Abstract
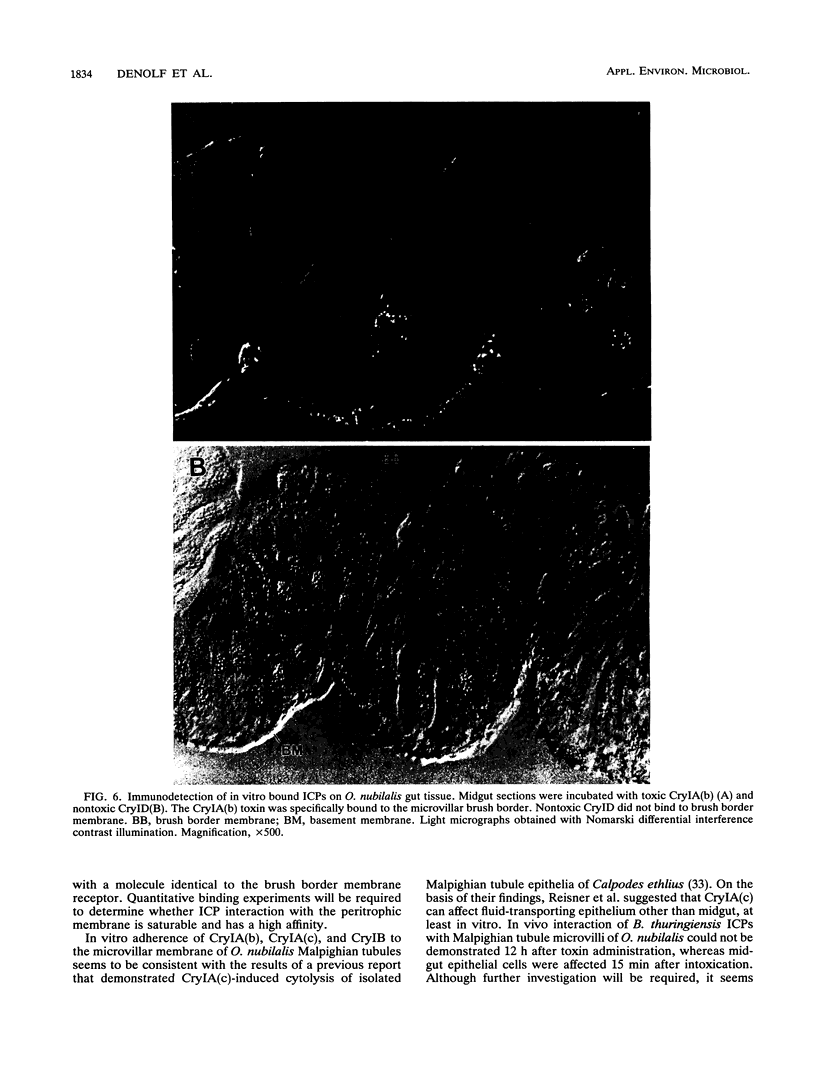
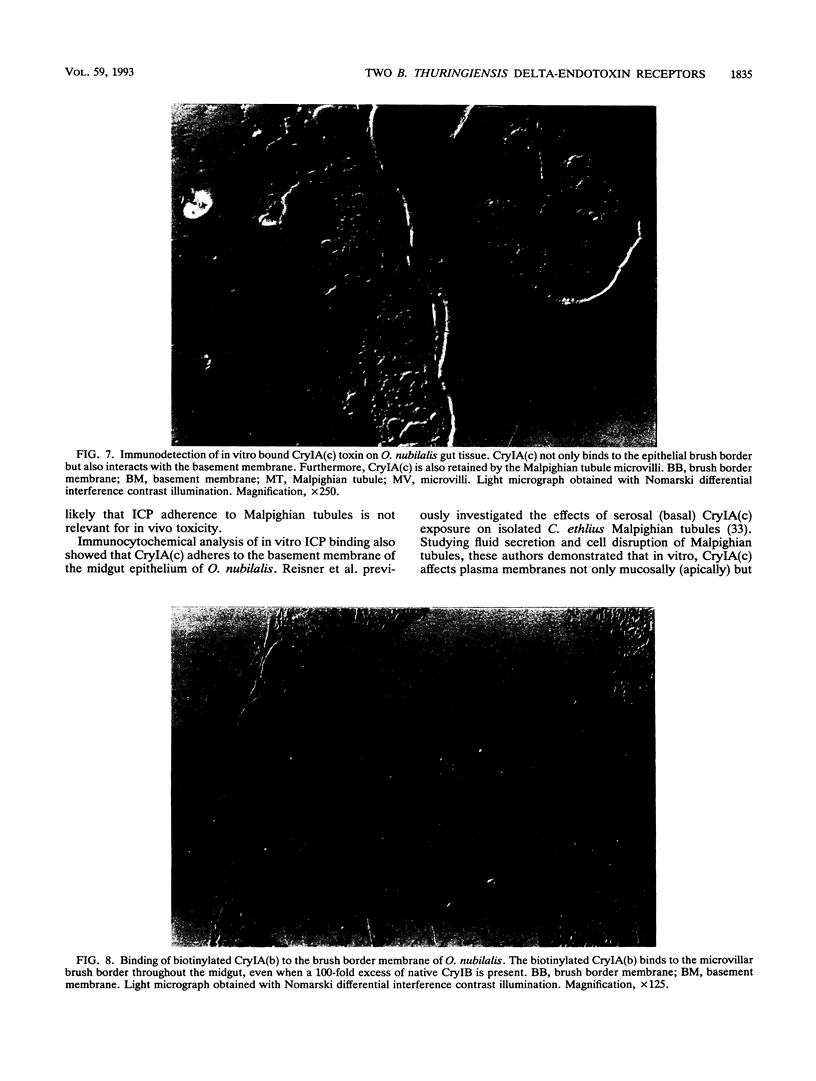
Binding of three Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal proteins (ICPs) to the midgut epithelium of Ostrinia nubilalis larvae was characterized by performing binding experiments with both isolated brush border membrane vesicles and gut tissue sections. Our results demonstrate that two independent ICP receptors are present in the brush border of O. nubilalis gut epithelium. From competition binding experiments performed with 125I-labeled and native ICPs it was concluded that CryIA(b) and CryIA(c) are recognized by the same receptor. An 11-fold-higher binding affinity of CryIA(b) for this receptor correlated with a 10-fold-higher toxicity of this ICP compared with CryIA(c). The CryIB toxin did not compete for the binding site of CryIA(b) and CryIA(c). Immunological detection of ingested B. thuringiensis ICPs on gut sections of O. nubilalis larvae revealed binding only along the epithelial brush border membrane. CryID and CryIE, two ICPs that are not toxic to O. nubilalis, were not bound to the apical microvilli of gut epithelial cells. In vitro binding experiments performed with native and biotinylated ICPs on tissue sections confirmed the correlation between ICP binding and toxicity. Moreover, by performing heterologous competition experiments with biotinylated and native ICPs, it was confirmed that the CryIB receptor is different from the receptor for CryIA(b) and CryIA(c). Retention of activated crystal proteins by the peritrophic membrane was not correlated with toxicity. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that CryIA(b), CryIA(c), and CryIB toxins interact in vitro with the epithelial microvilli of Malpighian tubules. In addition, CryIA(c) toxin also adheres to the basement membrane of the midgut epithelium.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denolf P., Jansens S., Van Houdt S., Peferoen M., Degheele D., Van Rie J. Biotinylation of Bacillus thuringiensis Insecticidal Crystal Proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jun;59(6):1821–1827. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.6.1821-1827.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré J., Real M. D., Van Rie J., Jansens S., Peferoen M. Resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis bioinsecticide in a field population of Plutella xylostella is due to a change in a midgut membrane receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garczynski S. F., Crim J. W., Adang M. J. Identification of putative insect brush border membrane-binding molecules specific to Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin by protein blot analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):2816–2820. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.2816-2820.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Vanderbruggen H., Höfte H., Van Rie J., Jansens S., Van Mellaert H. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins is correlated with the presence of high-affinity binding sites in the brush border membrane of target insect midguts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Whiteley H. R. Three classes of homologous Bacillus thuringiensis crystal-protein genes. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntosh S. C., Stone T. B., Sims S. R., Hunst P. L., Greenplate J. T., Marrone P. G., Perlak F. J., Fischhoff D. A., Fuchs R. L. Specificity and efficacy of purified Bacillus thuringiensis proteins against agronomically important insects. J Invertebr Pathol. 1990 Sep;56(2):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(90)90109-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mani G. S. Evolution of resistance in the presence of two insecticides. Genetics. 1985 Apr;109(4):761–783. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryerse J. S., Beck J. R., Jr, Lavrik P. B. Light microscope immunolocation of Bacillus thuringiensis kurstaki delta-endotoxin in the midgut and Malpighian tubules of the tobacco budworm, Heliothis virescens. J Invertebr Pathol. 1990 Jul;56(1):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(90)90148-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., Jansens S., Höfte H., Degheele D., Van Mellaert H. Receptors on the brush border membrane of the insect midgut as determinants of the specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1378–1385. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1378-1385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., Jansens S., Höfte H., Degheele D., Van Mellaert H. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. Importance of specific receptors on the brush border membrane of the mid-gut of target insects. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):239–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., McGaughey W. H., Johnson D. E., Barnett B. D., Van Mellaert H. Mechanism of insect resistance to the microbial insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2294593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan X. J., McCarthy W. J. Chemical modification of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. thuringiensis (HD-524) trypsin-activated endotoxin: implication of tyrosine residues in lepidopteran cell lysis. J Invertebr Pathol. 1991 Jan;57(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(91)90046-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]