Abstract
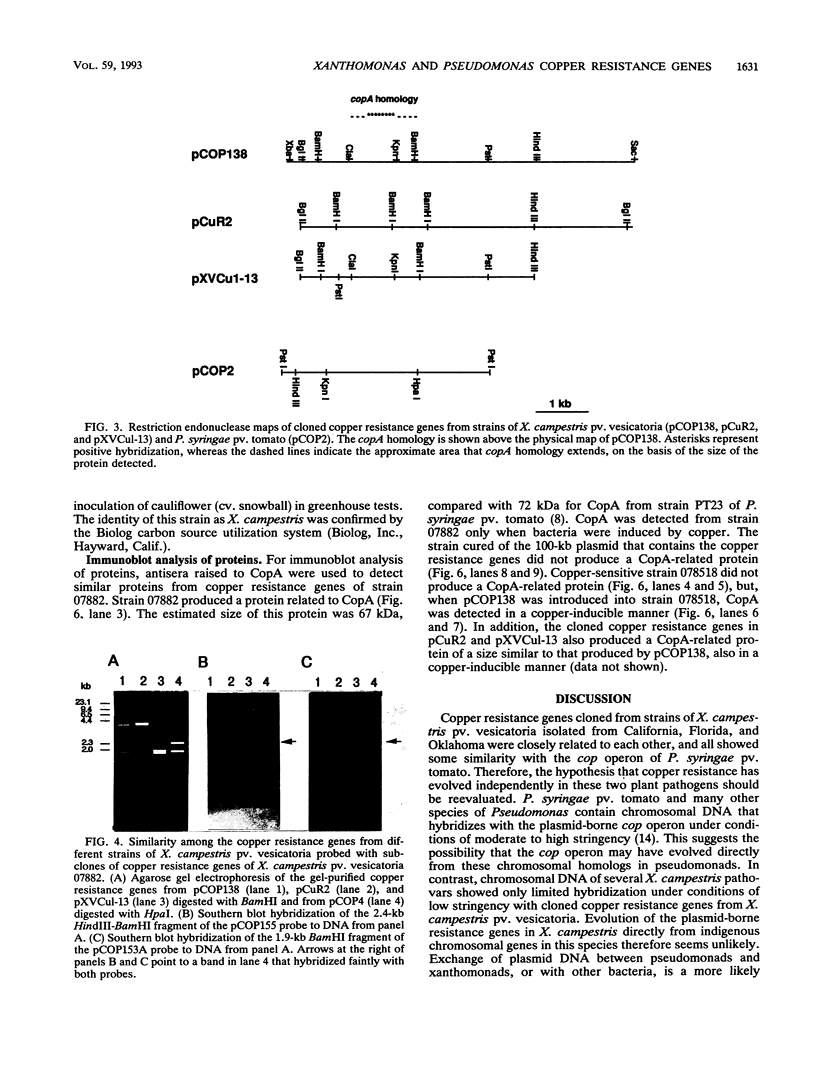
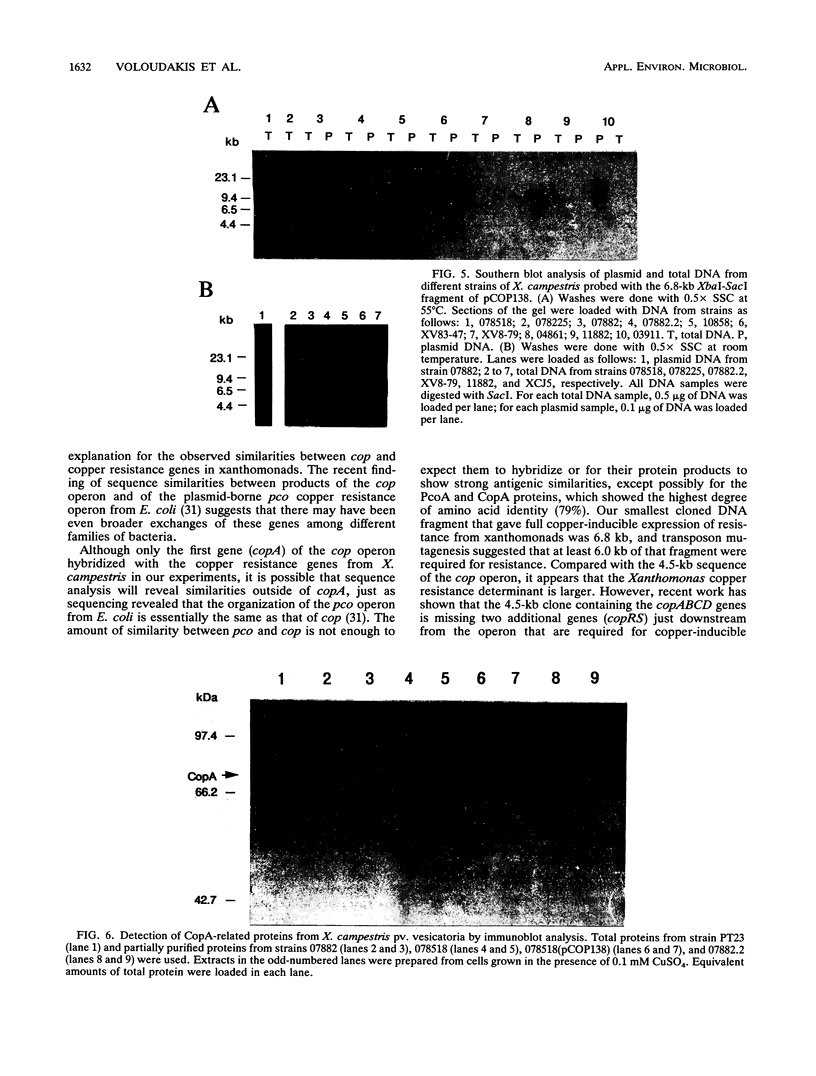
Plasmid-borne copper resistance genes from copper-resistant strains of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria from California, Florida, and Oklahoma shared structural similarities. A strain of X. campestris pv. campestris also contained plasmid-borne copper resistance genes similar to the resistance genes from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. Furthermore, a region of the copper resistance genes from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria 07882 hybridized with copA, the first gene of the copper resistance operon (cop) of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. A copper-inducible protein of similar size to CopA was detected by Western blot (immunoblot) analysis from the wild-type strain 07882 and from the cloned copper resistance genes of 07882 introduced into a copper-sensitive strain of X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. A low level of hybridization was observed with chromosomal DNA from other xanthomonads when the copper resistance genes from strain 07882 were used as probes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender C. L., Cooksey D. A. Indigenous plasmids in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato: conjugative transfer and role in copper resistance. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):534–541. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.534-541.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender C. L., Cooksey D. A. Molecular cloning of copper resistance genes from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):470–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.470-474.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender C. L., Malvick D. K., Conway K. E., George S., Pratt P. Characterization of pXV10A, a Copper Resistance Plasmid in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):170–175. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.170-175.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha J. S., Cooksey D. A. Copper resistance in Pseudomonas syringae mediated by periplasmic and outer membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8915–8919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey D. A., Azad H. R. Accumulation of copper and other metals by copper-resistant plant-pathogenic and saprophytic pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):274–278. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.274-278.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey D. A., Azad H. R., Cha J. S., Lim C. K. Copper resistance gene homologs in pathogenic and saprophytic bacterial species from tomato. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):431–435. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.431-435.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey D. A. Characterization of a Copper Resistance Plasmid Conserved in Copper-Resistant Strains of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):454–456. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.454-456.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey D. A. Copper uptake and resistance in bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey D. A. Plasmid-Determined Copper Resistance in Pseudomonas syringae from Impatiens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):13–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.13-16.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier T. C., Nester E. W. Isolation of covalently closed circular DNA of high molecular weight from bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1976 Dec;76(2):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90338-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garde S., Bender C. L. DNA probes for detection of copper resistance genes in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2435–2439. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2435-2439.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Tamaki S., Kobayashi D., Trollinger D. Improved broad-host-range plasmids for DNA cloning in gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellano M. A., Cooksey D. A. Induction of the copper resistance operon from Pseudomonas syringae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4399–4401. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4399-4401.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellano M. A., Cooksey D. A. Nucleotide sequence and organization of copper resistance genes from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2879–2883. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2879-2883.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouch D., Camakaris J., Lee B. T., Luke R. K. Inducible plasmid-mediated copper resistance in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Apr;131(4):939–943. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-4-939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskawicz B., Dahlbeck D., Keen N., Napoli C. Molecular characterization of cloned avirulence genes from race 0 and race 1 of Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5789–5794. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5789-5794.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubben D., Schmitt R. A transposable promoter and transposable promoter probes derived from Tn1721. Gene. 1987;53(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]