Abstract
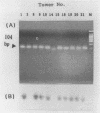
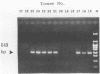
The presence of Legionella spp. in cooling tower water was investigated by using the polymerase chain reaction. Total Legionella spp. detection was performed with 20-mer 5S rRNA complementary DNA sequence primers, and specific Legionella pneumophila detection was performed with 20-mer and then 21-mer macrophage infectivity potentiator gene sequence primers. Of 27 cooling tower water samples, 25 were positive for Legionella spp., and 14 of these contained L. pneumophila.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bej A. K., Mahbubani M. H., Atlas R. M. Detection of viable Legionella pneumophila in water by polymerase chain reaction and gene probe methods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):597–600. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.597-600.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Carter C., Weber D. R., Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I. DNA sequence of mip, a Legionella pneumophila gene associated with macrophage infectivity. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1263–1270. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1263-1270.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki T., Hashimoto Y., Yamamoto H., Lucida M. L., Liu S. L., Kusunoki S., Asano K., Yabuuchi E. Evaluation of the microplate hybridization method for rapid identification of Legionella species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;9(3):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF01963841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry N. K., Rowbotham T. J., Saunders N. A., Embley T. M. Direct amplification and sequencing of the 16S ribosomal DNA of an intracellular Legionella species recovered by amoebal enrichment from the sputum of a patient with pneumonia. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 1;67(2):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90348-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higa F., Koide M., Shinzato T., Nakamoto A., Miyara T., Gaja M., Tateyama M., Owan I., Kusano N., Kitsukawa K. [Detection of Legionella pneumophila using a nested polymerase chain reaction]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1992 Aug;66(8):1084–1089. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.66.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaulhac B., Nowicki M., Bornstein N., Meunier O., Prevost G., Piemont Y., Fleurette J., Monteil H. Detection of Legionella spp. in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids by DNA amplification. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):920–924. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.920-924.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide M., Kamino T., Tsukahara Y., Maejima K., Saitoh A. [Isolation of Legionella spp. from cooling tower water in Kinki District, Japan]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1991 Dec;65(12):1578–1582. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.65.1578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonell M. T., Colwell R. R. The nucleotide sequence of the 5S rRNA from Legionella pneumophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1335–1335. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahbubani M. H., Bej A. K., Miller R., Haff L., DiCesare J., Atlas R. M. Detection of Legionella with polymerase chain reaction and gene probe methods. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Jun;4(3):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90051-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnbach M. N., Falkow S., Tompkins L. S. Species-specific detection of Legionella pneumophila in water by DNA amplification and hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1257–1261. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1257-1261.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]