Abstract
Pseudomonas sp. strain JS6 grows on a wide range of chloro- and methylaromatic substrates. The simultaneous degradation of these compounds is prevented in most previously studied isolates because the catabolic pathways are incompatible. The purpose of this study was to determine whether strain JS6 could degrade mixtures of chloro- and methyl-substituted aromatic compounds. Strain JS6 was maintained in a chemostat on a minimal medium with toluene or chlorobenzene as the sole carbon source, supplied via a syringe pump. Strain JS6 contained an active catechol 2,3-dioxygenase when grown in the presence of chloroaromatic compounds; however, in cell extracts, this enzyme was strongly inhibited by 3-chlorocatechol. When cells grown to steady state on toluene were exposed to 50% toluene-50% chlorobenzene, 3-chlorocatechol and 3-methylcatechol accumulated in the medium and the cell density decreased. After 3 h, the enzyme activities of the modified ortho ring fission pathway were induced, the metabolites disappeared, and the cell density returned to previous levels. In cell extracts, 3-methylcatechol was degraded by both catechol 1,2- and catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. Strain JS62, a catechol 2,3-dioxygenase mutant of JS6, grew on toluene, and ring cleavage of 3-methylcatechol was catalyzed by catechol 1,2-dioxygenase. The transient metabolite 2-methyllactone was identified in chlorobenzene-grown JS6 cultures exposed to toluene. These results indicate that strain JS6 can degrade mixtures of chloro- and methylaromatic compounds by means of a modified ortho ring fission pathway.
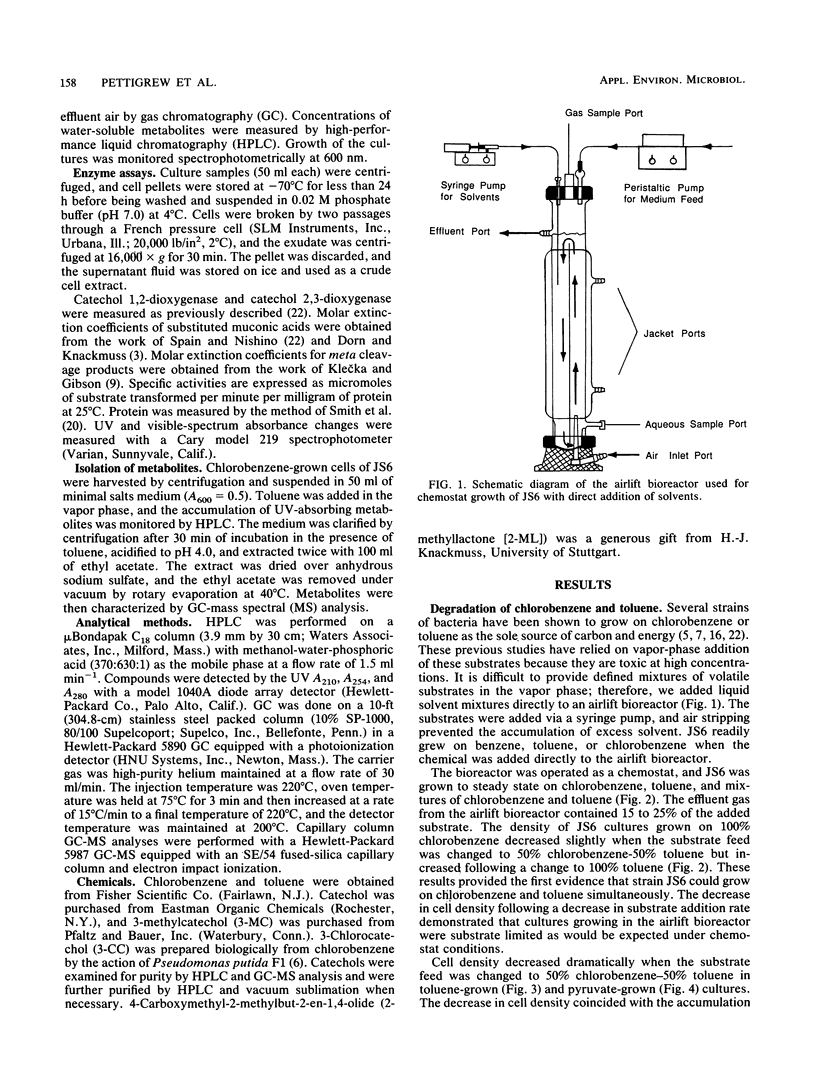
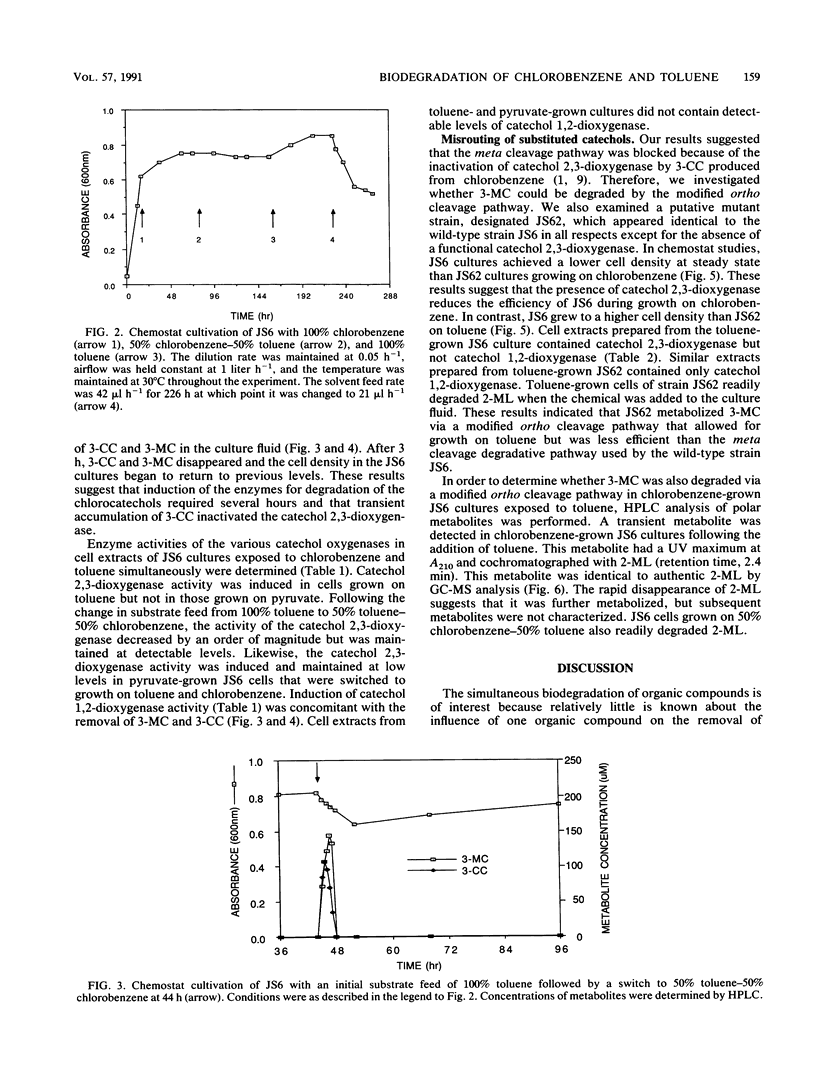
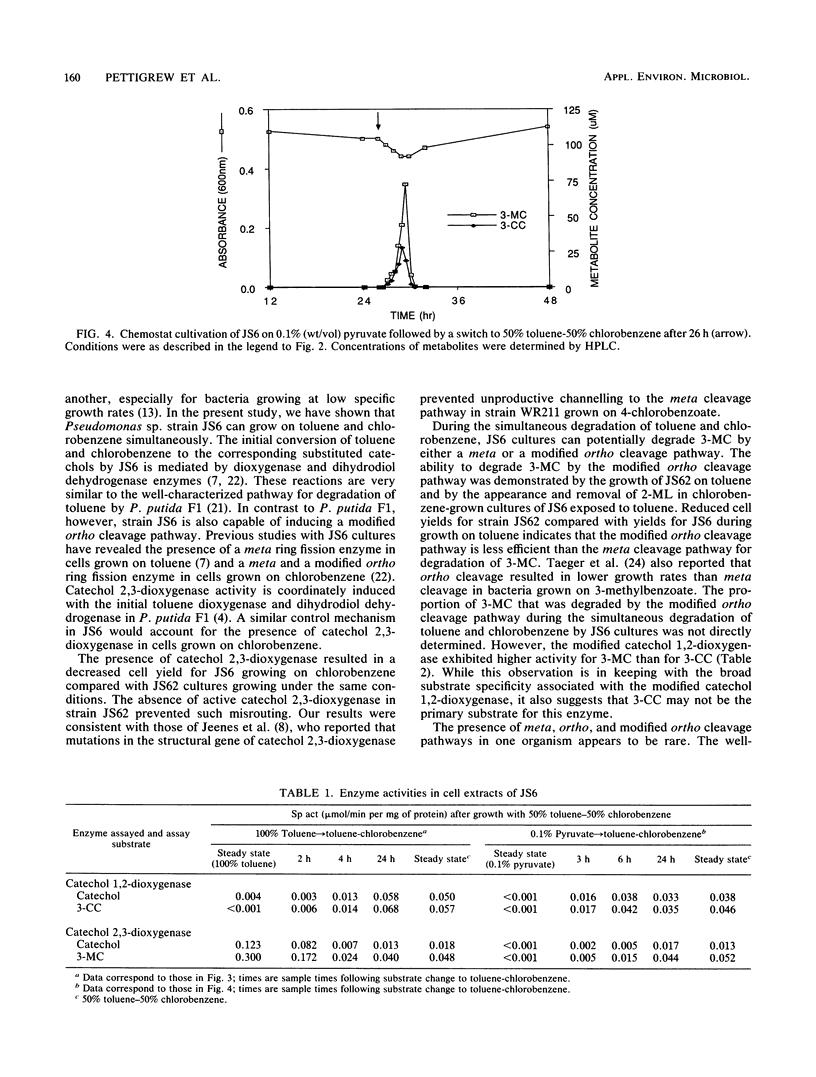
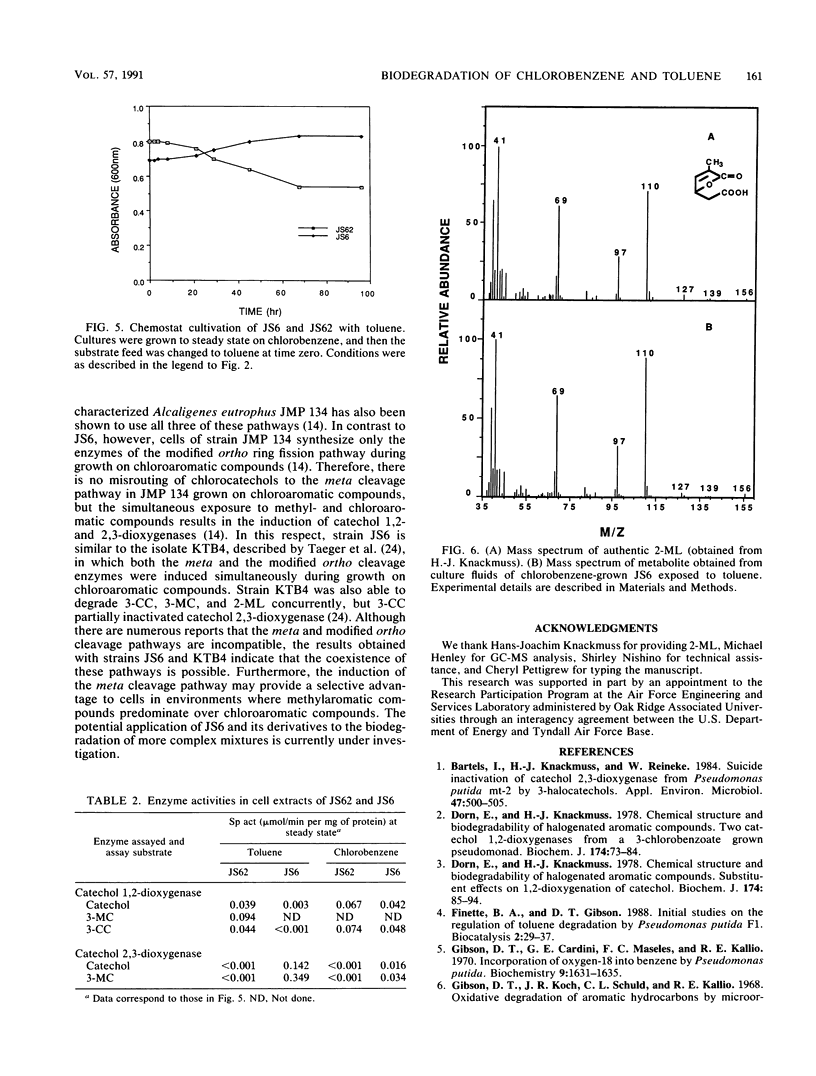
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartels I., Knackmuss H. J., Reineke W. Suicide Inactivation of Catechol 2,3-Dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 by 3-Halocatechols. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.500-505.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of catechol. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):85–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1740085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from a 3-chlorobenzoate-grown pseudomonad. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):73–84. doi: 10.1042/bj1740073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Cardini G. E., Maseles F. C., Kallio R. E. Incorporation of oxygen-18 into benzene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1631–1635. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler B. E., Spain J. C. Degradation of p-chlorotoluene by a mutant of Pseudomonas sp. strain JS6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):372–379. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.372-379.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeenes D. J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J., Williams P. A. TOL plasmid pWW0 in constructed halobenzoate-degrading Pseudomonas strains: enzyme regulation and DNA structure. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.180-187.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klecka G. M., Gibson D. T. Inhibition of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida by 3-chlorocatechol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1159-1165.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Jeenes D. J., Williams P. A., Knackmuss H. J. TOL plasmid pWW0 in constructed halobenzoate-degrading Pseudomonas strains: prevention of meta pathway. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.195-201.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Microbial metabolism of haloaromatics: isolation and properties of a chlorobenzene-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):395–402. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.395-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Pieper D. H., Engesser K. H., Knackmuss H. J., Timmis K. N. Assemblage of ortho cleavage route for simultaneous degradation of chloro- and methylaromatics. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1395–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.3479842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E., Hellwig M., Knackmuss H. J. Degradation of chlorophenols by a defined mixed microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1038–1044. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1038-1044.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Gibson D. T. Oxidation of substituted phenols by Pseudomonas putida F1 and Pseudomonas sp. strain JS6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1399–1404. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1399-1404.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Nishino S. F. Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1010-1019.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


