Abstract
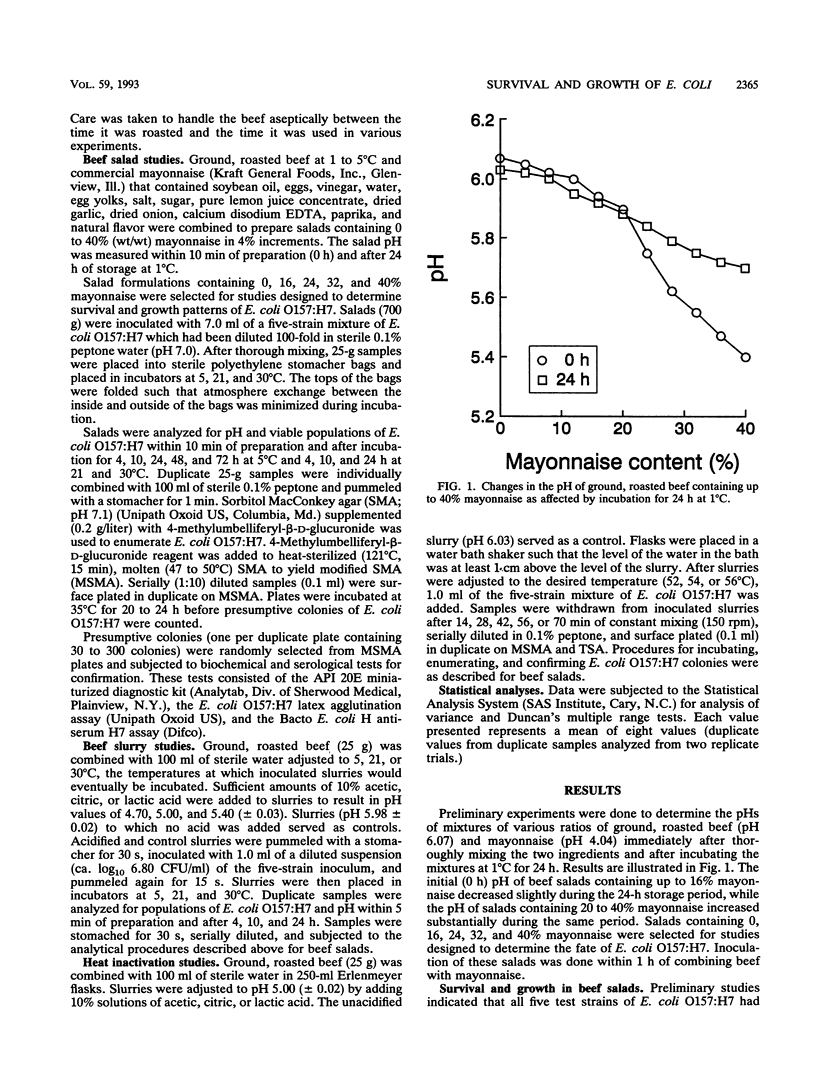
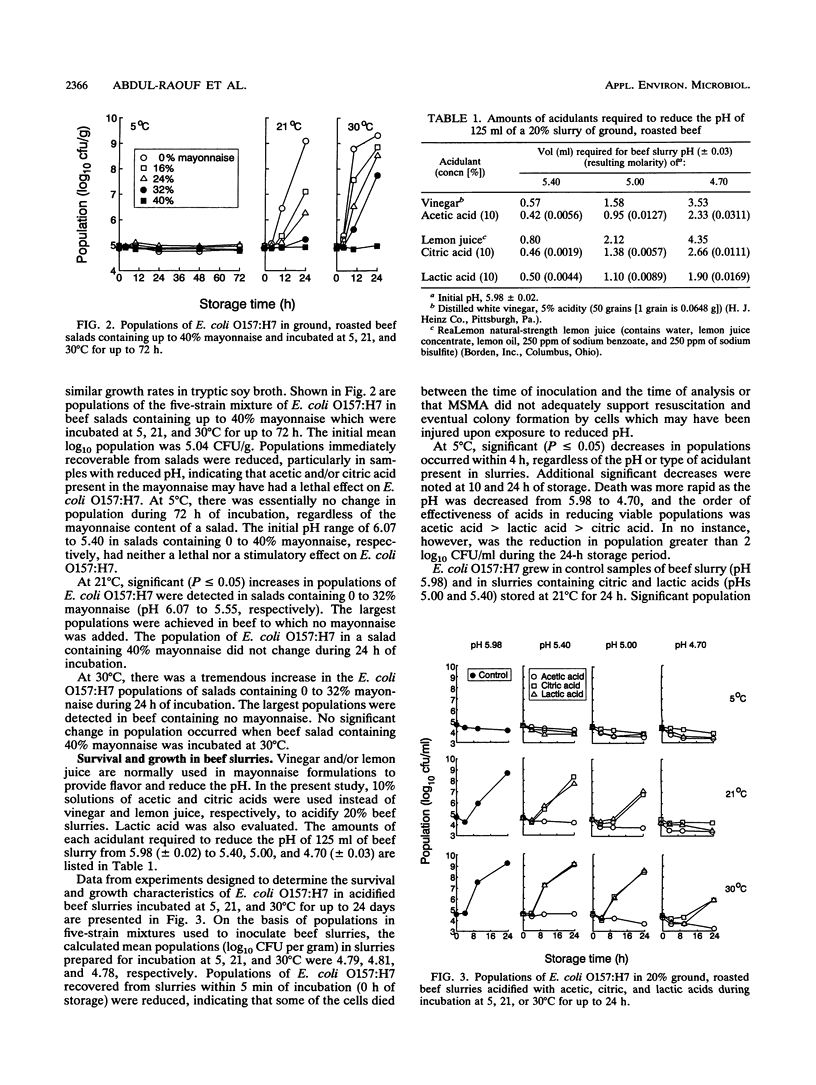
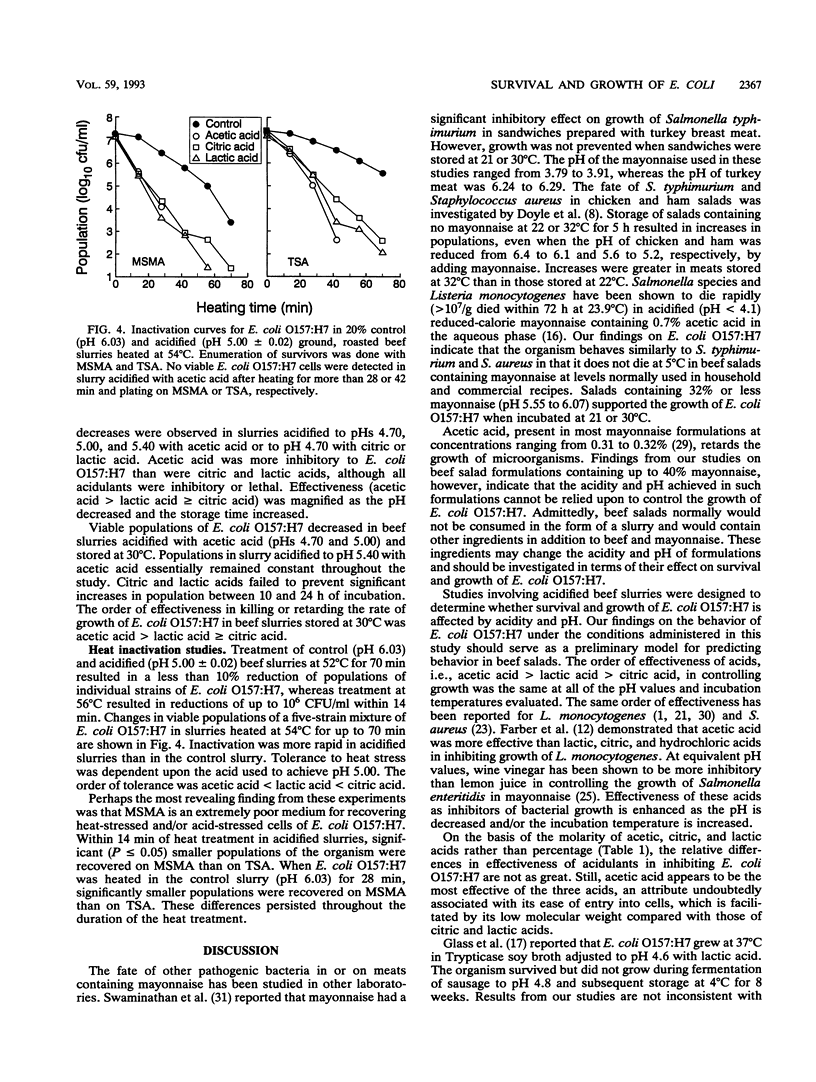
A study was undertaken to determine the fate of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground, roasted beef as influenced by the combined effects of pH, acidulants, temperature, and time. There was essentially no change in the viable population of E. coli O157:H7 when beef salads (pH 5.40 to 6.07) containing up to 40% mayonnaise were incubated at 5 degrees C for up to 72 h. At 21 and 30 degrees C, significant (P < or = 0.05) increases in populations of the organism occurred in salads containing 16 to 32% mayonnaise (pH 5.94 to 5.55) between 10 and 24 h of incubation. Death was more rapid as the pH of acidified beef slurries incubated at 5 degrees C was decreased from 5.98 to 4.70. E. coli O157:H7 grew in control slurries (pH 5.98) and in slurries containing citric and lactic acids (pHs 5.00 and 5.40) incubated at 21 degrees C for 24 h; decreases occurred in slurries acidified to pHs 4.70, 5.00, and 5.40 with acetic acid or pH 4.70 with citric or lactic acid. At 30 degrees C, populations decreased in slurries acidified to pHs 4.70 and 5.00 with acetic acid. Citric and lactic acids failed to prevent significant increases in populations in slurries at pH 4.70 to 5.40 between 10 and 24 h of incubation. The order of effectiveness of acidulants in inhibiting growth was acetic acid > lactic acid > or = citric acid. The same order was observed for inactivation of E. coli O157:H7 in acidified (pH 5.00) beef slurry heated at 54 degrees C.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beery J. T., Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Colonization of chicken cecae by Escherichia coli associated with hemorrhagic colitis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):310–315. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.310-315.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borczyk A. A., Karmali M. A., Lior H., Duncan L. M. Bovine reservoir for verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet. 1987 Jan 10;1(8524):98–98. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91928-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant H. E., Athar M. A., Pai C. H. Risk factors for Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in an urban community. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):858–864. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P. Escherichia coli O157:H7 and its significance in foods. Int J Food Microbiol. 1991 Apr;12(4):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(91)90143-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from retail fresh meats and poultry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2394–2396. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2394-2396.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan D. W., Razzell W. E. Klebsiella biotypes among coliforms isolated from forest environments and farm produce. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Dec;24(6):933–938. doi: 10.1128/am.24.6.933-938.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ercolani G. L. Bacteriological quality assessment of fresh marketed lettuce and fennel. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):847–852. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.847-852.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass K. A., Loeffelholz J. M., Ford J. P., Doyle M. P. Fate of Escherichia coli O157:H7 as affected by pH or sodium chloride and in fermented, dry sausage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2513–2516. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2513-2516.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall H. E., Brown D. F., Lewis K. H. Examination of market foods for coliform organisms. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1062–1069. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1062-1069.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Villar J. A. Cattle as reservoir of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet. 1987 Aug 1;2(8553):276–276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90860-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekla L., Milley D., Stackiw W., Sisler J., Drew J., Sargent D. Verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in ground beef--Manitoba. Can Dis Wkly Rep. 1990 Jun 2;16(22):103–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


