Abstract
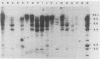
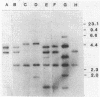
Thirty-three strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum within serogroup 110 were examined for genotypic diversity by using DNA-DNA hybridization analyses. The analysis of the DNA from 15 hydrogen-uptake-negative strains with the bradyrhizobial uptake hydrogenase probe pHU52 showed variation in degree of homology and restriction fragment length polymorphism of EcoRI-restricted DNA. Clustering analysis of the 33 strains on the basis of DNA-DNA hybridization analysis with four restriction enzymes and with the bradyrhizobial nodulation locus, pRJUT10, as probe indicated the existence of four groups of strains, which were less than 70% similar. Restriction digestion of genomic DNA with BamHI and DNA-DNA hybridization with pRJUT10 permitted classification of each of the strains according to a specific fingerprint pattern.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal A. K., Keister D. L. Physiology of Ex Planta Nitrogenase Activity in Rhizobium japonicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1592–1601. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1592-1601.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basit H. A., Angle J. S., Salem S., Gewaily E. M., Kotob S. I., van Berkum P. Phenotypic Diversity among Strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Belonging to Serogroup 110. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1570–1572. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1570-1572.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DATE R. A., DECKER A. M. MINIMAL ANTIGENIC CONSTITUTION OF 28 STRAINS OF RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Feb;11:1–8. doi: 10.1139/m65-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardly B. D., Materon L. A., Smith N. H., Johnson D. A., Rumbaugh M. D., Selander R. K. Genetic structure of natural populations of the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Rhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.187-194.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Cregan P. B. Nodulation and Competition for Nodulation of Selected Soybean Genotypes among Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serogroup 123 Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2631–2635. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2631-2635.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuykendall L. D., Elkan G. H. Rhizobium japonicum derivatives differing in nitrogen-fixing efficiency and carbohydrate utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.511-519.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert G. R., Cantrell M. A., Hanus F. J., Russell S. A., Haddad K. R., Evans H. J. Intra- and interspecies transfer and expression of Rhizobium japonicum hydrogen uptake genes and autotrophic growth capability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3232–3236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis J. N., Barbour W. M., Miller T. B., Israel D. W., Elkan G. H. Characterization of a Mannitol-Utilizing, Nitrogen-Fixing Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 Derivative. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):81–85. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.81-85.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis J. N., Israel D. W., Barbour W. M., Jarvis B. D., Elkan G. H. Analysis of the Symbiotic Performance of Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 and Its Derivative I-110 and Discovery of a New Mannitol-Utilizing, Nitrogen-Fixing USDA 110 Derivative. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.75-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis J. N., Kuykendall L. D., Elkan G. H. Restriction Endonuclease and nif Homology Patterns of Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 Derivatives With and Without Nitrogen Fixation Competence. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Mar;51(3):477–480. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.477-480.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinero D., Martinez E., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships among isolates of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2825–2832. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2825-2832.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Schell M. G., Nelson K. K., Halverson L. J., Sirotkin K. M., Stacey G. Isolation and characterization of the DNA region encoding nodulation functions in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1301-1308.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowsky M. J., Cregan P. B., Keyser H. H. DNA Hybridization Probe for Use in Determining Restricted Nodulation among Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serocluster 123 Field Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1768–1774. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1768-1774.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Zidwick M. J., Abebe H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum Serocluster 123 and Diversity among Member Isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1212–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1212-1215.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J., Brown G. G., Verma D. P. Slow-growing Rhizobium japonicum comprises two highly divergent symbiotic types. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):148–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.148-154.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. P., Demetriou L., Apte R. G. Rhizobium Population Genetics: Enzyme Polymorphism in Rhizobium leguminosarum from Plants and Soil in a Pea Crop. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):397–402. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.397-402.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berkum P. Evidence for a Third Uptake Hydrogenase Phenotype among the Soybean Bradyrhizobia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Dec;56(12):3835–3841. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.12.3835-3841.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]