Abstract
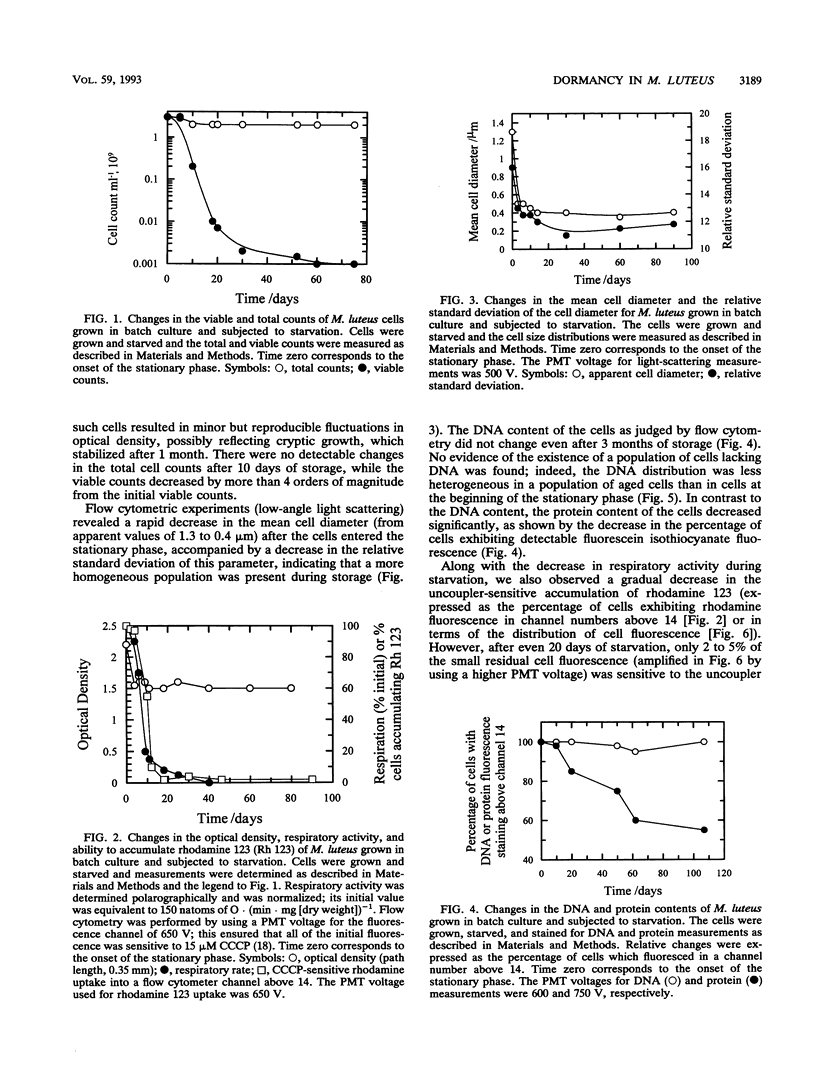
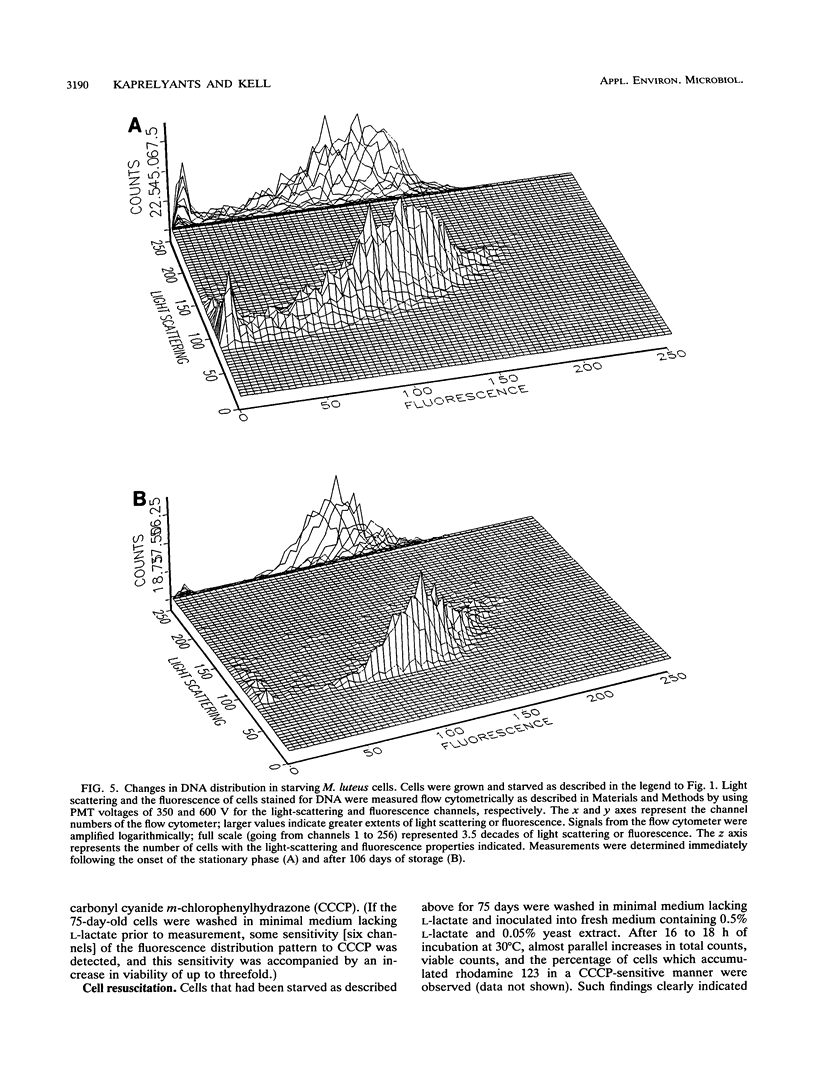
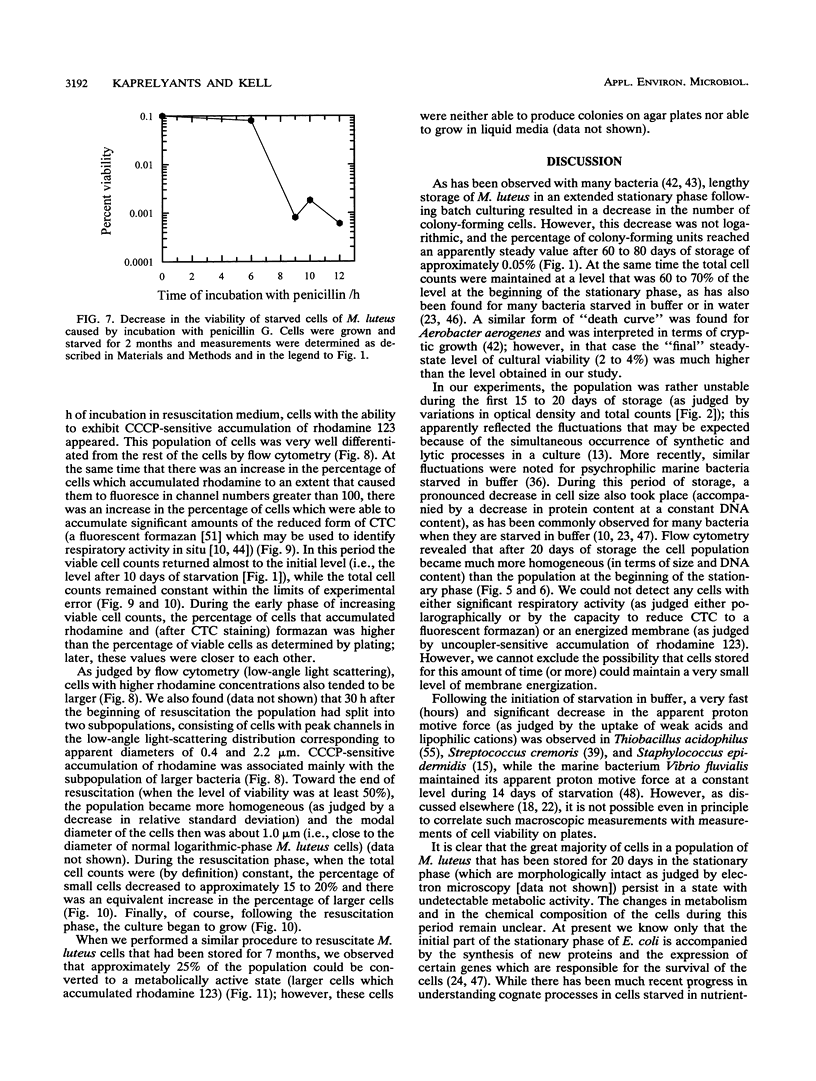
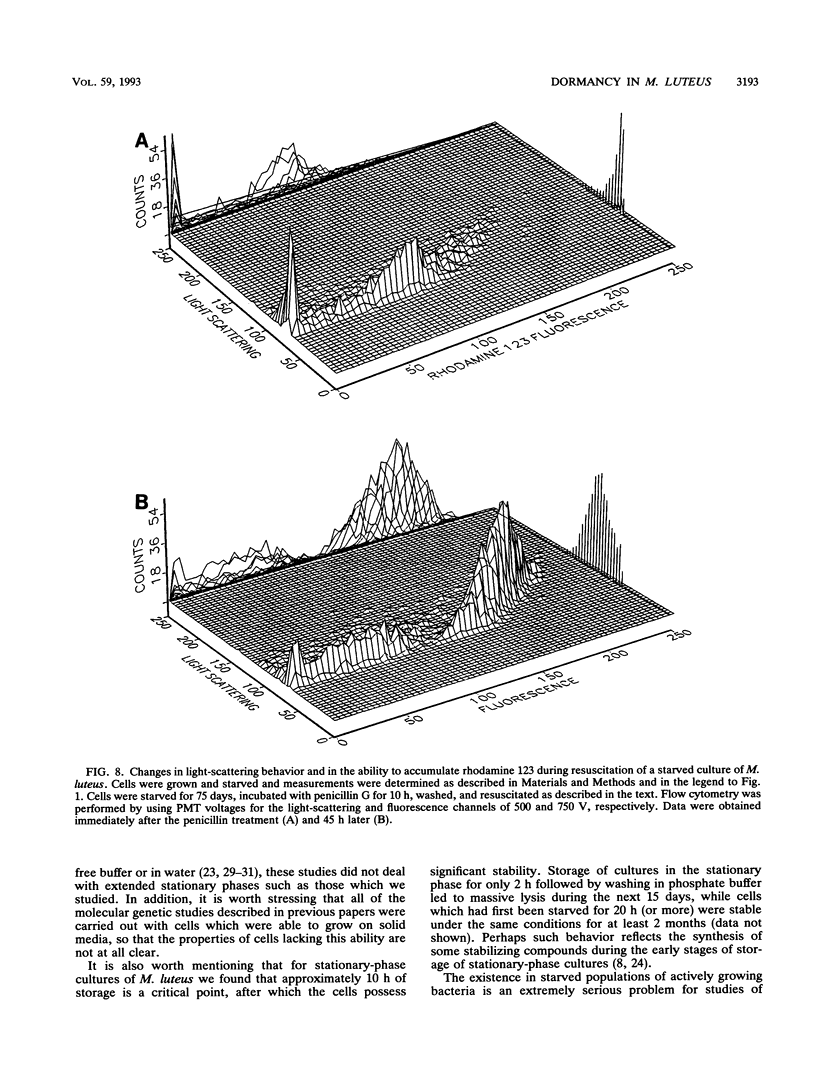
Cultures of the copiotrophic bacterium Micrococcus luteus were stored in spent growth medium for an extended period of time following batch culture. After an initial decrease, the total cell counts remained constant at approximately 60 to 70% of the counts at the beginning of storage. The level of viability, as judged by plate counts, decreased to less than 0.05%, while respiration and the ability to accumulate the lipophilic cation rhodamine 123 decreased to undetectable levels. However, using penicillin pretreatment (to remove viable cells) and flow cytometry and by monitoring both the total and viable counts, we found that at least 50% of the cells in populations of 75-day-old cultures were not dead but were dormant. Resuscitation in liquid medium was accompanied by the appearance of a population of larger cells, which could accumulate rhodamine 123 and reduce the dye 5-cyano-2,3-ditolyl tetrazolium chloride to a fluorescent formazan, while a similar fraction of the population was converted to colony-forming, viable cells. We surmise that dormancy may be far more common than death in starving microbial cultures.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benzer S., Freese E. INDUCTION OF SPECIFIC MUTATIONS WITH 5-BROMOURACIL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Feb;44(2):112–119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.2.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boye E., Steen H. B., Skarstad K. Flow cytometry of bacteria: a promising tool in experimental and clinical microbiology. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Apr;129(4):973–980. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-4-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns J., Overbaugh J., Miller S. The origin of mutants. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):142–145. doi: 10.1038/335142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaper J. P., Tither K., Edwards C. Rapid assessment of bacterial viability by flow cytometry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992 Nov;38(2):268–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00174481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duda V. I., Pronin S. V., El'-Registan G. I., Kaprel'iants A. S., Mitiushina L. L. Obrazovanie pokoiashchikhsia refraktil'nykh kletok u Bacillus cereus pod vliianiem autoreguliatornogo faktora. Mikrobiologiia. 1982 Jan-Feb;51(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. L. Directed mutation: between unicorns and goats. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1711–1716. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1711-1716.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschal J. C. Substrate capturing and growth in various ecosystems. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1992;21:39S–48S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb03623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder W., Dijkhuizen L. Physiological responses to nutrient limitation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. M., Kell D. B. The estimation of microbial biomass. Biosensors. 1985;1(1):17–84. doi: 10.1016/0265-928x(85)85005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horan N. J., Midgley M., Dawes E. A. Effect of starvation on transport, membrane potential and survival of Staphylococcus epidermidis under anaerobic conditions. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):223–230. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfle M. G. Long-Term Changes in Chemostat Cultures of Cytophaga johnsonae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1045–1053. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1045-1053.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEILIN D. The problem of anabiosis or latent life: history and current concept. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1959 Mar 17;150(939):149–191. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1959.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaprelyants A. S., Gottschal J. C., Kell D. B. Dormancy in non-sporulating bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993 Apr;10(3-4):271–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kell D. B., Ryder H. M., Kaprelyants A. S., Westerhoff H. V. Quantifying heterogeneity: flow cytometry of bacterial cultures. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1991 Oct-Nov;60(3-4):145–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00430362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M., Mårdén P., Jones G. W. The transient phase between growth and nongrowth of heterotrophic bacteria, with emphasis on the marine environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:25–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange R., Hengge-Aronis R. Growth phase-regulated expression of bolA and morphology of stationary-phase Escherichia coli cells are controlled by the novel sigma factor sigma S. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4474–4481. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4474-4481.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenski R. E., Slatkin M., Ayala F. J. Mutation and selection in bacterial populations: alternatives to the hypothesis of directed mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2775–2778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonell M. T., Hood M. A. Isolation and characterization of ultramicrobacteria from a gulf coast estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):566–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.566-571.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A. Physiology, molecular biology and applications of the bacterial starvation response. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1992;21:49S–57S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb03624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A. The molecular basis of carbon-starvation-induced general resistance in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):3–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittler J. E., Lenski R. E. Experimental evidence for an alternative to directed mutation in the bgl operon. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):446–448. doi: 10.1038/356446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. A., Cranwell P. A., Pickup R. W. Survival of Aeromonas salmonicida in lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1777–1782. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1777-1782.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer C. L., Morita R. Y. Effect of growth rate and starvation-survival on the viability and stability of a psychrophilic marine bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1122–1127. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1122-1127.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Oliver J. D., Kjelleberg S. Resuscitation of Vibrio vulnificus from the viable but nonculturable state. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5054–5059. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5054-5059.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez G. G., Phipps D., Ishiguro K., Ridgway H. F. Use of a fluorescent redox probe for direct visualization of actively respiring bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1801–1808. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1801-1808.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. S., Ellis A. E., Munro A. L. Evidence against dormancy in the bacterial fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 1;56(1-2):105–107. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90133-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Kolter R. Life after log. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.345-348.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen H. B., Skarstad K., Boye E. DNA measurements of bacteria. Methods Cell Biol. 1990;33:519–526. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellmach J., Severin E. A fluorescent redox dye. Influence of several substrates and electron carriers on the tetrazolium salt-formazan reaction of Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Histochem J. 1987 Jan;19(1):21–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01675289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weichart D., Oliver J. D., Kjelleberg S. Low temperature induced non-culturability and killing of Vibrio vulnificus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 15;100(1-3):205–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zychlinsky E., Matin A. Effect of starvation on cytoplasmic pH, proton motive force, and viability of an acidophilic bacterium, Thiobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):371–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.371-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


