Abstract
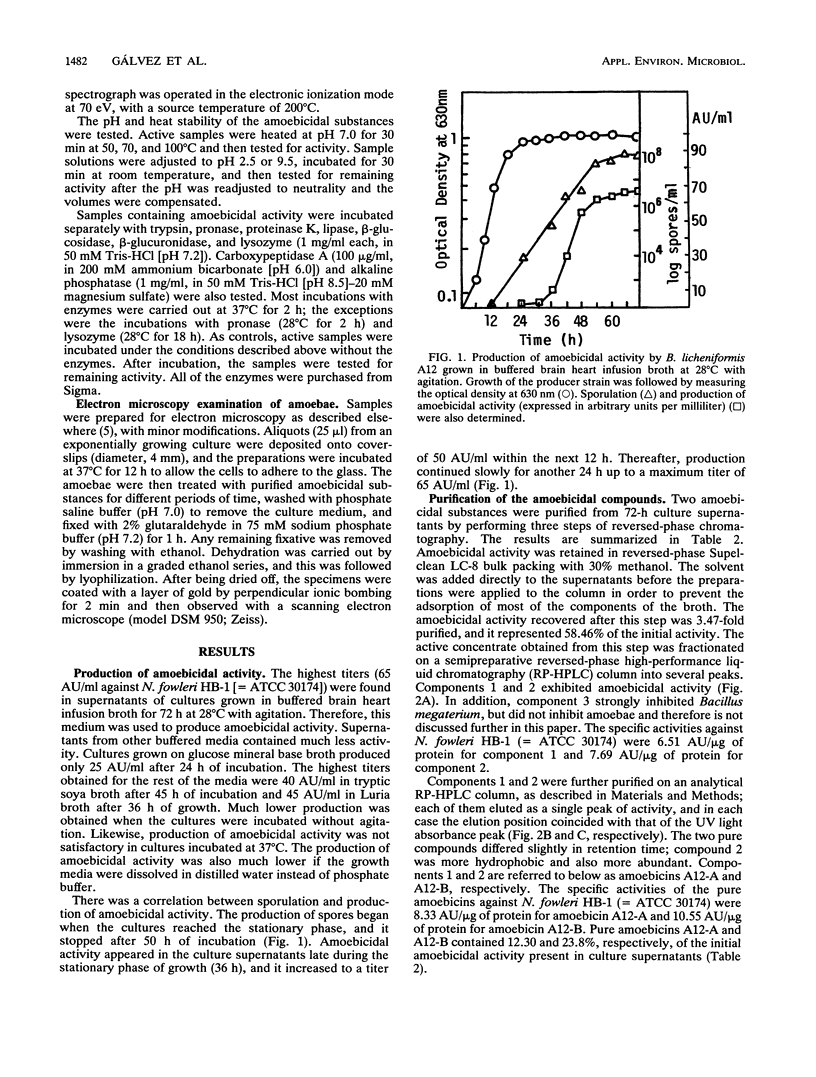
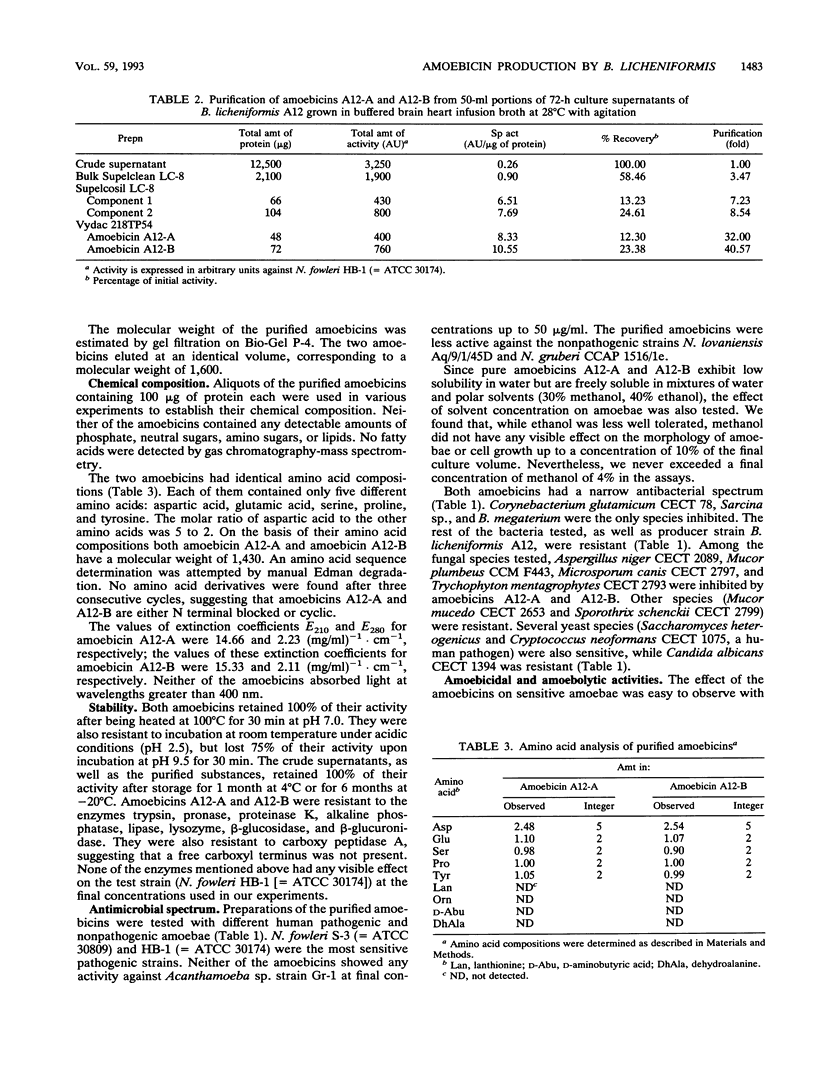
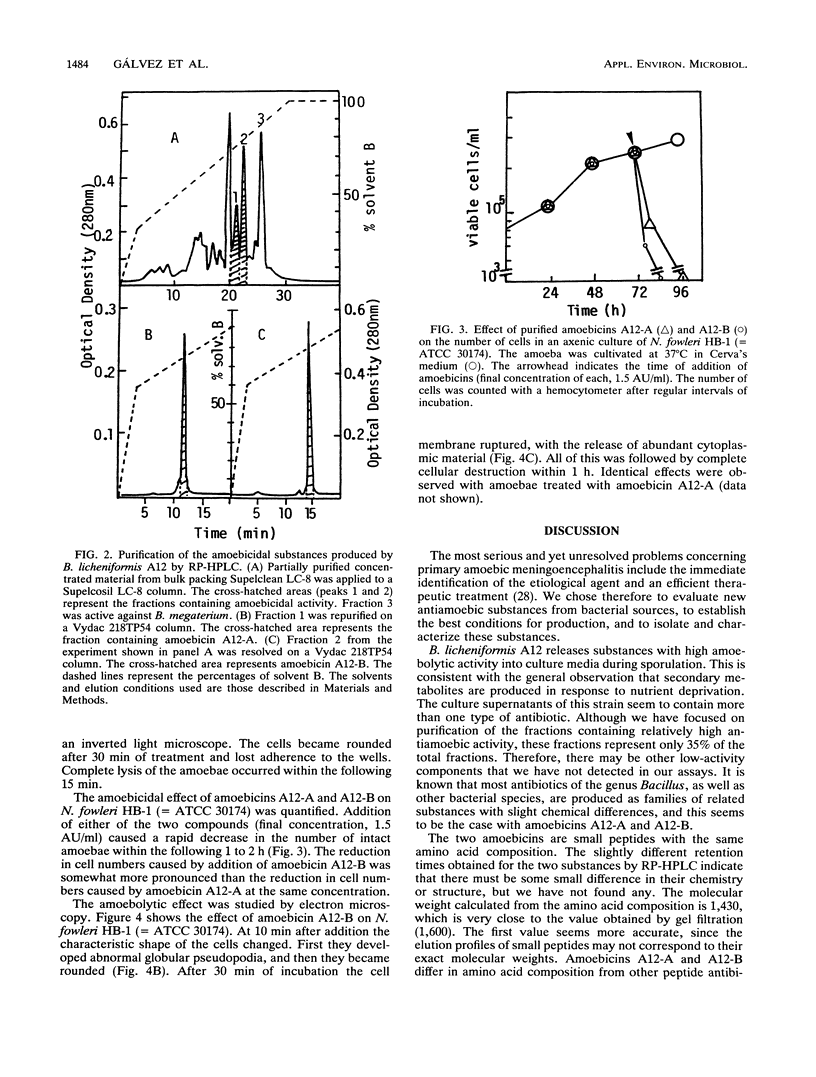
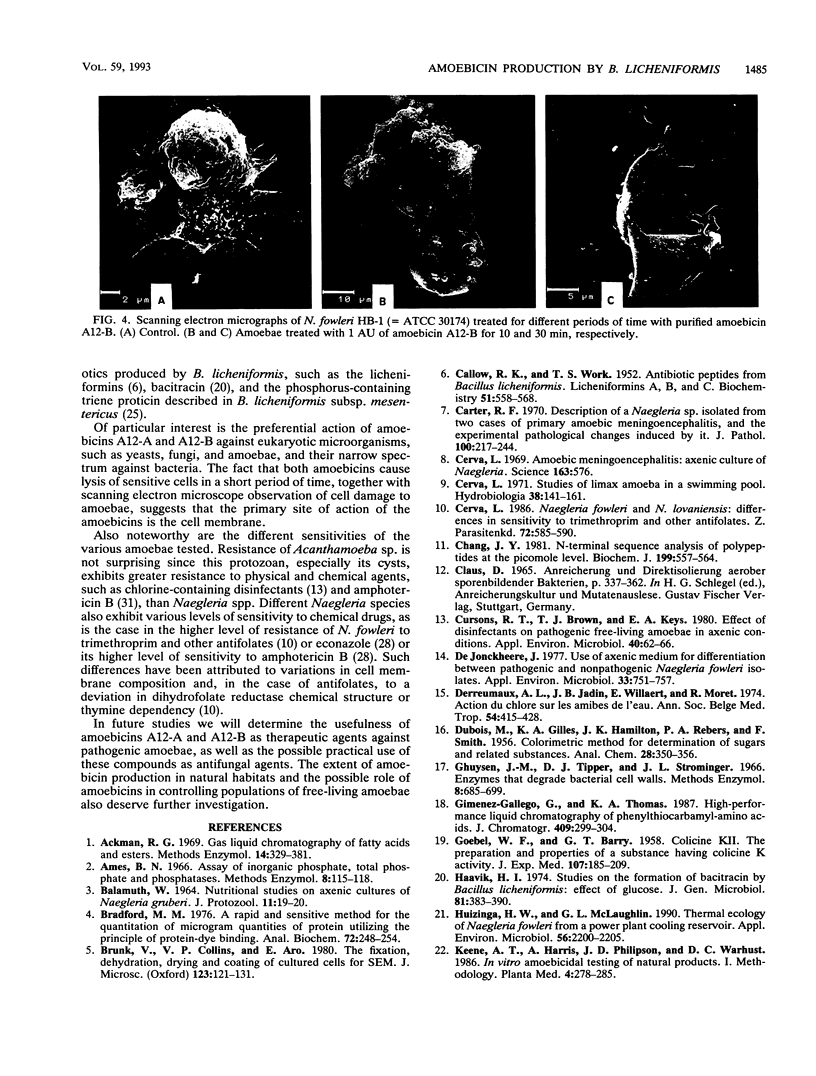
Bacillus licheniformis A12 produces two amoebolytic substances (amoebicins A12-A and A12-B) in liquid media during sporulation. Both substances have been purified and characterized. They are heat- and protease-resistant peptides containing aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine, proline, and tyrosine in a molar ratio of 5:2:2:2:2. No fatty acids or carbohydrates have been detected. Their molecular weight is 1,430. Purified amoebicins A12-A and A12-B exhibit amoebolytic action against Naegleria fowleri. They also exhibit antibiotic action against yeasts (Saccharomyces heterogenicus and Cryptococcus neoformans) and several fungal species (Aspergillus niger, Microsporum canis, Mucor plumbeus, and Trychophyton mentagrophytes). Their antibacterial spectrum appears to be restricted to Bacillus megaterium, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and Sarcina sp.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk U., Collins V. P., Arro E. The fixation, dehydration, drying and coating of cultured cells of SEM. J Microsc. 1981 Aug;123(Pt 2):121–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1981.tb01288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLOW R. K., WORK T. S. Antibiotic peptides from Bacillus licheniformis; licheniformins A, B and C. Biochem J. 1952 Jul;51(4):558–568. doi: 10.1042/bj0510558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. F. Description of a Naegleria sp. isolated from two cases of primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis, and of the experimental pathological changes induced by it. J Pathol. 1970 Apr;100(4):217–244. doi: 10.1002/path.1711000402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerva L. Amoebic meningoencephalitis: axenic culture of Naegleria. Science. 1969 Feb 7;163(3867):576–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerva L. Naegleria fowleri and N. lovaniensis: differences in sensitivity to trimethoprim and other antifolates. Z Parasitenkd. 1986;72(5):585–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00925478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. Y. N-terminal sequence analysis of polypeptide at the picomole level. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):557–564. doi: 10.1042/bj1990557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Keys E. A. Effect of disinfectants on pathogenic free-living amoebae: in axenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):62–66. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.62-66.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. Use of an axenic medium for differentiation between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria fowleri isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):751–757. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.751-757.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derreumaux A. L., Jadin J. B., Willaert E., Moret R. Action du chlore sur les amibes de l'eau. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1974;54(4-5):415–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBEL W. F., BARRY G. T. Colicine K. II. The preparation and properties of a substance having colicine K activity. J Exp Med. 1958 Feb 1;107(2):185–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez-Gallego G., Thomas K. A. High-performance liquid chromatography of phenylthiocarbamyl-amino acids. Application to carboxyl-terminal sequencing of proteins. J Chromatogr. 1987 Nov 13;409:299–304. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86806-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haavik H. I. Studies on the formation of bacitracin by Bacillus licheniformis: effect of glucose. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Apr;81(2):383–390. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga H. W., McLaughlin G. L. Thermal ecology of Naegleria fowleri from a power plant cooling reservoir. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2200–2205. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2200-2205.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P., Visvesvara G. S., Martinez A. J., Theodore F. H., Daggett P. M., Sawyer T. K. Naegleria and Acanthamoeba infections: review. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 May-Jun;12(3):490–513. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.3.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesemann G., Präve P., Sukatsch D., Vértesy L. Ein Polyen-Antibiotikum aus Bakterien. Naturwissenschaften. 1972 Feb;59(2):81–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00593477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco G., Tulloch G. S. Microfilariae of Dirofilaria striata in a dog. J Parasitol. 1970 Apr;56(2):248–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaglia M., Gatti S., Bernuzzi A. M., Cevini C., Chichino G., Rondanelli E. G. An in vitro comparative study on the effect of amphotericin B, econazole, and 5-fluorocytosine on Naegleria fowleri, Naegleria australiensis, and Naegleria australiensis s.sp. italica. Microbiologica. 1988 Oct;11(4):279–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel J. S., Harmatz P., Visvesvara G. S., Cohen A., Edwards J., Turner J. Successful treatment of primary amebic meningoencephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 11;306(6):346–348. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202113060607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Willaert E. Drug sensitivity and resistance of four Acanthamoeba species. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(6):806–808. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall R. L., Ironside K. S., Metler P. L., Tan E. L., Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B. Effect of thermal additions on the density and distribution of thermophilic amoebae and pathogenic Naegleria fowleri in a newly created cooling lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):722–732. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.722-732.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willaert E. Etude emmuno-taxonomique des genres Naegleria et Acanthamoeba (Protozoa: Amoebida) Acta Zool Pathol Antverp. 1976 Dec;(65):1–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



