Abstract
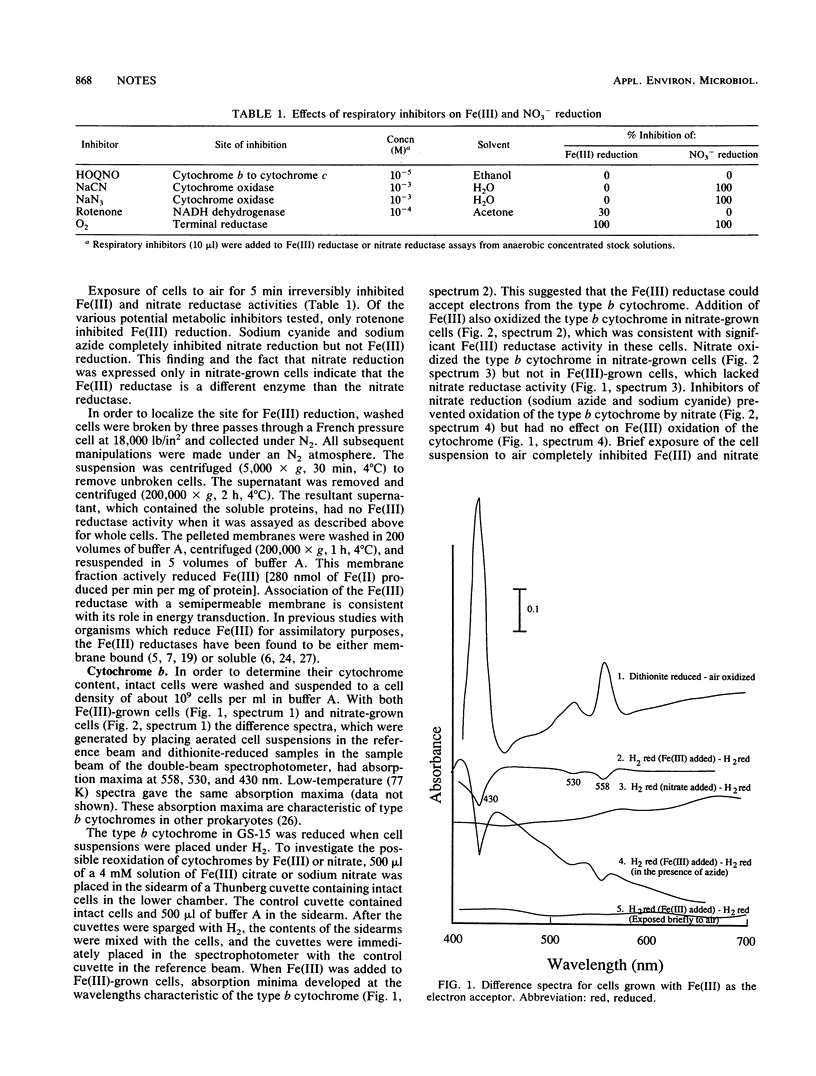
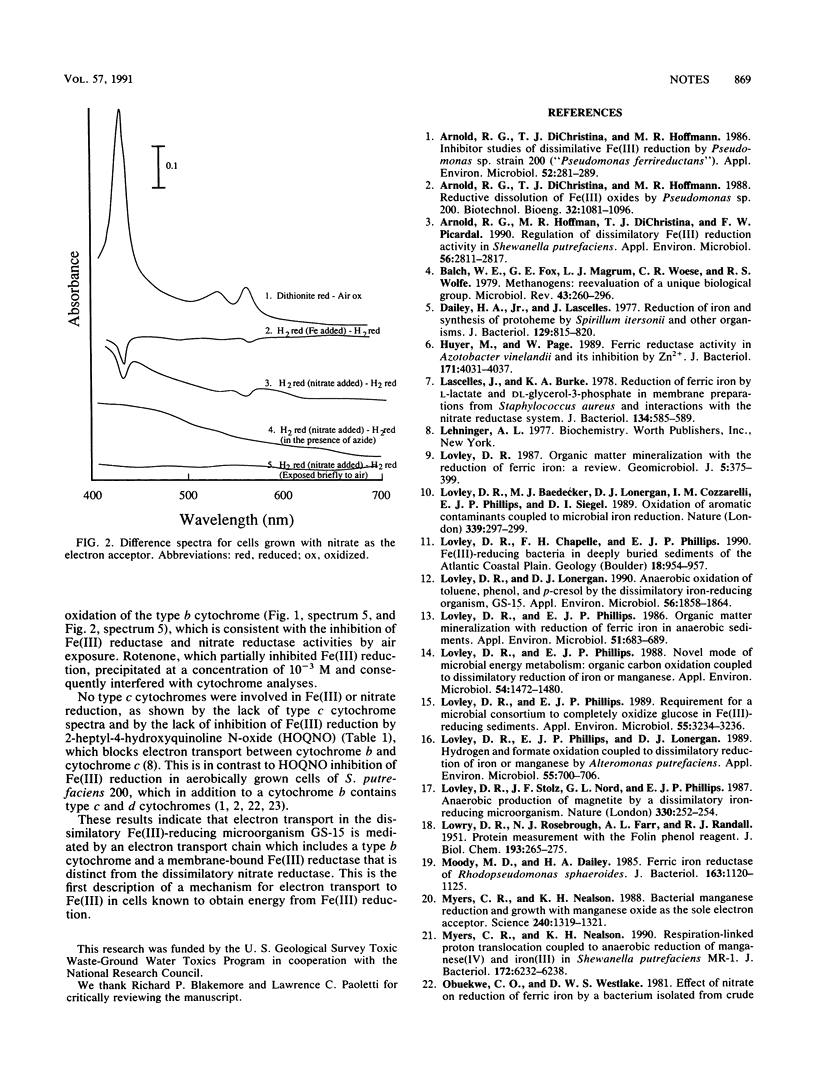
Mechanisms for electron transport to Fe(III) were investigated in GS-15, a novel anaerobic microorganism which can obtain energy for growth by coupling the complete oxidation of organic acids or aromatic compounds to the reduction of Fe(III) to Fe(II). The results indicate that Fe(III) reduction proceeds through a type b cytochrome and a membrane-bound Fe(III) reductase which is distinct from the nitrate reductase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold R. G., DiChristina T. J., Hoffmann M. R. Inhibitor studies of dissimilative Fe(III) reduction by Pseudomonas sp. strain 200 ("Pseudomonas ferrireductans") Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):281–289. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.281-289.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. G., Hoffmann M. R., Dichristina T. J., Picardal F. W. Regulation of Dissimilatory Fe(III) Reduction Activity in Shewanella putrefaciens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2811–2817. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2811-2817.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey H. A., Jr, Lascelles J. Reduction of iron and synthesis of protoheme by Spirillum itersonii and other organisms. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):815–820. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.815-820.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huyer M., Page W. J. Ferric reductase activity in Azotobacter vinelandii and its inhibition by Zn2+. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4031–4037. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4031-4037.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles J., Burke K. A. Reduction of ferric iron by L-lactate and DL-glycerol-3-phosphate in membrane preparations from Staphylococcus aureus and interactions with the nitrate reductase system. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):585–589. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.585-589.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Lonergan D. J. Anaerobic Oxidation of Toluene, Phenol, and p-Cresol by the Dissimilatory Iron-Reducing Organism, GS-15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1858–1864. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1858-1864.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J., Lonergan D. J. Hydrogen and Formate Oxidation Coupled to Dissimilatory Reduction of Iron or Manganese by Alteromonas putrefaciens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):700–706. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.700-706.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1472–1480. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1472-1480.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):683–689. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.683-689.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Requirement for a Microbial Consortium To Completely Oxidize Glucose in Fe(III)-Reducing Sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3234–3236. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3234-3236.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. D., Dailey H. A. Ferric iron reductase of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1120–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1120-1125.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C. R., Nealson K. H. Bacterial manganese reduction and growth with manganese oxide as the sole electron acceptor. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1319–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4857.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C. R., Nealson K. H. Respiration-linked proton translocation coupled to anaerobic reduction of manganese(IV) and iron(III) in Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6232–6238. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6232-6238.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obuekwe C. O., Westlake D. W. Effects of medium composition on cell pigmentation, cytochrome content, and ferric iron reduction in a Pseudomonas sp. isolated from crude oil. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Aug;28(8):989–992. doi: 10.1139/m82-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short K. A., Blakemore R. P. Iron respiration-driven proton translocation in aerobic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.729-731.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


