Abstract
We have sequenced and analyzed the hyperreiterated DNA region, HRS1, from Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 424. The 2.1-kb HRS1 fragment is closely linked to the B. japonicum common and genotype-specific nodulation genes in serogroup 123 and 127 strains. Southern hybridization analyses indicated that one copy of HRS1 is also located next to the fixRnifA locus in B. japonicum USDA 424. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed the presence of a 4-bp target site duplication in HRS1 which is identical to a terminal repeat found in the B. japonicum USDA 110 repeated sequence RS alpha. Computer searches of the PIR (Protein Identification Resource) protein data base revealed a high degree of amino acid sequence homology between a putative 329-amino-acid polypeptide from HRS1 and a large polypeptide from IS1380, an insertion sequence from Acetobacter pasteurianus. RNA slot blot hybridizations suggest that transcripts showing homology to HRS1 are constitutively produced in strains USDA 424 (serogroup 127) and USDA 438 (serogroup 123).
Full text
PDF

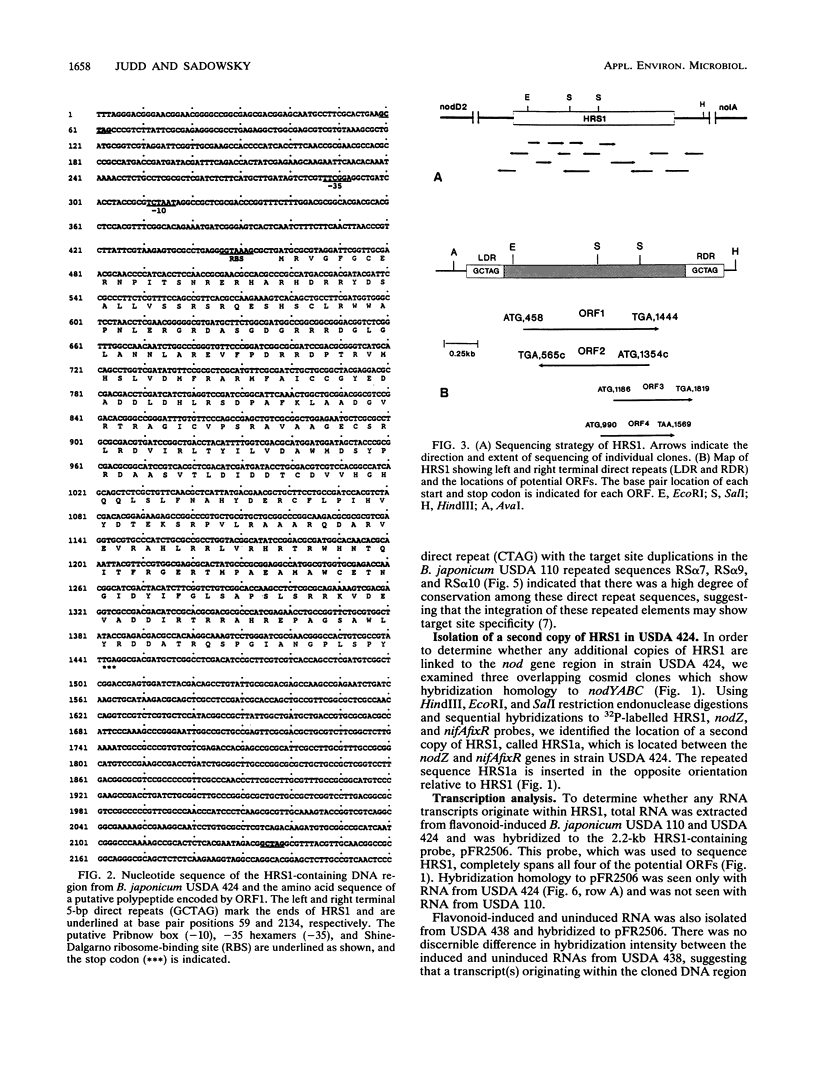



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dusha I., Kovalenko S., Banfalvi Z., Kondorosi A. Rhizobium meliloti insertion element ISRm2 and its use for identification of the fixX gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1403–1409. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1403-1409.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Brom S., Martínez E., Piñero D., Romero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Reiterated DNA sequences in Rhizobium and Agrobacterium spp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5782–5788. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5782-5788.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M., Holzhäuser D., Bäni D., Hennecke H. Structural and functional analysis of two different nodD genes in Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 May-Jun;5(3):257–265. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn M., Hennecke H. Mapping of a Bradyrhizobium japonicum DNA Region Carrying Genes for Symbiosis and an Asymmetric Accumulation of Reiterated Sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2247–2252. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2247-2252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza K., Hahn M., Hennecke H. Repeated sequences similar to insertion elements clustered around the nif region of the Rhizobium japonicum genome. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):535–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.535-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labes G., Simon R. Isolation of DNA insertion elements from Rhizobium meliloti which are able to promote transcription of adjacent genes. Plasmid. 1990 Nov;24(3):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer B. J., Schottel J. L. Characterization of cat messenger RNA decay suggests that turnover occurs by endonucleolytic cleavage in a 3' to 5' direction. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1095–1104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priefer U. B., Burkardt H. J., Klipp W., Pühler A. ISR1: an insertion element isolated from the soil bacterium Rhizobium lupini. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):87–91. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Quiñones F., Judd A. K., Sadowsky M. J., Liu R. L., Cregan P. B. Hyperreiterated DNA regions are conserved among Bradyrhizobium japonicum serocluster 123 strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1878–1885. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1878-1885.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Long S. R., Meade H. M., van den Bos R. C., Ausubel F. M. ISRm1: A Rhizobium meliloti insertion sequence that transposes preferentially into nitrogen fixation genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):405–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowsky M. J., Bohlool B. B., Keyser H. H. Serological Relatedness of Rhizobium fredii to Other Rhizobia and to the Bradyrhizobia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1785–1789. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1785-1789.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowsky M. J., Cregan P. B., Gottfert M., Sharma A., Gerhold D., Rodriguez-Quinones F., Keyser H. H., Hennecke H., Stacey G. The Bradyrhizobium japonicum nolA gene and its involvement in the genotype-specific nodulation of soybeans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):637–641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowsky M. J., Olson E. R., Foster V. E., Kosslak R. M., Verma D. P. Two host-inducible genes of Rhizobium fredii and characterization of the inducing compound. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):171–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.171-178.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowsky M. J., Tully R. E., Cregan P. B., Keyser H. H. Genetic Diversity in Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serogroup 123 and Its Relation to Genotype-Specific Nodulation of Soybean. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2624–2630. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2624-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Zidwick M. J., Abebe H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serocluster 123 and Diversity among Member Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1212–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1212-1215.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Horinouchi S., Beppu T. Novel insertion sequence IS1380 from Acetobacter pasteurianus is involved in loss of ethanol-oxidizing ability. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7070–7076. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7070-7076.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Laberge S. Identification and nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti insertion sequence ISRm3: similarity between the putative transposase encoded by ISRm3 and those encoded by Staphylococcus aureus IS256 and Thiobacillus ferrooxidans IST2. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2530–2538. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2530-2538.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Watson R. J. A Positive Strain Identification Method for Rhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):574–576. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.574-576.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




