Abstract
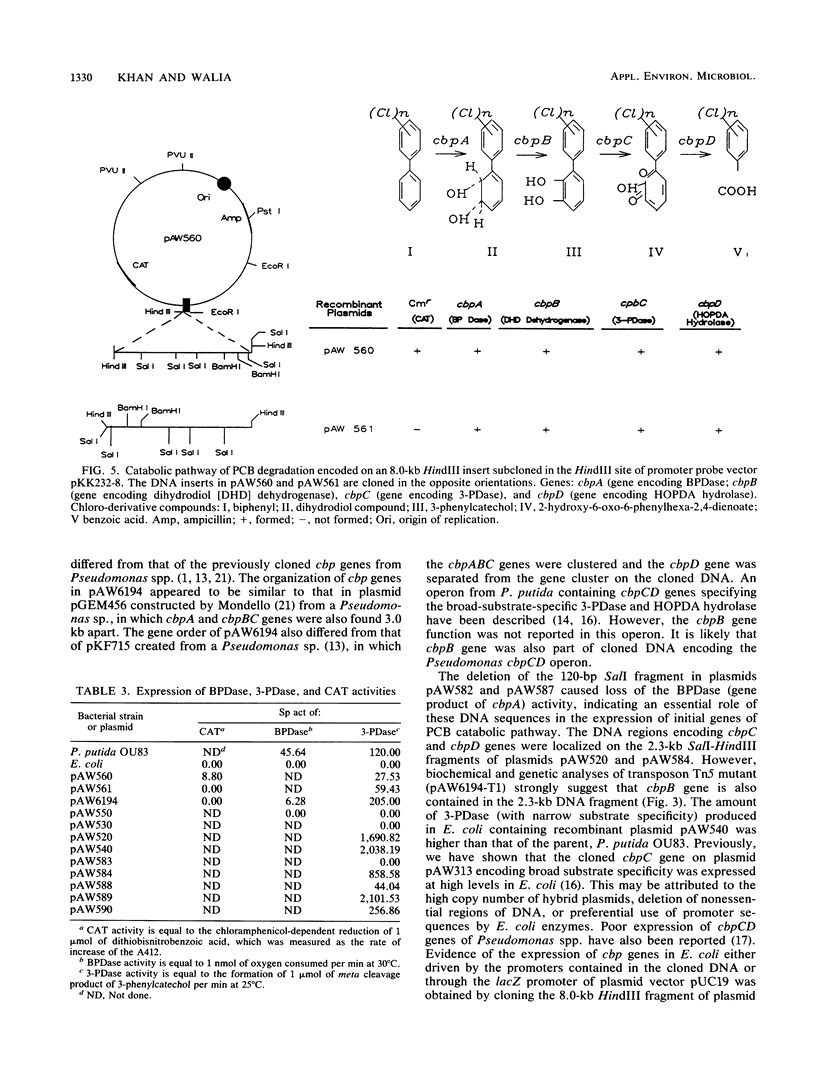
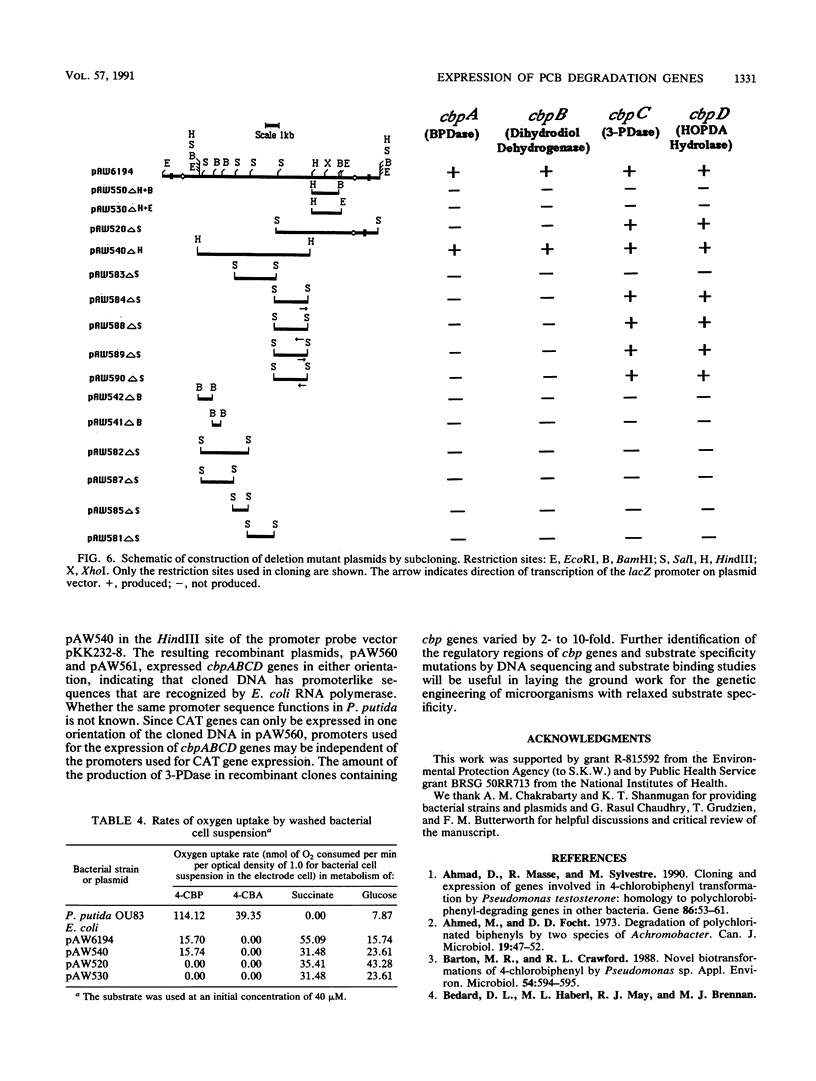
Genes of Pseudomonas putida strains that are capable of degrading polychlorinated biphenyls were cloned in the plasmid vector pUC19. The resultant hybrid plasmid, pAW6194, contained cbpABCD genes on a 9.0-kb DNA fragment that was necessary for the catabolism of polychlorinated biphenyls. These genes were further subcloned on an 8.0-kb HindIII fragment of pAW540. Degradation of 3-chlorobiphenyl, 2,4-dichlorobiphenyl, and 2,4,5-trichlorobiphenyl into a chloro derivative of benzoic acid was found in Escherichia coli harboring chimeric plasmid pAW540. Expression of cbpA (biphenyl dioxygenase, 6.2 U/mg of protein) and cbpC (3-phenylcatechol dioxygenase, 611.00 U/mg of protein) genes was also found in E. coli containing the hybrid plasmid pAW540. These enzyme activities were up to 10-fold higher than those found in P. putida OU83. These results led us to conclude that cbpABCD genes of P. putida OU83 were encoded on cloned DNA and expressed in E. coli. Whether the expression of cbpABCD genes of P. putida OU83 was driven by its own promoters located on the cloned DNA or by the lacZ promoter of pUC19 was examined by subcloning a 8.0-kb DNA fragment encoding the cbpABCD genes, in both orientations, in the HindIII site of the promoter probe vector pKK232-8. The resulting recombinant plasmids, pAW560 and pAW561, expressed cbpABCD genes and conferred chloramphenicol resistance only in E. coli harboring pAW560, indicating that the expression of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase is independent of cbpABCD gene expression.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

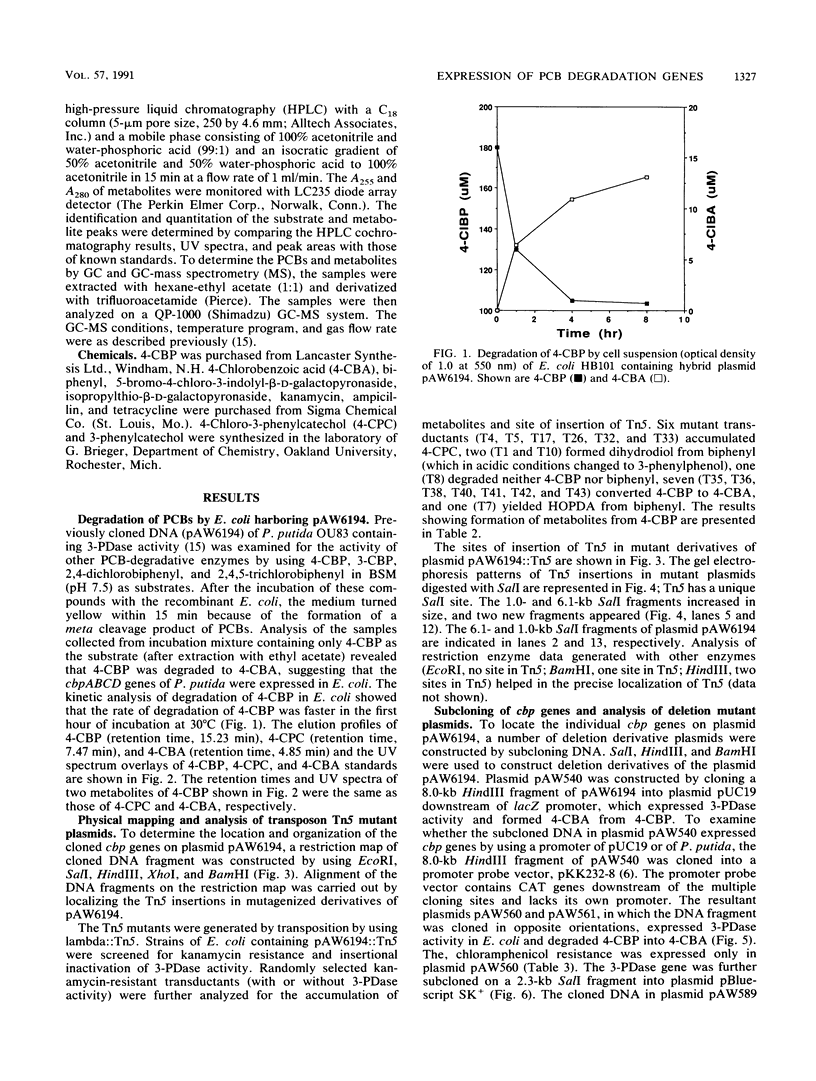
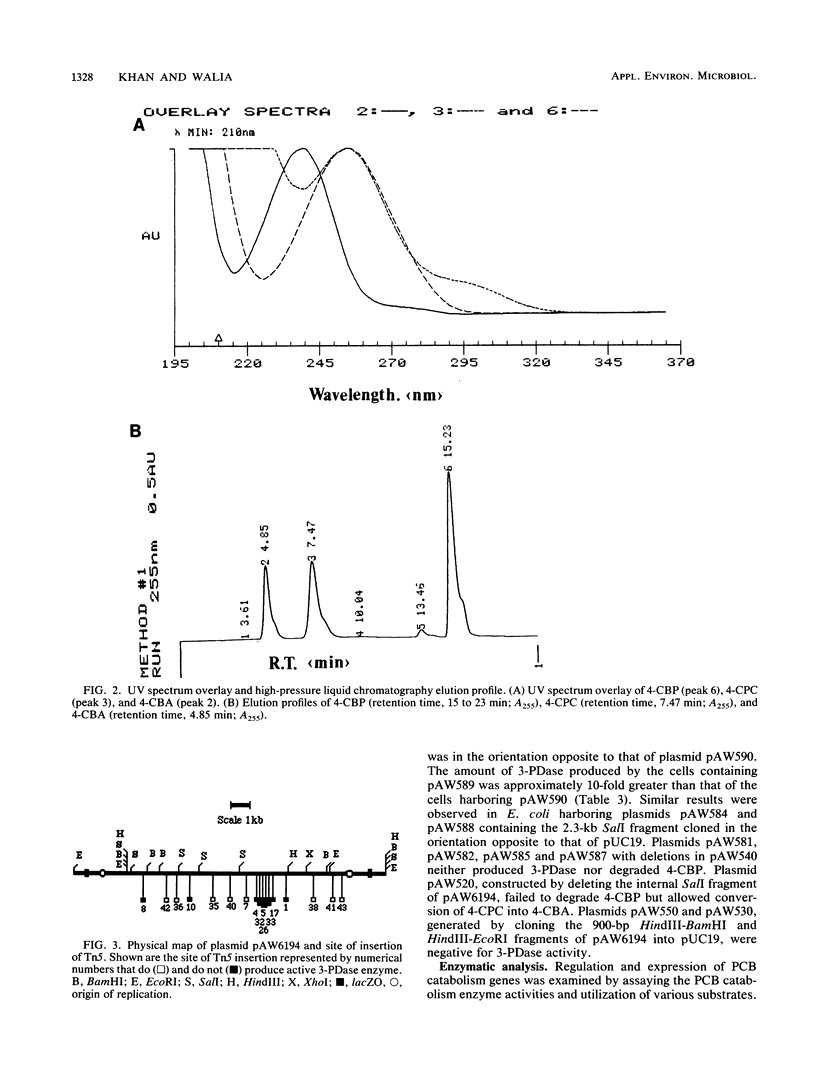
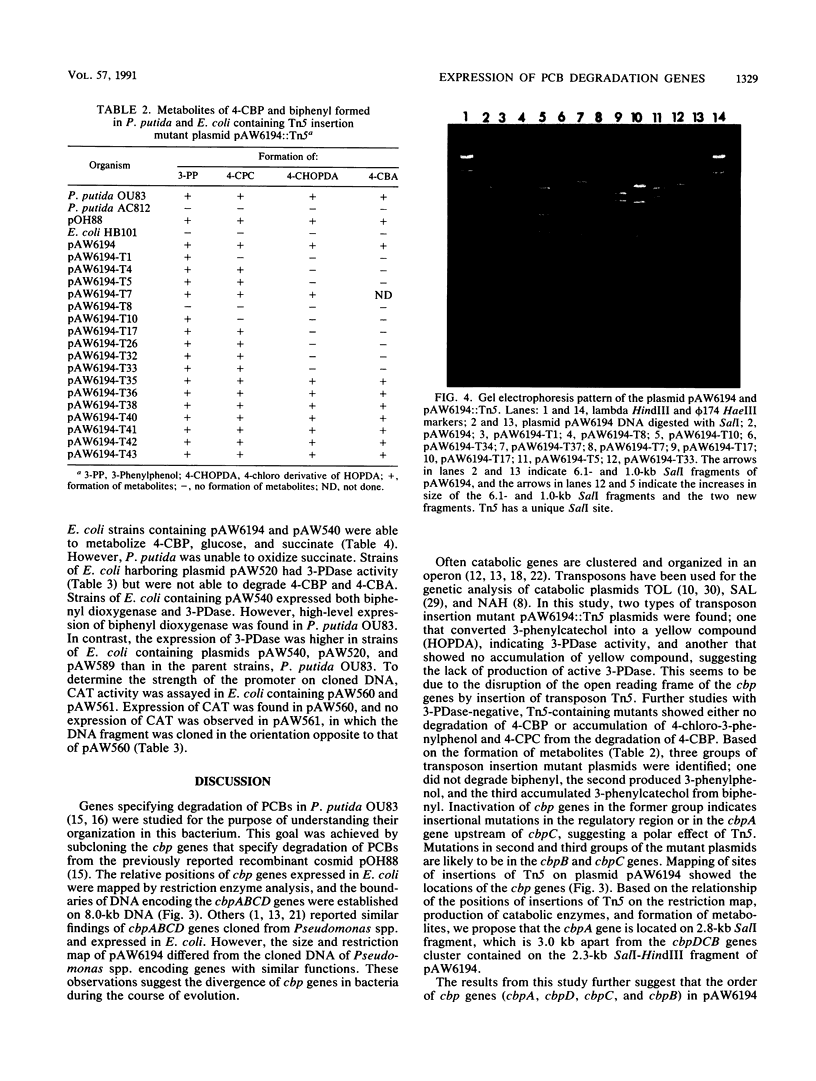

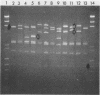
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad D., Massé R., Sylvestre M. Cloning and expression of genes involved in 4-chlorobiphenyl transformation by Pseudomonas testosteroni: homology to polychlorobiphenyl-degrading genes in other bacteria. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed M., Focht D. D. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by two species of Achromobacter. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;19(1):47–52. doi: 10.1139/m73-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton M. R., Crawford R. L. Novel biotransformations of 4-chlorobiphenyl by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):594–595. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.594-595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Plasmid vectors for the selection of promoters. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Restriction mapping of a chlorobenzoate degradative plasmid and molecular cloning of the degradative genes. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M., Bagdasarian M. M., Timmis K. N. Molecular and functional analysis of the TOL plasmid pWWO from Pseudomonas putida and cloning of genes for the entire regulated aromatic ring meta cleavage pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7458–7462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Chakrabarty A. M. Involvement of plasmids in total degradation of chlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):619–626. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.619-626.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Miyazaki T. Cloning of a gene cluster encoding biphenyl and chlorobiphenyl degradation in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):392–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.392-398.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayase N., Taira K., Furukawa K. Pseudomonas putida KF715 bphABCD operon encoding biphenyl and polychlorinated biphenyl degradation: cloning, analysis, and expression in soil bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1160–1164. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1160-1164.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. A., Walia S. K. Identification and localization of 3-phenylcatechol dioxygenase and 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoate hydrolase genes of Pseudomonas putida and expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):956–962. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.956-962.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A., Tewari R., Walia S. Molecular cloning of 3-phenylcatechol dioxygenase involved in the catabolic pathway of chlorinated biphenyl from Pseudomonas putida and its expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2664–2671. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2664-2671.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A., Walia S. Cloning of bacterial genes specifying degradation of 4-chlorobiphenyl from Pseudomonas putida OU83. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Apr;55(4):798–805. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.4.798-805.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbara K., Hashimoto T., Fukuda M., Koana T., Takagi M., Oishi M., Yano K. Cloning and sequencing of two tandem genes involved in degradation of 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl to benzoic acid in the polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading soil bacterium Pseudomonas sp. strain KKS102. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2740–2747. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2740-2747.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidigh B. J., Wheelis M. L. The clustering on the Pseudomonas putida chromosome of genes specifying dissimilatory functions. J Mol Evol. 1973 Nov 27;2(4):235–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01654092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondello F. J. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of Pseudomonas strain LB400 genes encoding polychlorinated biphenyl degradation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1725–1732. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1725-1732.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahlik M. S., Fleming T. P., McIntosh M. A. Cluster of genes controlling synthesis and activation of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid in production of enterobactin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4163–4170. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4163-4170.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quensen J. F., 3rd, Tiedje J. M., Boyd S. A. Reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls by anaerobic microorganisms from sediments. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):752–754. doi: 10.1126/science.242.4879.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira K., Hayase N., Arimura N., Yamashita S., Miyazaki T., Furukawa K. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase gene from the PCB-degrading strain of Pseudomonas paucimobilis Q1. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):3990–3996. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walia S., Khan A., Rosenthal N. Construction and applications of DNA probes for detection of polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading genotypes in toxic organic-contaminated soil environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):254–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.254-259.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R., Mondello F. J. Sequence similarities in the genes encoding polychlorinated biphenyl degradation by Pseudomonas strain LB400 and Alcaligenes eutrophus H850. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1733–1735. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1733-1735.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gunsalus I. C. Plasmid gene organization: naphthalene/salicylate oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):874–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., McCombie W. R., Gibson D. T., Finette B. A. Toluene degradation by Pseudomonas putida F1: genetic organization of the tod operon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1498–1503. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1498-1503.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]