Abstract
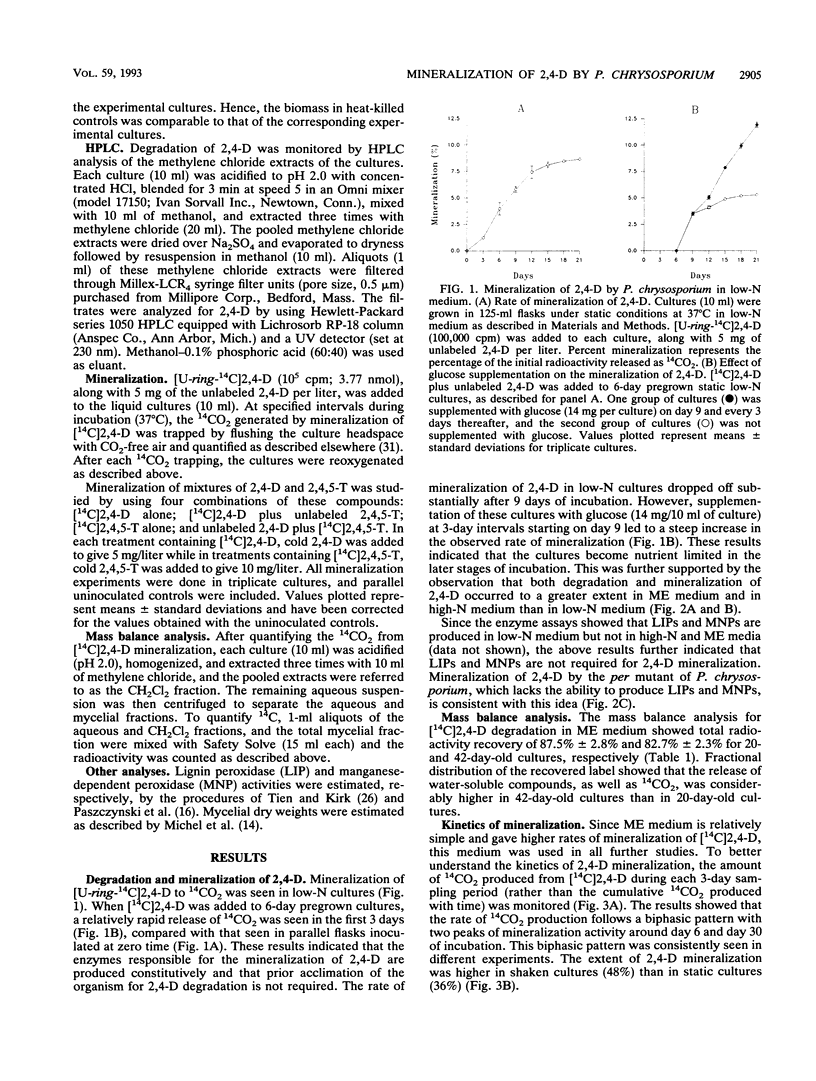
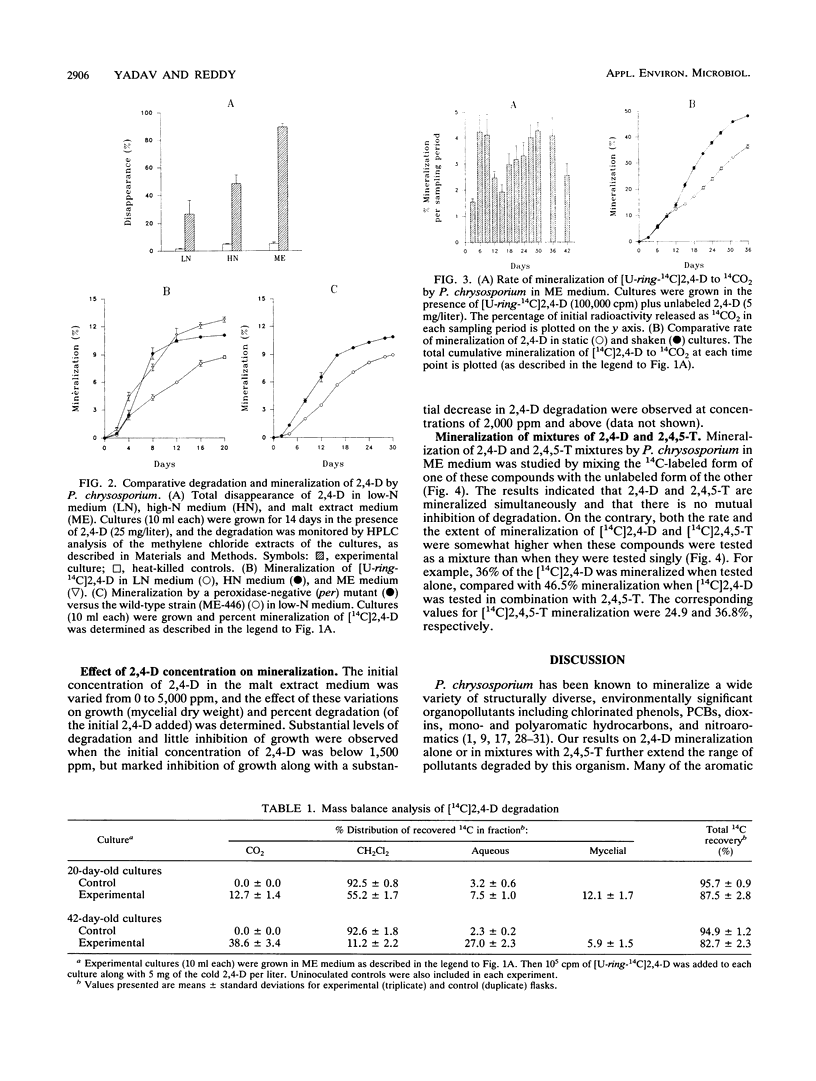
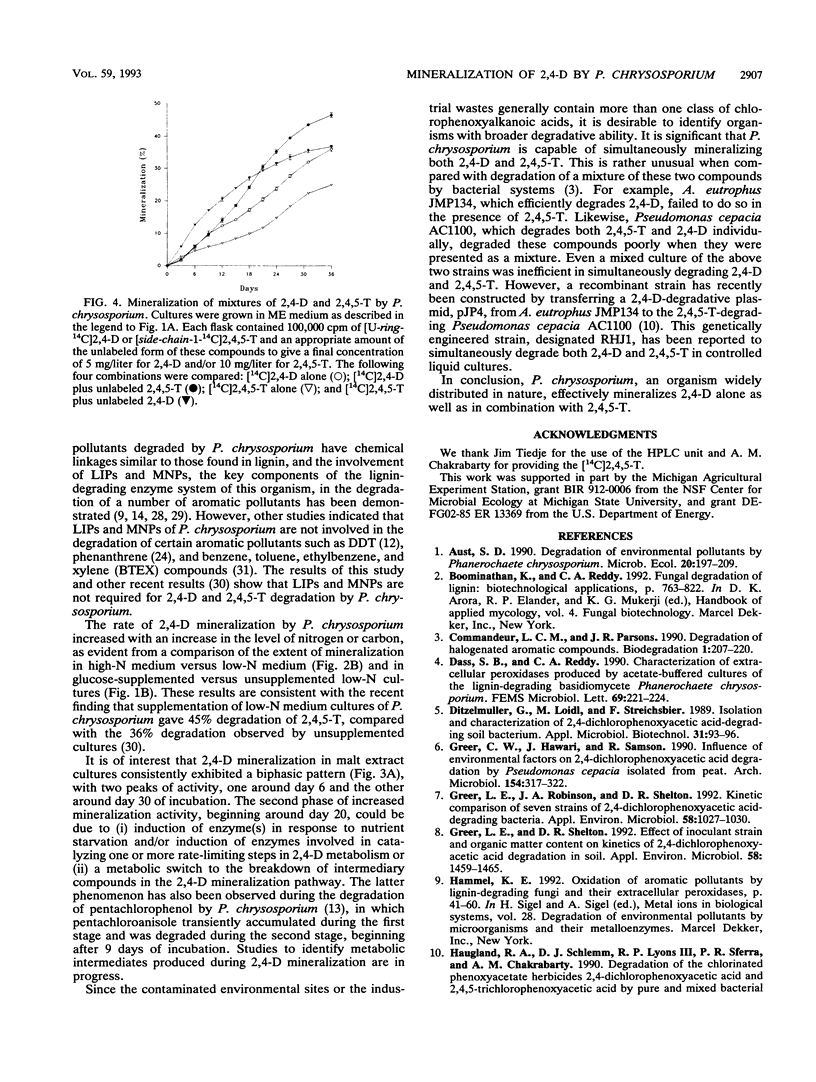
Evidence is presented for mineralization of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in nutrient-rich media (high-nitrogen and malt extract media) by wild-type Phanerochaete chrysosporium and by a peroxidase-negative mutant of this organism. Mass balance analysis of [U-ring-14C]2,4-D mineralization in malt extract cultures showed 82.7% recovery of radioactivity. Of this, 38.6% was released as 14CO2 and 27.0, 11.2, and 5.9% were present in the aqueous, methylene chloride, and mycelial fractions, respectively. 2,4-D and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) were simultaneously mineralized when presented as a mixture, and mutual inhibition of degradation was not observed. In contrast, a relatively higher rate of mineralization of 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T was observed when these compounds were tested as mixtures than when they were tested alone.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Commandeur L. C., Parsons J. R. Degradation of halogenated aromatic compounds. Biodegradation. 1990;1(2-3):207–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00058837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dass S. B., Reddy C. A. Characterization of extracellular peroxidases produced by acetate-buffered cultures of the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jun 1;57(3):221–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer C. W., Hawari J., Samson R. Influence of environmental factors on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation by Pseudomonas cepacia isolated from peat. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(4):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00276525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer L. E., Robinson J. A., Shelton D. R. Kinetic comparison of seven strains of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Mar;58(3):1027–1030. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.3.1027-1030.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer L. E., Shelton D. R. Effect of inoculant strain and organic matter content on kinetics of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1459-1465.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamar R. T., Larsen M. J., Kirk T. K. Sensitivity to and Degradation of Pentachlorophenol by Phanerochaete spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3519–3526. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3519-3526.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F. C., Jr, Dass S. B., Grulke E. A., Reddy C. A. Role of manganese peroxidases and lignin peroxidases of Phanerochaete chrysosporium in the decolorization of kraft bleach plant effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2368–2375. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2368-2375.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmann E. R., Loos M. A., van Dyk L. P. The microbial degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in soil. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 1988;101:1–53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3770-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler J. P. The genetic toxicology of phenoxy acids other than 2,4,5-T. Mutat Res. 1978;55(3-4):197–226. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(78)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland J. B., Selby A. L., Freeman J. P., Evans F. E., Cerniglia C. E. Metabolism of phenanthrene by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3310–3316. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3310-3316.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valli K., Brock B. J., Joshi D. K., Gold M. H. Degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by the lignin-degrading fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):221–228. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.221-228.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valli K., Wariishi H., Gold M. H. Degradation of 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2131–2137. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2131-2137.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav J. S., Reddy C. A. Degradation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes (BTEX) by the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Mar;59(3):756–762. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.3.756-762.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


