Abstract
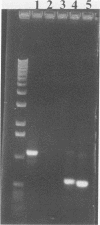
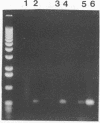
A primer-directed DNA amplification polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of seed contaminated with highly virulent Leptosphaeria maculans was developed. The primers were derived from a 5,238-bp repetitive sequence present only in the highly virulent isolates of the fungus. A procedure for isolating DNA from organisms infesting germinating seed was also developed. Seeds were added to liquid fungal minimal medium, and the culture was incubated for 3 days at room temperature with shaking. The organisms were collected from the cultures by centrifugation and lysed with a combination of sodium dodecyl sulfate and proteinase K. The DNA was extracted with organic solvents and with a high-salt-cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution. It was also precipitated with a low-salt-cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution. The extensive treatments used for minimizing polysaccharide contamination greatly improved the reliability of the assay. The minimum contamination level (2 of 1,000 seeds) that was tested was successfully detected with this DNA isolation procedure. The reliability of the assay was 96% at the 1 to 2% level of seed contamination. The described method is less laborious and requires only 4 to 5 days for completion in comparison to the 11 to 22 days required for the currently employed methods. In addition, large sample sizes can be easily handled, thus reducing the probability of contaminated seed escaping detection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Goodwin P. H., Annis S. L. Rapid identification of genetic variation and pathotype of Leptosphaeria maculans by random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2482–2486. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2482-2486.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales V. M., Pelcher L. E., Taylor J. L. Comparison of the 5.8s rDNA and internal transcribed spacer sequences of isolates of Leptosphaeria maculans from different pathogenicity groups. Curr Genet. 1993 May-Jun;23(5-6):490–495. doi: 10.1007/BF00312640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Thompson W. F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4321–4325. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollo F., Salvi R., Torchia P. Highly sensitive and fast detection of Phoma tracheiphila by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990 Feb;32(5):572–576. doi: 10.1007/BF00173730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schesser K., Luder A., Henson J. M. Use of Polymerase Chain Reaction To Detect the Take-All Fungus, Gaeumannomyces graminis, in Infected Wheat Plants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):553–556. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.553-556.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsen H. Y., Chen T. R. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for specific detection of type A, D and E enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in foods. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992 Aug;37(5):685–690. doi: 10.1007/BF00240750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]