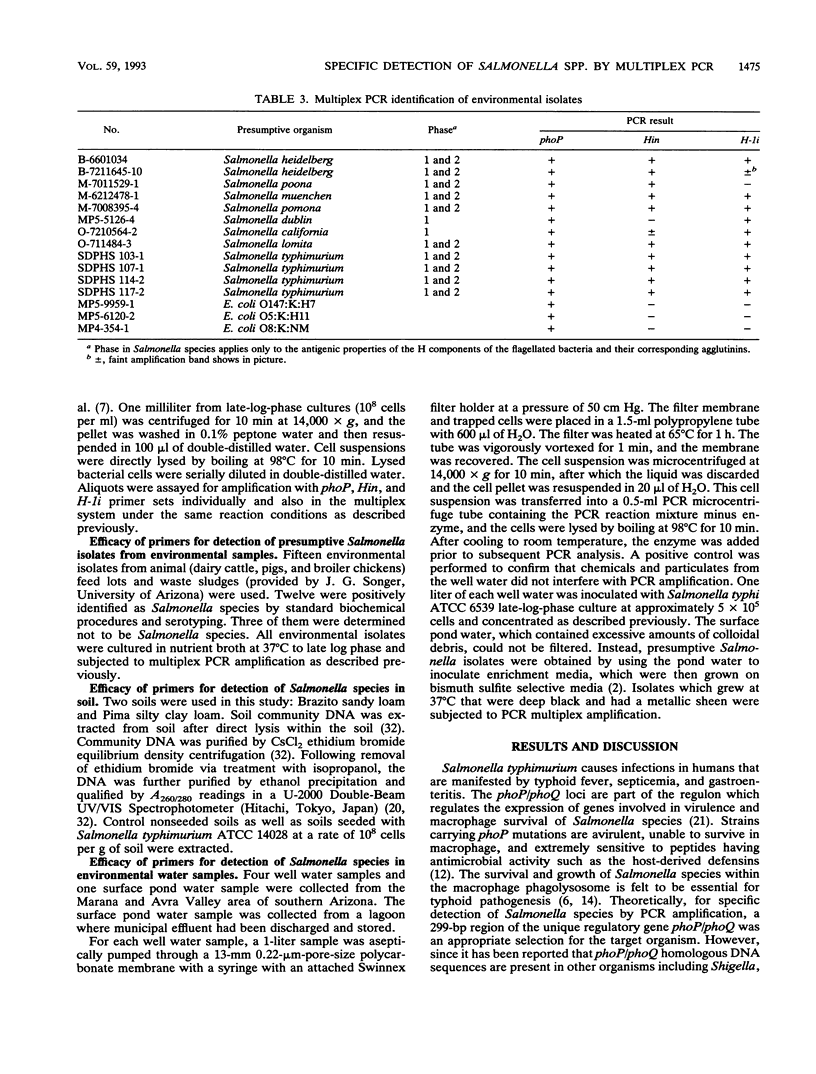
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcaide E., Martinez J. P., Garay E. Comparative study on Salmonella isolation from sewage-contaminated natural waters. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;56(3):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb01363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bej A. K., Steffan R. J., DiCesare J., Haff L., Atlas R. M. Detection of coliform bacteria in water by polymerase chain reaction and gene probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):307–314. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.307-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. The route of enteric infection in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1189–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debue M., Gautier P., Hackel C., Van Elsen A., Herzog A., Bigaignon G., Bollen A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in biological samples using the polymerase chain reaction assay. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jun;142(5):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90189-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edel W., Kampelmacher E. H. Comparative studies on the isolation of "sublethally injured" salmonellae in nine European laboratories. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;48(2):167–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitts R., Diamond M., Hamilton C., Neri M. DNA-DNA hybridization assay for detection of Salmonella spp. in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1146-1151.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Chiao E., Lipps C. J., Heffron F. Salmonella typhimurium phoP virulence gene is a transcriptional regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7077–7081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussong D., Enkiri N. K., Burge W. D. Modified agar medium for detecting environmental salmonellae by the most-probable-number method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):1026–1030. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.1026-1030.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joys T. M. The covalent structure of the phase-1 flagellar filament protein of Salmonella typhimurium and its comparison with other flagellins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Sayler G. S., Baldini M. M., Colwell R. R. Ambient-temperature primary nonselective enrichment for isolation of Salmonella spp. from an estuarine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):829–835. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.829-835.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight I. T., Shults S., Kaspar C. W., Colwell R. R. Direct detection of Salmonella spp. in estuaries by using a DNA probe. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1059–1066. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1059-1066.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Kukral A. M., Mekalanos J. J. A two-component regulatory system (phoP phoQ) controls Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5054–5058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriñigo M. A., Borrego J. J., Romero P. Comparative study of different methods for detection and enumeration of Salmonella spp. in natural waters. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;61(2):169–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriñigo M. A., Martinez-Manzanares E., Muñoz A., Cornax R., Romero P., Borrego J. J. Evaluation of different plating media used in the isolation of salmonellas from environmental samples. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;66(4):353–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1989.tb02488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou C. Y., Kwok S., Mitchell S. W., Mack D. H., Sninsky J. J., Krebs J. W., Feorino P., Warfield D., Schochetman G. DNA amplification for direct detection of HIV-1 in DNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.3336784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A. Direct cloning and sequence analysis of enzymatically amplified genomic sequences. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.3461561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomason B. M., Dodd D. J., Cherry W. B. Increased recovery of salmonellae from environmental samples enriched with buffered peptone water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Sep;34(3):270–273. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.3.270-273.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. Covalent structure of three phase-1 flagellar filament proteins of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. The nucleotide sequence of the H-1r gene of Salmonella rubislaw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8227–8227. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Hilmen M., Simon M. Regulation of gene expression by site-specific inversion. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Silverman M., Hilmen M., Simon M. Recombinational switch for gene expression. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):170–172. doi: 10.1126/science.322276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Simon M. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of an invertible controlling element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]