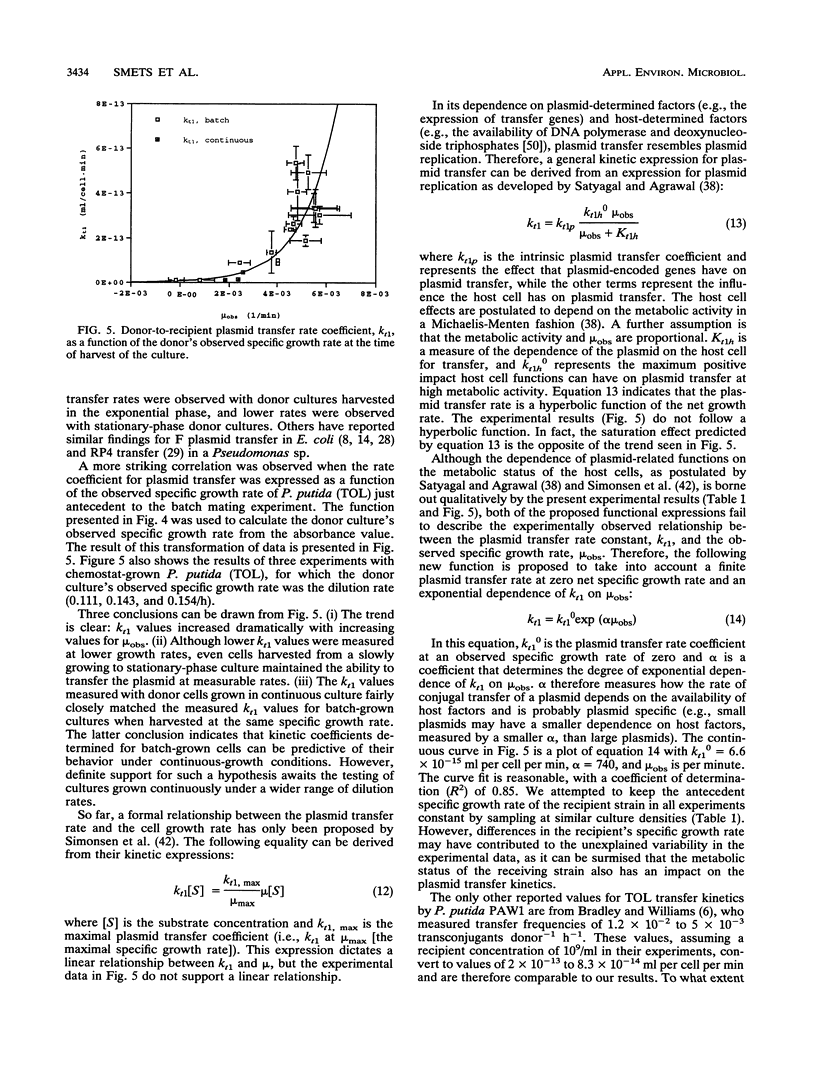
Abstract
The kinetics of the conjugal transfer of a TOL plasmid were investigated by using Pseudomonas putida PAW1 as the donor strain and P. aeruginosa PAO 1162 as the recipient strain. Short-term batch mating experiments were performed in a nonselective medium, while the evolution of the different cell types was determined by selective plating techniques. The experimental data were analyzed by using a mass action model that describes plasmid transfer kinetics. This method allowed analysis of the mating experiments by a single intrinsic kinetic parameter for conjugal plasmid transfer. Further results indicated that the specific growth rate of the donor strain antecedent to the mating experiment had a strong impact on the measured intrinsic plasmid transfer rate coefficient, which ranged from 1 x 10(-14) to 5 x 10(-13) ml per cell per min. Preliminary analysis suggested that the transfer rates of the TOL plasmid are large enough to maintain the TOL plasmid in a dense microbial community without selective pressures.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altherr M. R., Kasweck K. L. In situ studies with membrane diffusion chambers of antibiotic resistance transfer in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):838–843. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.838-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Fry J. C., Day M. J. Transfer and occurrence of large mercury resistance plasmids in river epilithon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):972–978. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.972-978.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Williams P. A. The TOL plasmid is naturally derepressed for transfer. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Dec;128(12):3019–3024. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-12-3019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewlow L. J., Cresswell N., Wellington E. M. Mathematical Model of Plasmid Transfer between Strains of Streptomycetes in Soil Microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Oct;56(10):3139–3145. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.10.3139-3145.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullum J., Collins J. F., Broda P. Factors affecting the kinetics of progeny formation with F'lac in Escherichia coli K12. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):536–544. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullum J., Collins J. F., Broda P. The spread of plasmids in model populations of Escherichia coli K12. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn N. W., Holloway B. W. Pleiotrophy of p-fluorophenylalanine-resistant and antibiotic hypersensitive mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1971 Oct;18(2):185–197. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300012593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Astorga A., Muela A., Cisterna R., Iriberri J., Barcina I. Biotic and abiotic factors affecting plasmid transfer in Escherichia coli strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):392–398. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.392-398.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Freter R. R., Brickner H. Experimental and mathematical models of Escherichia coli plasmid transfer in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):60–84. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.60-84.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. M. Rate of plasmid transfer among Escherichia coli strains isolated from natural populations. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jan;138(1):17–21. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. B., Istock C. A. Genetic exchange in Bacillus subtilis in soil. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):287–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00267620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney D. G., Jr Promiscuous transfer of drug resistance in gram-negative bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):320–329. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):421–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.421-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N., Köhler T., Rekik M., Harayama S. Growth-phase-dependent expression of the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid pWW0 catabolic genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6651–6660. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6651-6660.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg S. T., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmid-assisted molecular breeding: new technique for enhanced biodegradation of persistent toxic chemicals. Science. 1981 Dec 4;214(4525):1133–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.7302584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröckel L., Focht D. D. Construction of chlorobenzene-utilizing recombinants by progenitive manifestation of a rare event. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2470–2475. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2470-2475.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrbach P. R., Zeyer J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J., Timmis K. N. Enzyme recruitment in vitro: use of cloned genes to extend the range of haloaromatics degraded by Pseudomonas sp. strain B13. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1025–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1025-1032.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. R., Stewart F. M., Rice V. A. The kinetics of conjugative plasmid transmission: fit of a simple mass action model. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach P. A., Grimes D. J. R-plasmid transfer in a wastewater treatment plant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1395–1403. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1395-1403.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Gonzalez M. I., Duque E., Ramos J. L. Conjugational transfer of recombinant DNA in cultures and in soils: host range of Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):3020–3027. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.3020-3027.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Construction of haloaromatics utilising bacteria. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):385–386. doi: 10.1038/277385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Hybrid pathway for chlorobenzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas sp. B13 derivatives. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):467–473. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.467-473.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahasrabudhe S. R., Modi V. V. Microbial degradation of chlorinated aromatic compounds. Microbiol Sci. 1987 Oct;4(10):300–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwien U., Schmidt E. Improved degradation of monochlorophenols by a constructed strain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.33-39.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen L. Dynamics of plasmid transfer on surfaces. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1001–1007. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-6-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen L., Gordon D. M., Stewart F. M., Levin B. R. Estimating the rate of plasmid transfer: an end-point method. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Nov;136(11):2319–2325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-11-2319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton P., Anson A. E. Conjugal transfer of R-plasmid R1drd-19 in Escherichia coli below 22 degrees C. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):789–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.789-791.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart F. M., Levin B. R. The Population Biology of Bacterial Plasmids: A PRIORI Conditions for the Existence of Conjugationally Transmitted Factors. Genetics. 1977 Oct;87(2):209–228. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stotzky G., Babich H. Survival of, and genetic transfer by, genetically engineered bacteria in natural environments. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1986;31:93–138. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Wilkins B. Processing of plasmid DNA during bacterial conjugation. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):24–41. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.24-41.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Murray K. Metabolism of benzoate and the methylbenzoates by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence for the existence of a TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):416–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.416-423.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


